Antwort What is the motivation theory of 3? Weitere Antworten – What are the three-three motivation theories
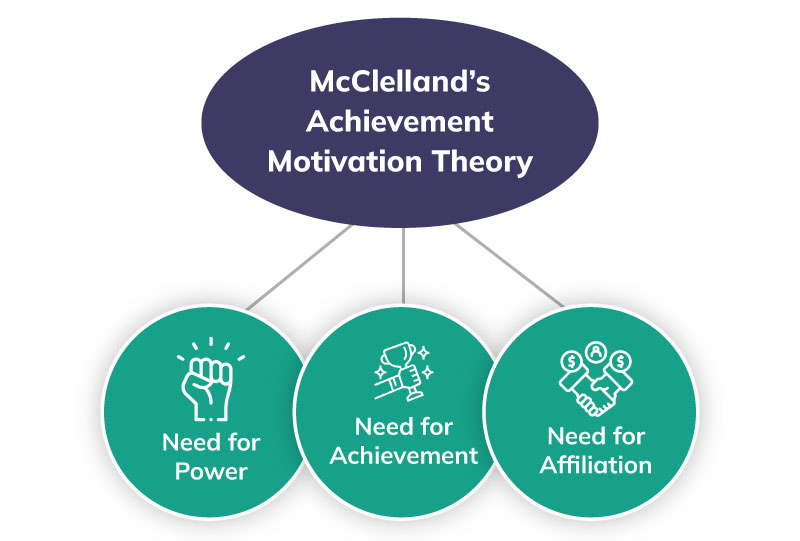
So what are the main theories of work motivation We've selected three high-profile theories that offer an interesting take on what motivates different individuals: Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, McClelland's Three Needs Theory, and Herzberg's Motivation Theory.Motivation theory is the study of understanding what drives a person to work towards a particular goal or outcome. It's relevant to all of society but is especially important to business and management. That's because a motivated employee is more productive, and a more productive employee is more profitable.According to this theory, individuals acquire three types of needs as a result of their life experiences. These needs are need for achievement, need for affiliation, and need for power. All individuals possess a combination of these needs. Those who have high need for achievement have a strong need to be successful.
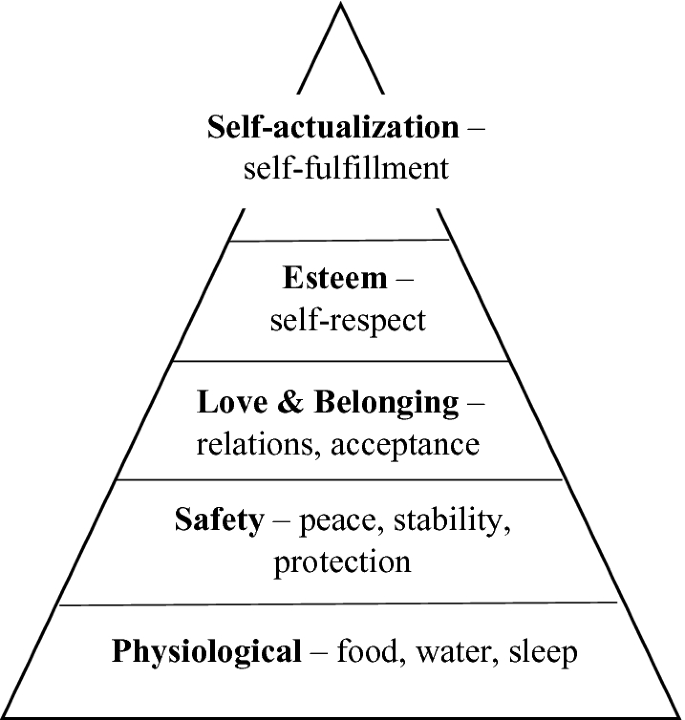
What is Maslow’s theory of motivation : Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory is regarded as one of the most popular theories on motivation. It is a theory of psychology that explains that humans are highly motivated in order to fulfill their needs, which is based on hierarchical order.
What is motivation 3
Extrinsic motivation or 2.0: which motivates us to move due to external factors, usually due to the existence of penalties and / or rewards. Intrinsic motivation or 3.0: is the one that encourages us to do things for ourselves, as we enjoy it.
What are the top 3 motivators : But it turns out that each one of us is primarily triggered by one of three motivators: achievement, affiliation, or power. This is part of what was called Motivation Theory, developed by David McClelland back in 1961.
Need theory, also known as Three needs theory, proposed by psychologist David McClelland, is a motivational model that attempts to explain how the needs for achievement, affiliation, and power affect the actions of people from a managerial context.
McClelland's Human Motivation Theory states that every person has one of three main driving motivators: the needs for achievement, affiliation, or power. These motivators are not inherent; we develop them through our culture and life experiences.
What is the big three motives theory
McClelland's human motives model distinguishes three major motives: the need for achievement, affiliation, and power.Maslow states that people are motivated by unmet needs which are in a hierarchical order that prevents people from being motivated by a need area unless all lower level needs have been met. Herzberg states that satisfaction and dissatisfaction are not on the same continuum and are therefore not opposites.Key Points. McClelland's Human Motivation Theory states that every person has one of three main driving motivators: the needs for achievement, affiliation, or power. These motivators are not inherent; we develop them through our culture and life experiences. Achievers like to solve problems and achieve goals.
The Rule of Three declares that if you make a list of everything you do in a week or a month—which may be twenty or thirty activities, for the average person—you will find that only three of those activities account for fully 90 percent of the value of all the work you do.
What is motivation 3.0 summary : Motivation 3.0 is built on the self-determination theory (SDT), which says that human beings have an innate drive to be autonomous, self-determined and connected. If we focus on creating environments where this drive can be expressed, people are more productive, fulfilled and happy.
What are the three 3 major motivating factors : Daniel Pink, in his book, Drive, lists three elements of the motivation formula: autonomy, mastery, and purpose. In situations where people are paid fairly, this trio drives, engages, and stimulates us to do our best work.
What is McClelland’s 3 Needs theory
McClelland's theory says that everyone is driven by one of three needs — achievement, affiliation or power. Different people are motivated by different drivers, so understanding what specifically motivates a person to complete a task can vastly improve the likelihood that they'll complete the assignment and do it well.
McClelland's human motives model distinguishes three major motives: the need for achievement, affiliation, and power. The power motive stems from a person's desire to influence, teach or encourage others.Drawing on Maslow's hierarchy of needs, McGregor argues that a need, once satisfied, no longer motivates. The company uses monetary rewards and benefits to satisfy employees' lower-level needs. Once those needs have been satisfied, the motivation disappears.
What is the Herzberg theory of motivation : Herzberg's two-factor theory is a motivation theory that suggests that satisfaction and dissatisfaction at work are influenced by two sets of factors: hygiene factors and motivators. Hygiene factors are basic job necessities, such as working conditions and salary, that, if not met, can cause dissatisfaction.