Antwort Why is half duplex used for WiFi? Weitere Antworten – Why does Wi-Fi use half-duplex

Half duplex: Half-duplex wireless devices are those that cannot transmit and receive signals simultaneously. Most wireless devices today are half duplex. This is because the signals a wireless device transmits are more powerful than the ones it receives.As an evolution of 802.11, Wi-Fi 7 is still a shared medium, half-duplex technology.The operational underpinnings of Wi-Fi 6E are based in the IEEE 802.11 framework. As with previous Wi-Fi standards, Wi-Fi 6E is a half-duplex technology bound by the laws of physics for interference and coexistence with signals in the same unlicensed spectrum.
Can Wi-Fi ever be full duplex : Not only Wi-Fi cannot work as full-duplex, but also two or more devices cannot transmit or receive traffic simultaneously. Unlike 3G/4G, Wi-Fi uses unlicensed frequencies in the spectrum, which simply means you do not have to pay for using them.
Why is half-duplex still used
Half-duplex systems are usually used to conserve bandwidth, at the cost of reducing the overall bidirectional throughput, since only a single communication channel is needed and is shared alternately between the two directions.
Can Wi-Fi be full duplex : Go to solution. Not only Wi-Fi cannot work as full-duplex, but also two or more devices cannot transmit or receive traffic simultaneously.
99.9% of the time Wireless is half duplex. There are experiments that can result in a "full duplex" wireless network but that's all lab-based and not real-world. With Wireless the devices cannot send and receive simultaneously and they cannot sense collisions.

Yes. Wi-Fi 7 is designed to maintain full backward compatibility, ensuring seamless compatibility between the latest Wi-Fi 7 devices and legacy devices from earlier generations.
Why do we need half-duplex
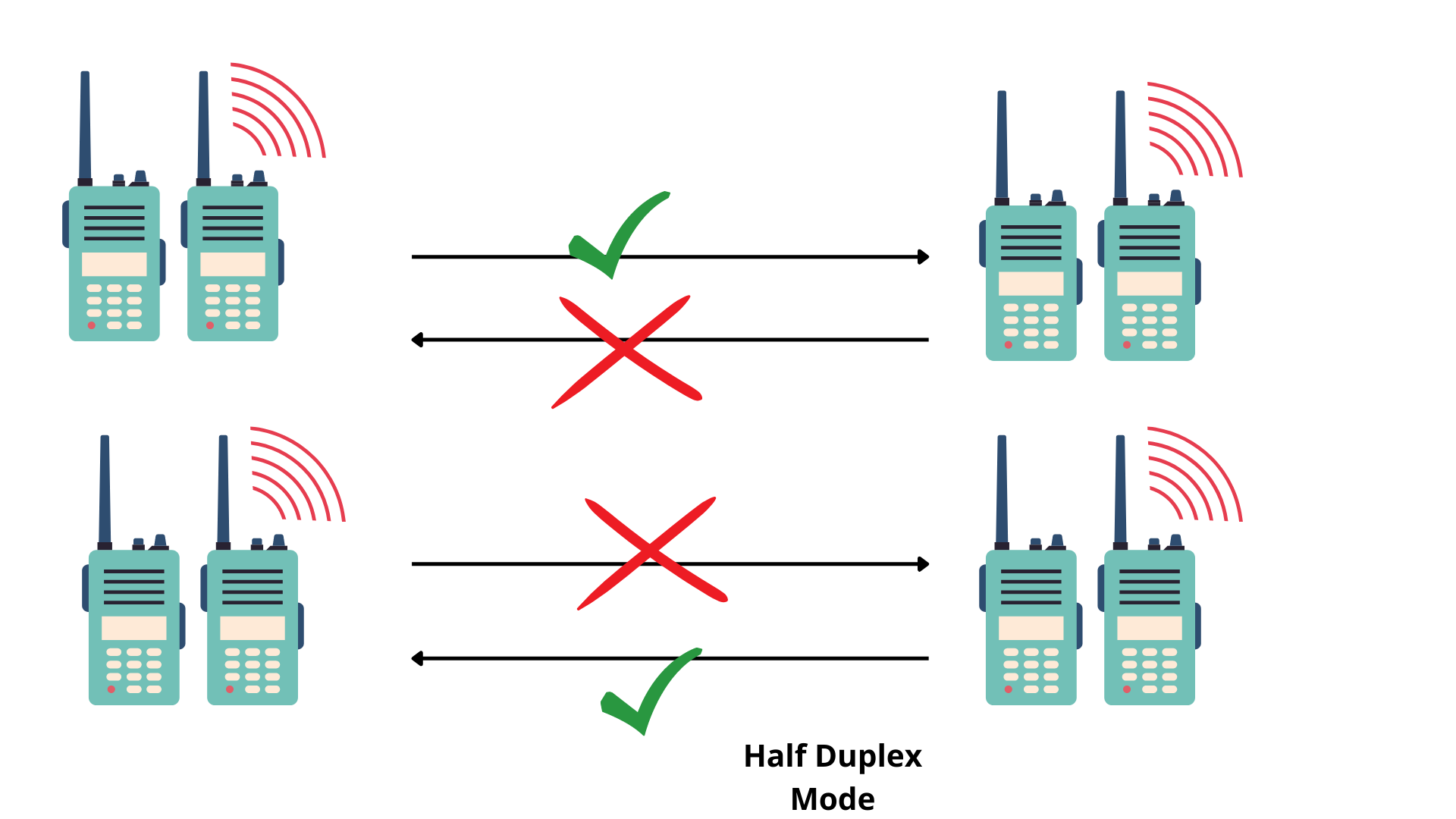
In half-duplex mode, each station can both transmit and receive, but not at the same time. When one device is sending, the other can only receive, and vice versa. The half-duplex mode is used in cases where there is no need for communication in both directions at the same time.Full-duplex communication allows for faster data transfer as devices can both send and receive information simultaneously. This increases data transfer speeds compared to half-duplex or simplex communication. (Simplex communication is unidirectional data transmission, like a keyboard.)Full duplex means that data flowing up to the internet runs at the same time as data down from the internet (using your computer as point of view) Most of the transport within the internet is full duplex, but there are links that are half duplex – which means UL request occurs, then down link response occurs after.
A half-duplex transmission could be considered a one-way street between sender and receiver. Full-duplex, on the other hand, enables two-way traffic at the same time. A communications channel can be used to communicate one way at a time or in both directions at once.
Is internet half-duplex : Full duplex means that data flowing up to the internet runs at the same time as data down from the internet (using your computer as point of view) Most of the transport within the internet is full duplex, but there are links that are half duplex – which means UL request occurs, then down link response occurs after.
Is 802.11 half-duplex or full duplex : The 802.11 family consists of a series of half-duplex over-the-air modulation techniques that use the same basic protocol.
Can Wi-Fi ever be full-duplex
Not only Wi-Fi cannot work as full-duplex, but also two or more devices cannot transmit or receive traffic simultaneously. Unlike 3G/4G, Wi-Fi uses unlicensed frequencies in the spectrum, which simply means you do not have to pay for using them.
Full-duplex: A can send to B and B can send data to A simultaneously. Since 802.11 / WiFi is CSMA/CA protocol based and since it faces collisions, its a half-duplex communication. Full Duplex is not available in Wifi at all.Wi-Fi 8 is the next generation of Wi-Fi and a successor to the IEEE 802.11be (Wi-Fi 7) standard. In line with all previous Wi-Fi standards, Wi-Fi 8 will aim to improve wireless performance in general along with introducing new and innovative features to further advance Wi-Fi technology.
Does 6ghz Wi-Fi exist : The 6 GHz Wi-Fi spectrum is 1200 MHz wide (more than double the size of the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz spectrums) and supports up to seven even larger 160 MHz channels. These channels are only accessible to new Wi-Fi 6E devices, and they enable gigabit Wi-Fi speeds and allow operations free from legacy Wi-Fi interference.