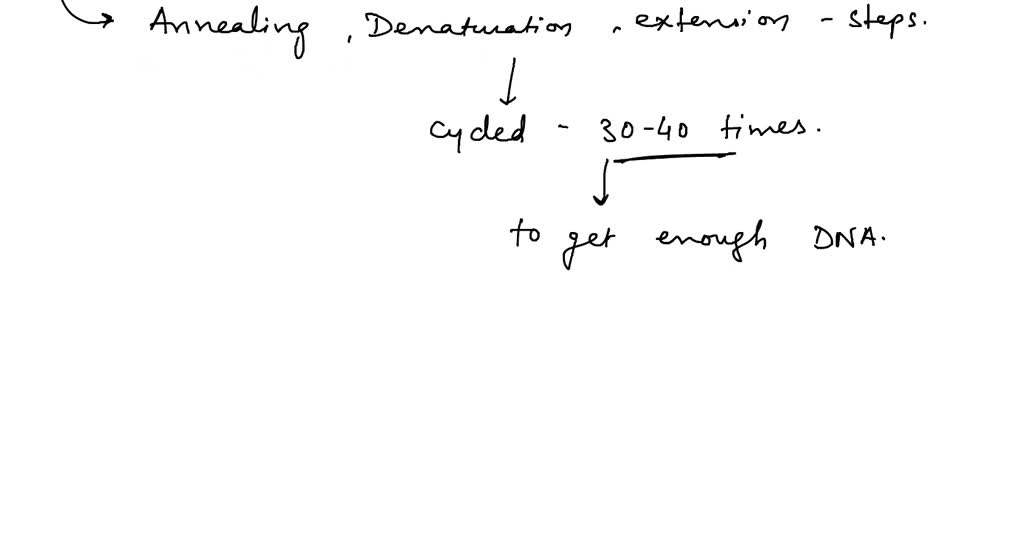Antwort Why is a PCR cycle repeated 30 times? Weitere Antworten – How many copies of a target are made after 30 cycles of PCR
a billion copies
After 30 cycles, as many as a billion copies of the target sequence are produced from a single starting molecule.PCR is a very sensitive technique that allows rapid amplification of a specific segment of DNA. PCR makes billions of copies of a specific DNA fragment or gene, which allows detection and identification of gene sequences using visual techniques based on size and charge.one billion exact
The cycle of denaturing and synthesizing new DNA is repeated as many as 30 or 40 times, leading to more than one billion exact copies of the original DNA segment. The entire cycling process of PCR is automated and can be completed in just a few hours.
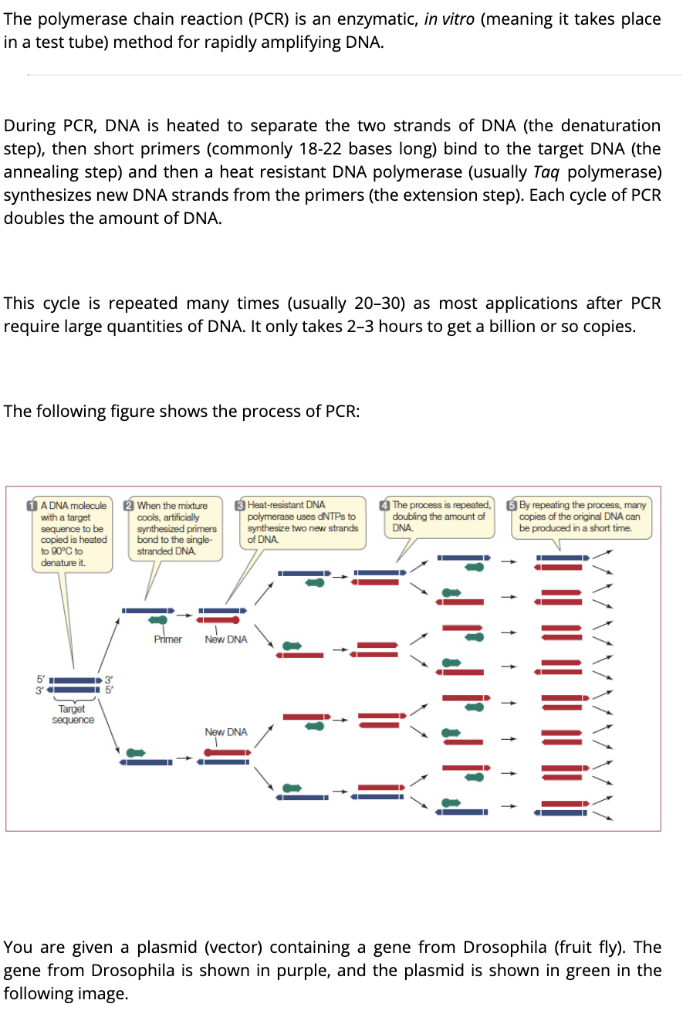
What happens at 50 degrees in PCR : The sample mixture is then cooled to between 50 to 60°C (122 to 140°F) allowing the DNA primers and the DNA polymerase enzyme to bind to the individual strands of DNA that were separated by the heat (this is termed annealing of the primers).
What is the purpose of the 30 cycles in PCR
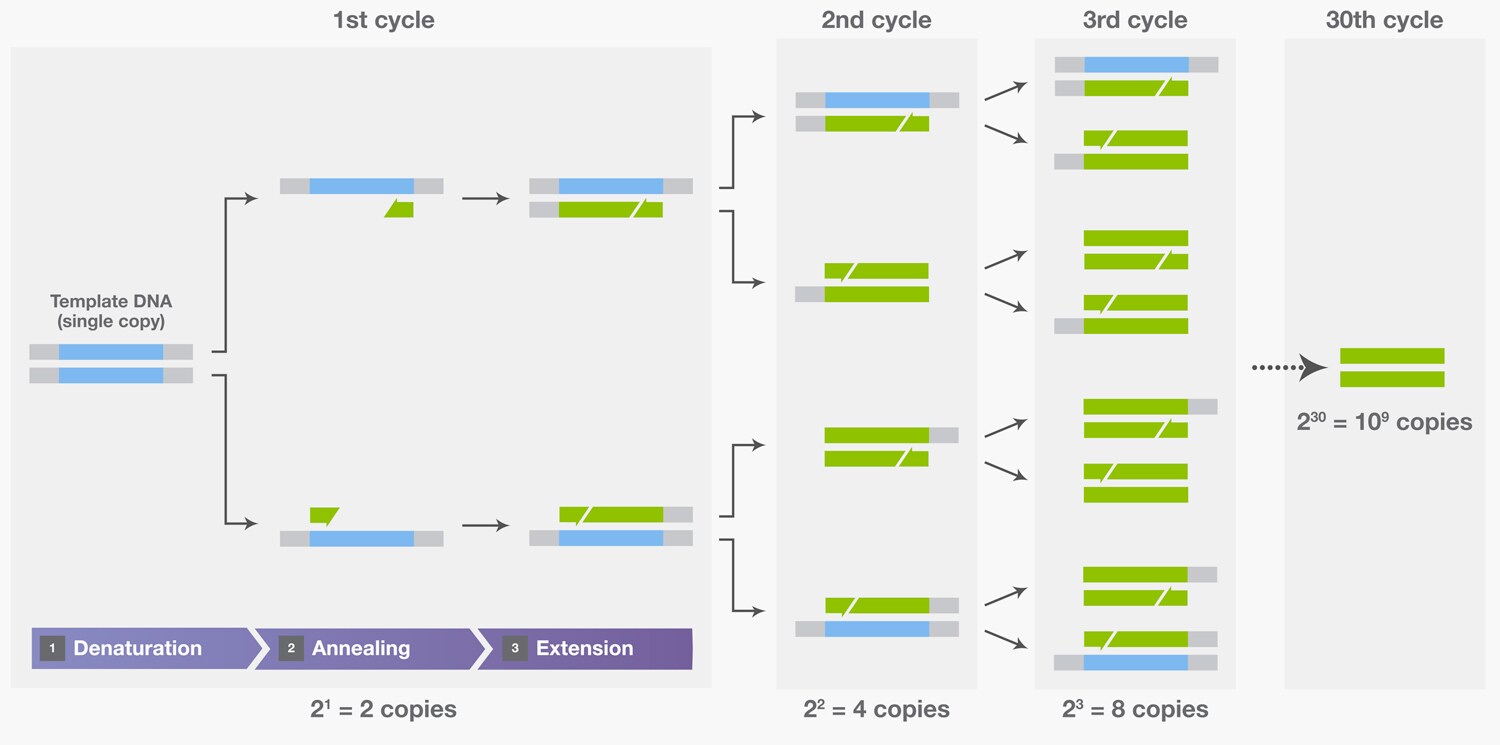
After 30 cycles, what began as a single molecule of DNA has been amplified into more than a billion copies (230=1.02×109). With PCR, it is routinely possible to amplify enough DNA from a single hair follicle for DNA typing.
Why is a PCR cycle repeated 30 times in Quizlet : For accurate and reliable results, the repetition of cycles ensures that enough DNA is produced.
PCR cloning is a rapid method for cloning genes, and is often used for projects that require higher throughput than traditional cloning methods can accommodate. It allows for the cloning of DNA fragments that are not available in large amounts.
Throughout the PCR process, DNA is subjected to repeated heating and cooling cycles during which important chemical reactions occur. During these thermal cycles, DNA primers bind to the target DNA sequence, enabling DNA polymerases to assemble copies of the target sequence in large quantities.
Why is PCR normally carried out for about 30 cycles
Each cycle doubles the copy number of the amplified gene: ten cycles ideally produces 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 512 1,024 (210) copies. Thus, 30 cycles yields a (210×3) = 109-fold amplification. This produces a sufficient quantity of the gene region of interest for direct analysis, for example by DNA sequencing.DNA amplification rate in PCR is as follows: The total number of DNA molecules produced after "n" PCR cycle = 2. 109 is approximately 230 and hence 30 cycles is needed to amplify DNA 109 times.More than 45 cycles is not recommended as nonspecific bands start to appear with higher numbers of cycles. Also, accumulation of by-products and depletion of reaction components drastically lower PCR efficiency, resulting in a characteristic plateau phase for a PCR amplification curve (Figure 7).
The three steps are repeated for multiple cycles, with each cycle doubling the amount of DNA in the sample. The number of cycles is determined by the amount of target DNA in the initial sample and the sensitivity required for the experiment.
Why is the PCR cycle repeated 20/30 times 4 pts : The repeat stage is the third stage in the PCR cycling process. The cycling stage is repeated for 20-40 cycles, with each cycle doubling the DNA target amount. The final number of cycles is optimized to ensure efficient amplification of the target DNA sequence without generating nonspecific amplification products.
Why is PCR done 30 times : At the end of a cycle of these three steps, each target region of DNA in the vial has been duplicated. This cycle is usually repeated 30 times. Each new DNA piece can act in the next cycle as a new template, so after 30 cycles, 1 million copies of a single fragment of DNA can be produced (Scheme – Diagram of PCR).
Why is PCR repeated so many times
PCR steps of denaturation, annealing, and extension are repeated (or “cycled”) many times to amplify the target DNA. The number of cycles is usually carried out 25–35 times but may vary upon the amount of DNA input and the desired yield of PCR product.
Rather, PCR involves the synthesis of multiple copies of specific DNA fragments using an enzyme known as DNA polymerase. This method allows for the creation of literally billions of DNA molecules within a matter of hours, making it much more efficient than the cloning of expressed genes.16 copies
The number of double stranded DNA pieces is doubled in each cycle, so that after n cycles you have 2^n (2 to the n:th power) copies of DNA. For example, after 4 cycles you have 16 copies, after 20 cycles you have about one million copies, etc.
How does PCR clone : In its simplest form, PCR based cloning is about making a copy of a piece of DNA and at the same time adding restriction sites to the ends of that piece of DNA so that it can be easily cloned into a plasmid of interest.