Antwort Why was it called modern age? Weitere Antworten – What is the meaning of modern age
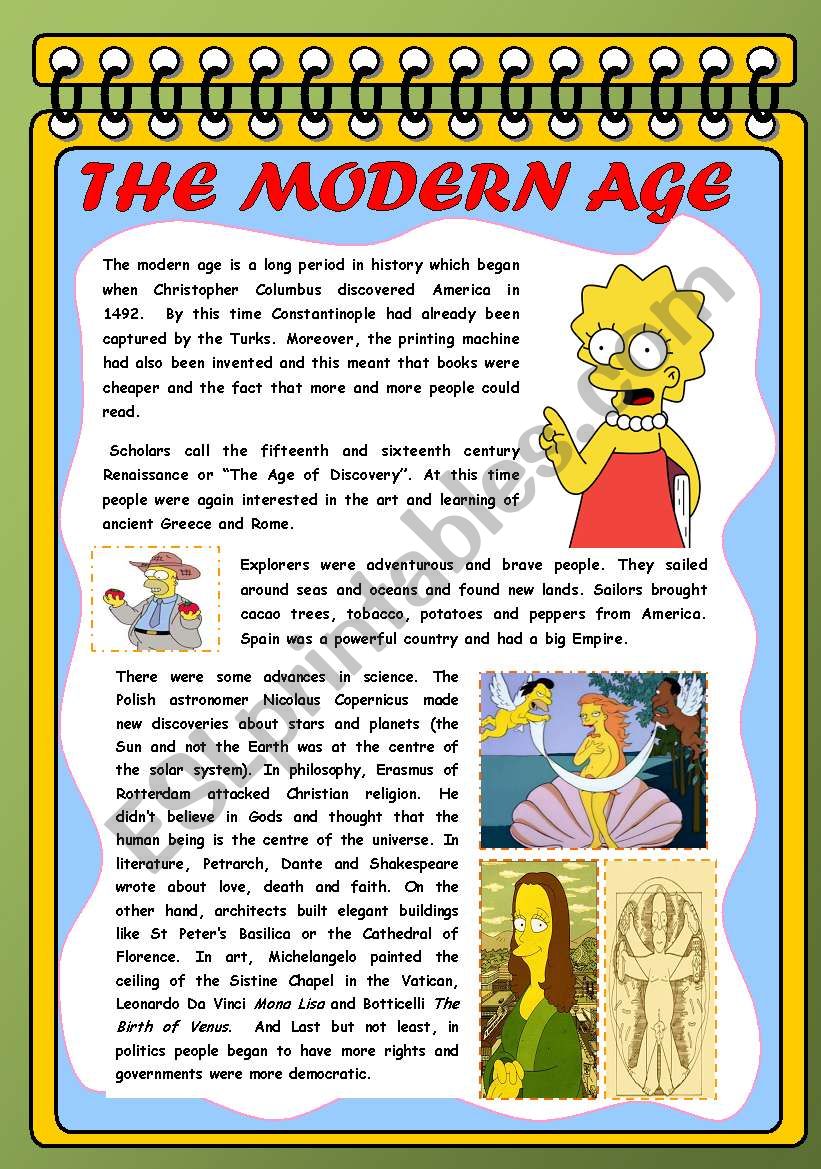
The Modern Era, also known as the Modern Age or Modern Period, was a historical time period that spanned the years 1500 to 1945. The Modern Era occurred following the Middle Ages and can be further divided into two time periods: the Early Modern Period and the Late Modern Period.Definitions of modern era. the present or recent times. types: digital age, information age. a period beginning in the last quarter of the 20th century when information became easily accessible through publications and through the manipulation of information by computers and computer networks.Learning Objectives
| Modern Era | Early Modern Period (late 1400s–1700s) |
|---|---|
| Late Modern Period (1700s–1900s) | |
| Postmodern Age (1950s–present) | Marked by skepticism, self-consciousness, celebration of differences, and the digitalization of culture. |
What are the special features of the modern age : The characteristic features of the Modern Period are: urbanization technological advancement democratic institutions fundamental civil liberties rationalism and humanism and industrialization.
Why is it called modern era
The concept of the modern world as distinct from an ancient or medieval world rests on a sense that the modern world is not just another era in history, but rather the result of a new type of change. This is usually conceived of as progress driven by deliberate human efforts to better their situation.
Why is the present age called the modern period : The present age is called as “The Modern Age”, Because our current generation/ population are evident to the most developments and modernization whatever have been done by human beings till date.
just recently
In history, though, the modern era is the period from the end of the Middle Ages to the present. In that sense, modern is technically a modern word—the first records of it come from the late 1400s. It comes from the Latin modernus, from modō, meaning “just recently.”
The concept of the modern world as distinct from an ancient or medieval world rests on a sense that the modern world is not just another era in history, but rather the result of a new type of change. This is usually conceived of as progress driven by deliberate human efforts to better their situation.
Does modern mean now
The early modern word meant "now existing", or "pertaining to the present times", not necessarily with a positive connotation. English author and playwright William Shakespeare used the term modern in the sense of "every-day, ordinary, commonplace".Modernity refers to the time modern period or era of humanity that was defined by scientific, technological and socioeconomic changes that started in Europe around the year 1650 and ended in around 1950. People in the modernity period placed little faith and importance on scientific progress.Definitions and Characteristics of Modernity
- Rise of the nation state.
- Growth of tolerance as a political and social belief.
- Industrialization.
- Rise of mercantilism and capitalism.
- Discovery and colonization of the Non-Western world.
- Rise of representative democracy.
- Increasing role of science and technology.
- Urbanization.
The modern era is closely associated with the development of individualism, capitalism, urbanization, and a belief in the positive possibilities of technological and political progress.
What led to the Modern Age : Timeline of the Modern Era
The Renaissance, the Age of Discovery, the Industrial Revolution, and the two World Wars all took place during this period. These events brought about significant changes in society, politics, and technology, setting the stage for the world as we know it today.
What is the origin of the word modern : In that sense, modern is technically a modern word—the first records of it come from the late 1400s. It comes from the Latin modernus, from modō, meaning “just recently.” Most of the time, modern simply refers to something related to the present or recent past, as opposed to the past or the distant past.
What created modernity
Modernity may be described as the "age of ideology". For Marx, what was the basis of modernity was the emergence of capitalism and the revolutionary bourgeoisie, which led to an unprecedented expansion of productive forces and to the creation of the world market.
The modern era is closely associated with the development of individualism, capitalism, urbanization, and a belief in the positive possibilities of technological and political progress.Modernism refers to a global movement in society and culture that from the early decades of the twentieth century sought a new alignment with the experience and values of modern industrial life.
Why did the modern age begin in Europe : Historians variously mark the beginning of the early modern period with the invention of moveable type printing in the 1450s, the Fall of Constantinople and end of the Hundred Years' War in 1453, the end of the Wars of the Roses in 1485, the beginning of the High Renaissance in Italy in the 1490s, the end of the …