Antwort What is wave function in chemistry? Weitere Antworten – What is wave function in simple words
What is Wave Function In quantum physics, a wave function is a mathematical description of a quantum state of a particle as a function of momentum, time, position, and spin. The symbol used for a wave function is a Greek letter called psi, 𝚿.Wave Functions. A wave function (Ψ) is a mathematical function that relates the location of an electron at a given point in space (identified by x, y, and z coordinates) to the amplitude of its wave, which corresponds to its energy. Thus each wave function is associated with a particular energy E.Ψ Fundamental particles, such as electrons, may be described as particles or waves. Electrons may be described using a wave function. The wave function's symbol is the Greek letter psi, Ψ or ψ.
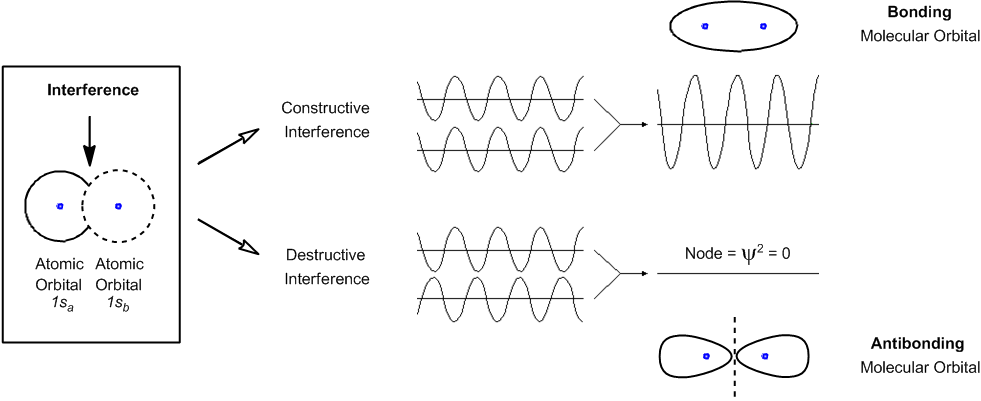
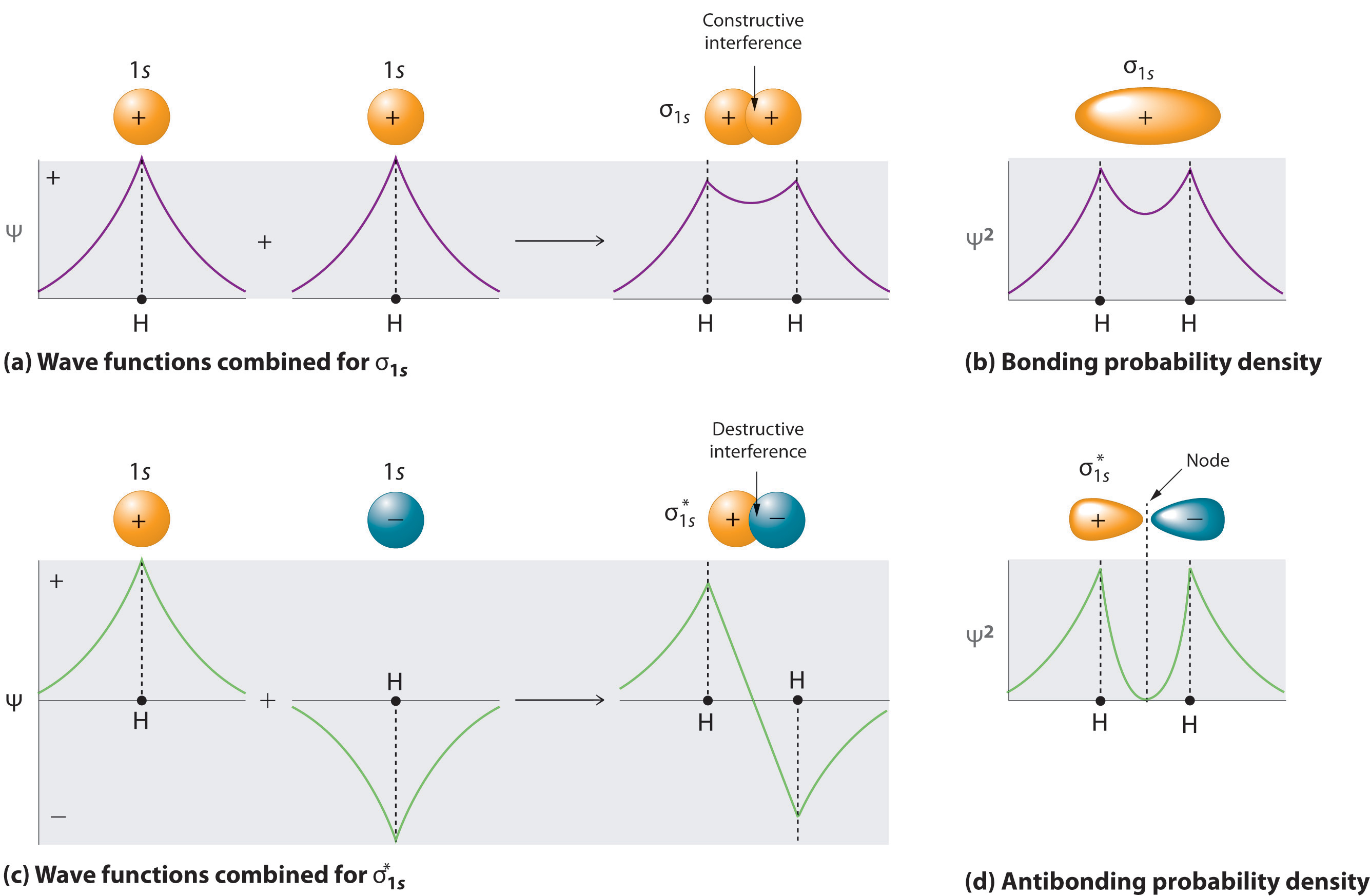
What is wave function of a molecule : The wave function describes the wavelike properties of an electron. Molecular orbitals are combinations of atomic orbital wave functions. Combining waves can lead to constructive interference, in which peaks line up with peaks, or destructive interference, in which peaks line up with troughs (Figure 2.2. 2).
What is wave function and its formula
The wavefunction of a light wave is given by E(x,t), and its energy density is given by |E|2, where E is the electric field strength. The energy of an individual photon depends only on the frequency of light, ϵphoton=hf, so |E|2 is proportional to the number of photons.
How do waves function : Waves transmit energy, not water, and are commonly caused by the wind as it blows across the ocean, lakes, and rivers. Waves caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun are called tides. The ebb and flow of waves and tides are the life force of our world ocean.
ψ is a wave function and refers to the amplitude of electron wave i.e. probability amplitude. It has got no physical significance. The wave function ψ may be positive, negative or imaginary. [ψ]2 is known as probability density and determines the probability of finding an electron at a point within the atom.
ψ is a wave function and refers to the amplitude of electron wave i.e. probability amplitude. It has got no physical significance. The wave function ψ may be positive, negative or imaginary. [ψ]2 is known as probability density and determines the probability of finding an electron at a point within the atom.
What is an example of a wave function
If the equation represents a wave, then the function is a wave function. For example, a simple wave with constant amplitude and varying in time can be described by: Asint. Its wave function would be f(t)=Asint.A wave function, in quantum physics, refers to a mathematical description of a particle's quantum state as a function of spin, time, momentum, and position. Moreover, it is a function of the degrees of freedom that correspond to a maximal set of commuting observables. Furthermore, psi, 𝚿, is the wave function symbol.probability density
Ψ2 is probability density or charge density. It represents the probability of finding an electron in an atom.
ψ is a wave function and refers to the amplitude of electron wave i.e. probability amplitude. It has got no physical significance. The wave function ψ may be positive, negative or imaginary. [ψ]2 is known as probability density and determines the probability of finding an electron at a point within the atom.
Do humans have a wave function : Even more, this phenomenon isn't just restricted to light. We see this is in all quantum particles, such as electrons, protons, and neutrons, and even in large collections of atoms. Even human beings act like quantum waves.
Is the wave function a real thing : The wavefunction is a real physical object after all, say researchers.
What is an example of a wave function equation
The simplest example is that of a constant potential V(x)=V0<E, for which the wave function is ψ(x)=Asin(kx+δ) with δ a constant and k=√(2m/ℏ2)(E−V0). On the other hand, for V(x)>E, the curvature is always away from the axis. This means that ψ(x) tends to diverge to infinity.
How do we Measure Wave Function The measurement of the wave function can take place with the help of the Schrodinger equation. Furthermore, experts define the Schrodinger equation as the linear partial differential equation that can describe the wave function, 𝚿. The name of this equation is after Erwin Schrodinger.Ψ as such has no physical significance. Ψ2 gives the probability of finding the electron at any point around the nucleus.
Is everything a wave function : According to quantum physics, everything is actually made up of waves, but these are quantum waves (or q-waves for short), meaning that the entities that are doing the waving are what Dirac called q-numbers (as opposed to the ordinary c-numbers, “c” being classical).