Antwort What is the theory of mountain building? Weitere Antworten – What is the theory related to mountain building
The theory of plate tectonics explains why different types of Earth movements, epirogenic and orogenic takes place which involves the processes of mountain building, Earthquake, volcanism and tsunamis, etc. All the great mountain ranges of the world can be explained with the plate tectonic theory.Folding, faulting, volcanic activity, igneous intrusion and metamorphism can all be parts of the orogenic process of mountain building. The formation of mountains is not necessarily related to the geological structures found on it. Thrust and reverse fault movement are an important component of mountain formation.The theory of plate tectonics revolutionized the earth sciences by explaining how the movement of geologic plates causes mountain building, volcanoes, and earthquakes.
What is the meaning of mountain building : Orogeny, or mountain building, is the result of collision between two landmasses.
What is the mountain theory
The Mountain Theory is a streamlined representation of the idea that everything goes faster at high altitude. You age faster up on a mountaintop than down in the valley, even if it's only a matter of a couple of microseconds.
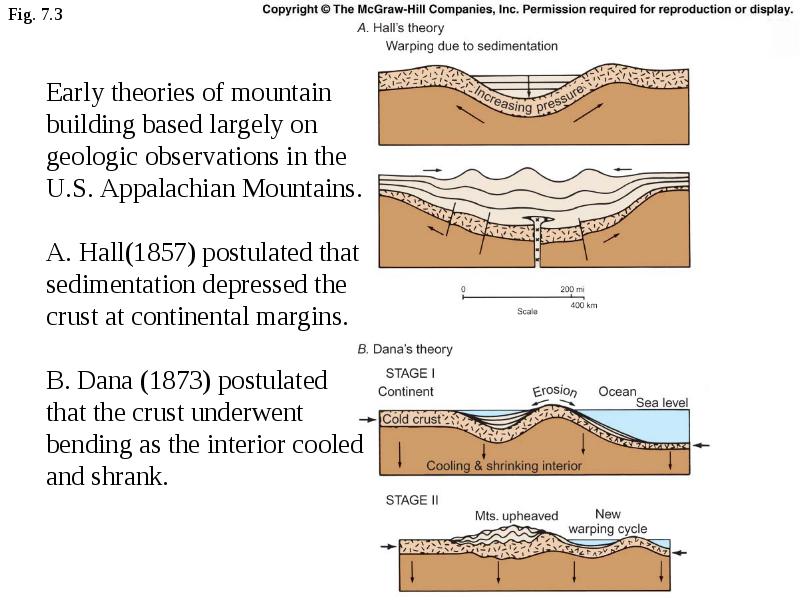
What was Darwin’s explanation of mountain building : The theory argued that mountains were built during paroxysmal upheavals of the land caused by a wave-like undulation of the crust that occurred because molten matter beneath was pulsating or moving with a wave-like motion.
Mountain architecture is organically massed to taper down into the site. Multiple volumes conform to the existing terrain and are in scale with the existing landscape. Large, symmetrical, obtrusive building forms are often avoided. Some single story elements help keep a mountain home residential in scale.
This evolution is marked by three stages: accumulation, orogeny, and uplift/block‐faulting. Accumulation. Many mountains contain sequences of sedimentary and volcanic rocks that reach thicknesses of 2,000 to 3,000 meters.
What is the theory of mountain building by Jolly
Joly has tried to show by mathematical calculation that it may take 33 to 56 million years for the accumulated heat derived from radioactivity to melt the basaltic rocks. down into the sima. As a result the oceanic water covers the low continental margins and there is transgression of the sea.Mountain building results from a variety of geological processes. The largest mountain ranges form over millions of years as tectonic plates collide, or as one tectonic plate over-rides another plate. Mountains form from a variety of processes, most of which are associated with the movement of tectonic plates.He proposed that upward convection might lift or even rupture the crust, that lateral movement could propel the crust sideways like a conveyor belt, and that where convection turned downwards, the buoyant continents would crumple up and form mountains.
Wegener's drift hypothesis also provided an alternate explanation for the formation of mountains (orogenesis). The theory being discussed during his time was the "Contraction theory" which suggested that the planet was once a molten ball and in the process of cooling the surface cracked and folded up on itself.
What did Darwin think about the mountains : Darwin surmised that mountains were formed slowly, rising incrementally, over millions of years; evidence was the discovery of fish/mollusk fossils on mountaintops 14,000 feet above sea level. This is similar to the evolutionary process which also takes a very long time.
How is a mountain building formed : Mountain building results from a variety of geological processes. The largest mountain ranges form over millions of years as tectonic plates collide, or as one tectonic plate over-rides another plate. Mountains form from a variety of processes, most of which are associated with the movement of tectonic plates.
Is tectonic plate a theory
Introduction to Plate Tectonics
The mantle sits between Earth's dense, very hot core and its thin outer layer, the crust. Plate tectonics has become the unifying theory of geology. It explains the earth's surface movement, current and past, which has created the tallest mountain ranges and the deepest oceans.
But the majority of mountain building on Earth is the result of plate tectonic forces that deform Earth's crust through faulting and folding. Mountain building through folding and faulting may or may not be supplemented by volcanic activity.A crack called a fault forms when large blocks of rock break and move past each other. The blocks of rock on either side of a fault are called fault blocks. The movement of faults can create mountains and other landforms. The three main kinds of faults are strike-slip faults, normal faults, and reverse faults.
How do scientists know how mountains are formed : Earth > Power of Plate Tectonics > Mountains
Mountains form where two continental plates collide. Since both plates have a similar thickness and weight, neither one will sink under the other. Instead, they crumple and fold until the rocks are forced up to form a mountain range.