Antwort Why do banks like swaps? Weitere Antworten – Why do banks sell swaps
This is how banks that provide swaps routinely shed the risk, or interest rate exposure, associated with them. Initially, interest rate swaps helped corporations manage their floating-rate debt liabilities by allowing them to pay fixed rates, and receive floating-rate payments.They enable investors to trade credit risk independently from the underlying debt instrument, providing greater flexibility and efficiency. Credit default swap contracts allow market participants to take long or short positions on a reference entity's creditworthiness without owning the actual debt.A credit default swap (CDS) is a contract between two parties in which one party purchases protection from another party against losses from the default of a borrower for a defined period of time.
How do banks make money from swaps : Investment bankers sometimes make money with swaps. Swaps create profit opportunities through a complicated form of arbitrage, where the investment bank brokers a deal between two parties that are trading their respective cash flows.
Why are swaps so popular
People typically enter swaps either to hedge against other positions or to speculate on the future value of the floating leg's underlying index/currency/etc. For speculators like hedge fund managers looking to place bets on the direction of interest rates, interest rate swaps are an ideal instrument.
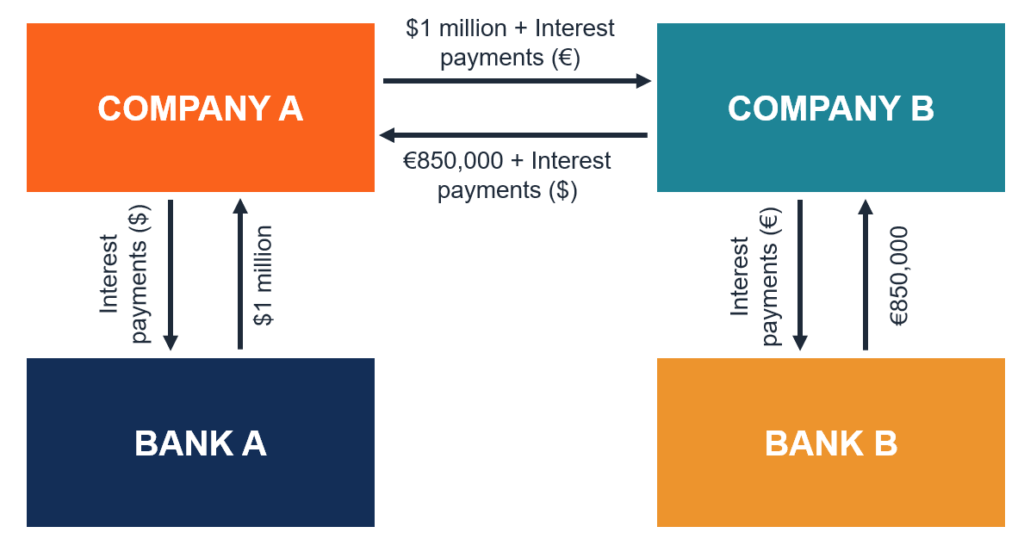
Why are swaps desirable : Swap contracts normally allow for payments to be netted against each other to avoid unnecessary payments. Here, Company B pays $66,000, and Company A pays nothing. At no point does the principal change hands, which is why it is referred to as a notional amount.
A credit default swap (CDS) is a financial derivative that allows an investor to swap or offset their credit risk with that of another investor. To swap the risk of default, the lender buys a CDS from another investor who agrees to reimburse them if the borrower defaults.
Credit default swaps provide a measure of protection against previously agreed upon credit events. Below are the most common credit events that trigger a payment from the risk “buyer” to the risk “seller” in a CDS. The settlement terms of a CDS are determined when the CDS contract is written.
Why use swaps
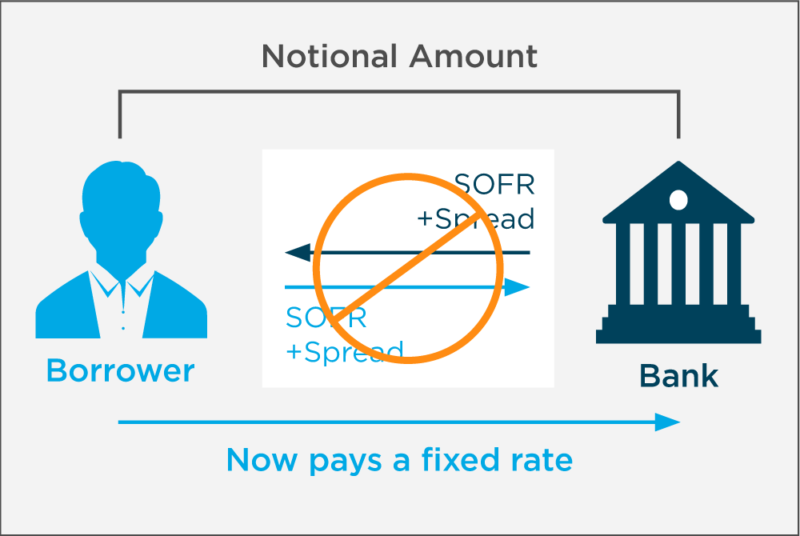
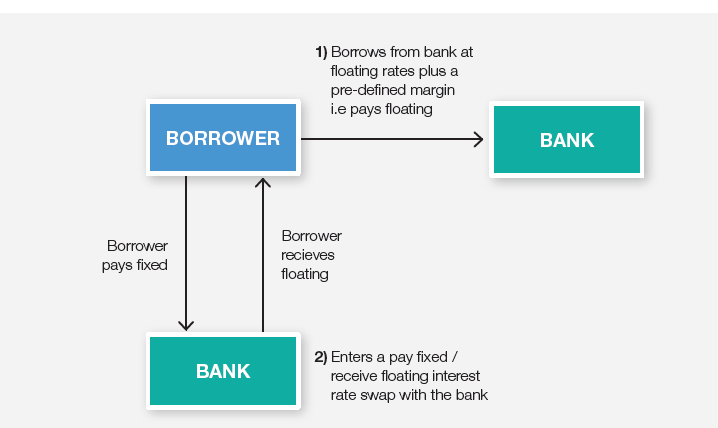
For example, a company paying a variable rate of interest may swap its interest payments with another company that will then pay the first company a fixed rate. Swaps can also be used to exchange other kinds of value or risk like the potential for a credit default in a bond.This risk has been partially mitigated since the financial crisis, with a large portion of swap contacts now clearing through central counterparties (CCPs). However, the risk is still higher than that of investing in a “risk-free” U.S. Treasury bond.Typically, swaps are used by: Companies to reduce their risks and manage their debt more efficiently. For instance, this may be achieved by exchanging a floating (variable) interest-rate exposure for a fixed interest-rate exposure. Pension schemes and insurance companies to manage interest-rate risk.
In a CDS, one party “sells” risk and the counterparty “buys” that risk. The “seller” of credit risk – who also tends to own the underlying credit asset – pays a periodic fee to the risk “buyer.” In return, the risk “buyer” agrees to pay the “seller” a set amount if there is a default (technically, a credit event).
How did Michael Burry buy CDS : And collected premiums from him because. They thought the housing market was always stable. That's why they thought Michael burry was offering them free money and they would never have to pay him.
Do swaps have default risk : In swap contracts, there are two most basic forms of risk: price risk and default risk.
Why do hedge funds use swaps
HEDGE FUNDS AND SWAPS
While banks are the largest participants in swap transactions, hedge funds have now become the second largest user of swaps. Hedge funds are attracted to the swap markets by the leverage made possible by swaps and the ability to lock-in higher investment returns for specified risk levels.
Understanding Swap Banks
A swap is a derivative contract through which two parties exchange financial instruments. These instruments can be almost anything, but most swaps involve cash flows based on a notional principal amount to which both parties agree. Usually, the principal does not change hands.In addition to hedging credit risk, the potential benefits of CDS include: Requiring only a limited cash outlay (which is significantly less than for cash bonds) Access to maturity exposures not available in the cash market. Access to credit risk with limited interest rate risk.
What swaps did Michael Burry buy : Through the purchase of credit default swaps from Goldman Sachs GS (an agreement that the seller of CDS will compensate the buyer in the event of a default) and other big banks on the mortgage bond market, Burry made a windfall profit of $100 million in the months following the housing crisis of 2008.