Antwort What was the most brutal Gulag? Weitere Antworten – Which was the worst Gulag
Vorkuta became one of the most well known Gulags, it gained a reputation of being one of the worst in the Soviet Union. About two million prisoners had gone to Vorkutlag from 1932 until the closure in 1962, the number of deaths in the camp was estimated to be 200,000.Siberian Russia
Solovetsky Island, prison island located in Siberian Russia, part of a system of prisons and labour camps that came to be known as the Gulag Archipelago through the writings of Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn, who spent eight years as a political prisoner of the Soviet regime.During the day prisoners ate (if they had food) outside at communal works. The basic food in all of the Gulag camps was a thin soup known as balanda. “In Igarka the food was awful. They boiled soya, which is heavy and falls to the bottom of the boiler.
Why was the gulag so bad : These political prisoners suffered the most because, on top of the brutal hard labour conditions and the despotism of guards, they were terrorised by criminal prisoners. Historians estimate the total number of Gulag prisoners at 20 million, of whom about 2 million did not survive their incarceration.
Can you visit Russian Gulags
However, the tracks, many railway bridges and several large gulag camps have miraculously remained very well-preserved, hidden away in the forest tundra of central Yamal. Some of the biggest camps have up to twenty wooden buildings that you can explore, as well as watch towers, barbed wire fences and more.
Were the Gulags real : What was the Gulag The Gulag was a system of Soviet labour camps and accompanying detention and transit camps and prisons. From the 1920s to the mid-1950s it housed political prisoners and criminals of the Soviet Union. At its height, the Gulag imprisoned millions of people.
In most years, the camp death rate hovered around 5 percent. In particularly bad years the death rate was much higher: 15 percent in 1933, a year of widespread famine; 25 percent in 1942, the hungriest year of World War II. In 1937 and 1938, tens of thousands were simply executed.
Six years later, on 25 January 1960, the Gulag system was officially abolished when the remains of its administration were dissolved by Khrushchev. The legal practice of sentencing convicts to penal labor continues to exist in the Russian Federation, but its capacity is greatly reduced.
Do Gulags still exist
Six years later, on 25 January 1960, the Gulag system was officially abolished when the remains of its administration were dissolved by Khrushchev. The legal practice of sentencing convicts to penal labor continues to exist in the Russian Federation, but its capacity is greatly reduced.Yet contrary to official propaganda millions of children were left abandoned, orphaned or separated from their families. Many of these unfortunate children found themselves victims of the Gulag.Gulag, (Russian: “Chief Administration of Corrective Labour Camps”), system of Soviet labour camps and accompanying detention and transit camps and prisons that from the 1920s to the mid-1950s housed the political prisoners and criminals of the Soviet Union.
The prisoners' slave labour was used in timber production and mining and on gigantic construction projects (the White Sea Canal, dams, motorways, and railways). After Stalin's death in 1953, the number of prisoners declined considerably and the Gulag was officially done away with in 1960.
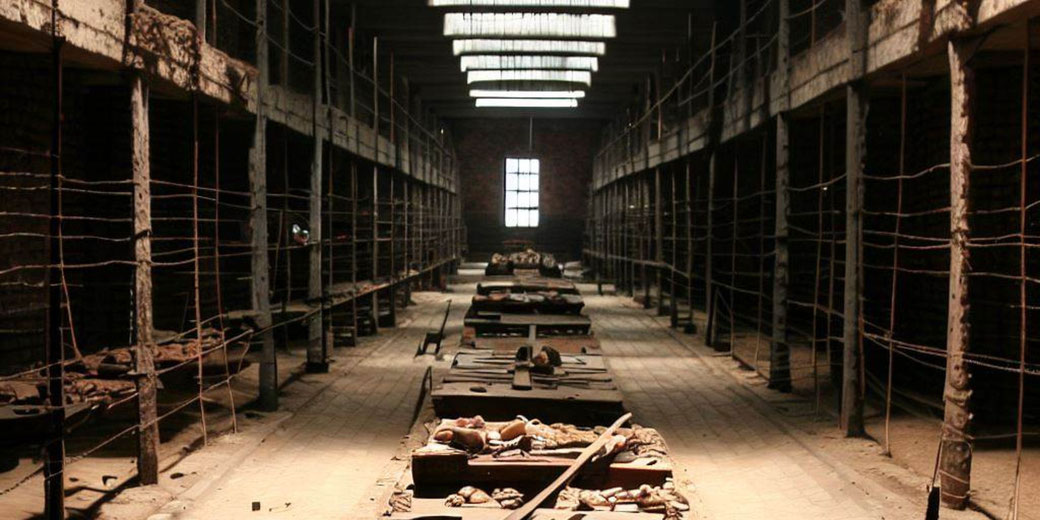
What did gulags look like : Living in the Gulag. During their non-working hours, prisoners typically lived in a camp zone surrounded by a fence or barbed wire, overlooked by armed guards in watch towers. The zone contained a number of overcrowded, stinking, poorly-heated barracks. Life in a camp zone was brutal and violent.
What were Stalin’s gulags like : Food rations were tight, and workdays were long. If prisoners didn't complete their work quotas, they received less food. Gulag living conditions were cold, overcrowded and unsanitary. Violence was common among the camp inmates, who were made up of both hardened criminals and political prisoners.
What were Stalin’s Gulags like
Food rations were tight, and workdays were long. If prisoners didn't complete their work quotas, they received less food. Gulag living conditions were cold, overcrowded and unsanitary. Violence was common among the camp inmates, who were made up of both hardened criminals and political prisoners.
Barnes described the Gulag as an institution of forced labor, where workers had real prospects of being released. According to the author 18 million people passed through the work camps. While approximately 1.6 million died, a large number were released and reintegrated into Soviet society.Gulag living conditions were cold, overcrowded and unsanitary. Violence was common among the camp inmates, who were made up of both hardened criminals and political prisoners. In desperation, some stole food and other supplies from each other.
Did children go to gulags : Yet contrary to official propaganda millions of children were left abandoned, orphaned or separated from their families. Many of these unfortunate children found themselves victims of the Gulag.