Antwort Why is Wi-Fi not full duplex? Weitere Antworten – Why is Wi-Fi not full-duplex
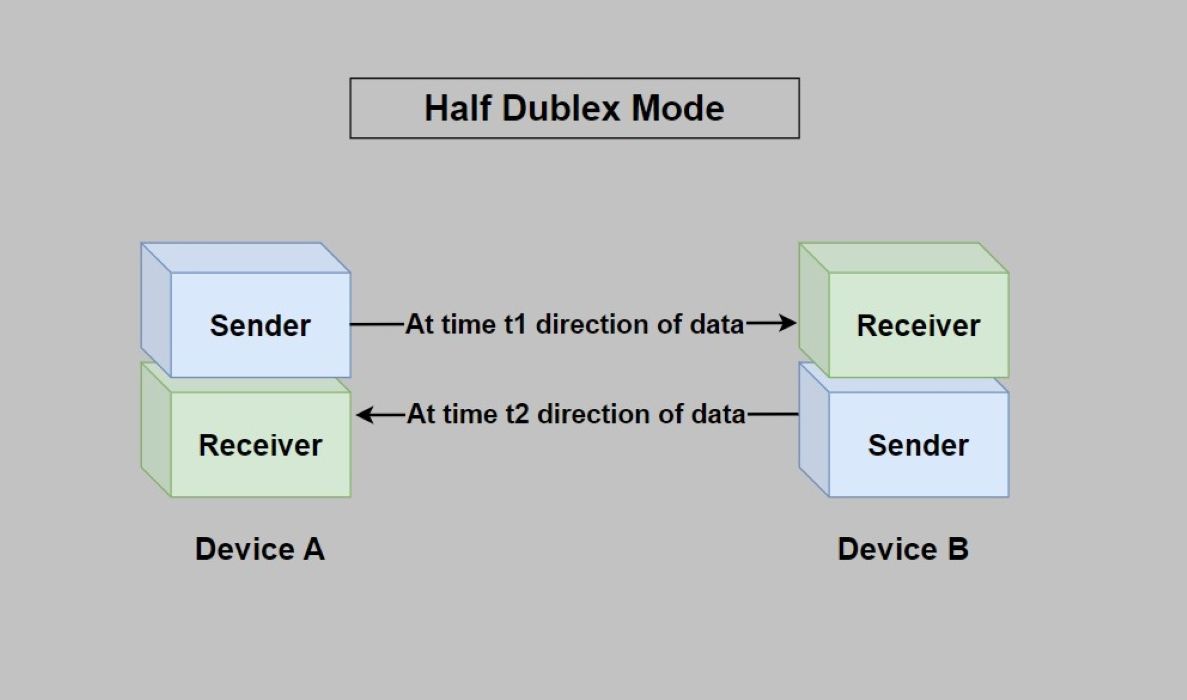
Wireless networks have commonly been built on half-duplex radios. A wireless node cannot transmit and receive simultane- ously, because the interference generated by outgoing signals can easily overwhelm the incoming signals that are much weaker, so called self-interference effect.Wi-Fi is half duplex, so a device can only send or receive at one time and needs to switch between the two. Each device connects to the AP or router, and in typical 802.11b/g/n/ac, end devices don't talk to each other.Half duplex: Half-duplex wireless devices are those that cannot transmit and receive signals simultaneously. Most wireless devices today are half duplex. This is because the signals a wireless device transmits are more powerful than the ones it receives.
How do I change my Wi-Fi to full duplex : Configuring Speed and Duplex in Microsoft* Windows*
- Navigate to the Device Manager.
- Open Properties on the adapter you would like to configure.
- Click the Link Speed tab.
- Select the appropriate speed and duplex from the Speed and Duplex pull down menu.
- Click OK.
Is Wi-Fi full-duplex or half-duplex
Wi-Fi routers operate in half duplex mode, but advancements in full duplex router technology are gaining traction to address self-interference challenges and increase spectral efficiency.
Is WiFi 7 full-duplex : As an evolution of 802.11, Wi-Fi 7 is still a shared medium, half-duplex technology.
Full-duplex: A can send to B and B can send data to A simultaneously. Since 802.11 / WiFi is CSMA/CA protocol based and since it faces collisions, its a half-duplex communication. Full Duplex is not available in Wifi at all.
As an evolution of 802.11, Wi-Fi 7 is still a shared medium, half-duplex technology.
How to enable full duplex
Right-click on Ethernet and then select Properties. Click Configure. Click the Advanced tab and set the Ethernet card Speed & Duplex settings to 100 Mbps Full Duplex. Note: The option in the Property field may be named Link Speed & Duplex or just Speed & Duplex.As with all 802.11 standards, 802.11ac is half-duplex, shared medium radio technology that works best when employed in wireless networking environments designed by qualified professionals.The 802.11 family consists of a series of half-duplex over-the-air modulation techniques that use the same basic protocol.
The operational underpinnings of Wi-Fi 6E are based in the IEEE 802.11 framework. As with previous Wi-Fi standards, Wi-Fi 6E is a half-duplex technology bound by the laws of physics for interference and coexistence with signals in the same unlicensed spectrum.
Why is WLAN half-duplex : This is because a wireless client & AP cannot communicate at the same time. If AP transmit then others should listen & If a client transmitt others should listen.
How to change Wi-Fi to full duplex : Configuring Speed and Duplex in Microsoft* Windows*
- Navigate to the Device Manager.
- Open Properties on the adapter you would like to configure.
- Click the Link Speed tab.
- Select the appropriate speed and duplex from the Speed and Duplex pull down menu.
- Click OK.
Why is Wi-Fi half-duplex
Half duplex: Half-duplex wireless devices are those that cannot transmit and receive signals simultaneously. Most wireless devices today are half duplex. This is because the signals a wireless device transmits are more powerful than the ones it receives.
With OFDMA, you're just dividing a 20 Mhz channel into 2 Mhz sub-channels. It's still half duplex. Think of it as a half duplex switch with shared bandwidth.The operational underpinnings of Wi-Fi 6E are based in the IEEE 802.11 framework. As with previous Wi-Fi standards, Wi-Fi 6E is a half-duplex technology bound by the laws of physics for interference and coexistence with signals in the same unlicensed spectrum.
Does Wi-Fi 7 exist : Yes. Wi-Fi 7 is designed to maintain full backward compatibility, ensuring seamless compatibility between the latest Wi-Fi 7 devices and legacy devices from earlier generations.