Antwort Why do banks use swap rates? Weitere Antworten – Why do banks use interest rate swaps
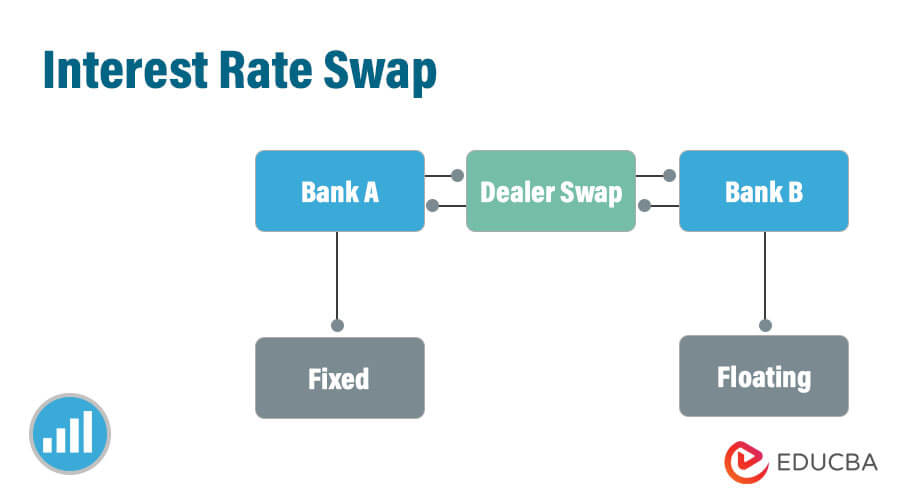
This is how banks that provide swaps routinely shed the risk, or interest rate exposure, associated with them. Initially, interest rate swaps helped corporations manage their floating-rate debt liabilities by allowing them to pay fixed rates, and receive floating-rate payments.An interest rate swap is an agreement between different parties to exchange one stream of interest payments for another over a specified time period. They are derivative contracts that trade over the counter (OTC) and can be customized by the participating parties to match their needs.Investment bankers sometimes make money with swaps. Swaps create profit opportunities through a complicated form of arbitrage, where the investment bank brokers a deal between two parties that are trading their respective cash flows.
Why do companies use swaps : Typically, swaps are used by: Companies to reduce their risks and manage their debt more efficiently. For instance, this may be achieved by exchanging a floating (variable) interest-rate exposure for a fixed interest-rate exposure. Pension schemes and insurance companies to manage interest-rate risk.
How do swaps benefit investors
By entering into a swap agreement, investors can exchange fixed-rate interest payments for floating-rate interest payments or vice versa. This enables them to hedge against adverse interest rate movements, ensuring more predictable cash flows and minimizing potential losses.
How do swaps work : A swap is an agreement for a financial exchange in which one of the two parties promises to make, with an established frequency, a series of payments, in exchange for receiving another set of payments from the other party. These flows normally respond to interest payments based on the nominal amount of the swap.
So in easier terms, a swap rate is a rate based on what the markets think interest rates will be in the future. If the rates rise, then mortgage lenders will look to increase their rates so that they don't lose out. Meaning if swap rates go down, mortgage rates tend to go down. If they go up, so do mortgage rates too.
The objective of a swap is to change one scheme of payments into another one of a different nature. A swap is defined technically in function of the following factors: The start and end dates of the swap. Nominal: The amount upon which the payments of both parties are calculated.
How do banks make money on swaps
The bank's profit is the difference between the higher fixed rate the bank receives from the customer and the lower fixed rate it pays to the market on its hedge. The bank looks in the wholesale swap market to determine what rate it can pay on a swap to hedge itself.Swaps are mainly used by institutional investors such as banks and other financial institutions, governments, and some corporations. They are intended to be used to manage a variety of risks, such as interest rate risk, currency risk, and price risk.A swap is an agreement or a derivative contract between two parties for a financial exchange so that they can exchange cash flows or liabilities. Through a swap, one party promises to make a series of payments in exchange for receiving another set of payments from the second party.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CurrencySwapBasics-effa071aba184066b9683bf80750c254.png)