Antwort What is the main difference between PCR and qPCR? Weitere Antworten – What is the basic difference between PCR and qPCR
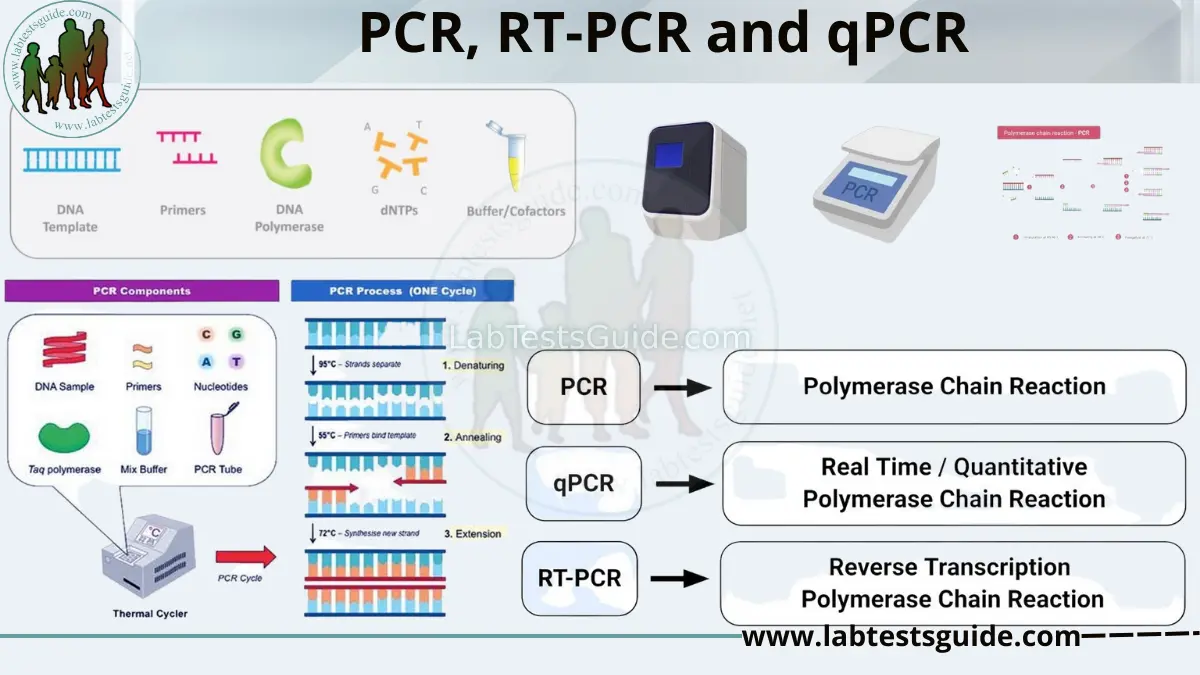
Both PCR and qPCR are polymerase chain reaction techniques used to amplify specific sections of DNA. The main difference between the two is that qPCR is a real-time method, while PCR is not. This means that with qPCR, you can monitor the amplification of your target DNA in real-time as it is happening.The main advantages of qPCR are that it provides fast and high-throughput detection and quantification of target DNA sequences in different matrices. The lower time of amplification is facilitated by the simultaneous amplification and visualization of newly formed DNA amplicons.RT-PCR as a relatively simple, inexpensive, extremely sensitive and specific tool to determine the expression level of target genes. Real-time PCR is a quantitative method for determining copy number of PCR templates, such as DNA or cDNA, and consists of two types: probe-based and intercalator-based.
Why is qPCR more accurate : The primary strength of qPCR is its high sensitivity and specificity (Kralik and Ricchi, 2017). qPCR can detect very small amounts of target sequences, and accurately differentiate between variants of similar nucleic acid sequences.
What distinguishes qPCR from regular PCR
qPCR and RT-qPCR
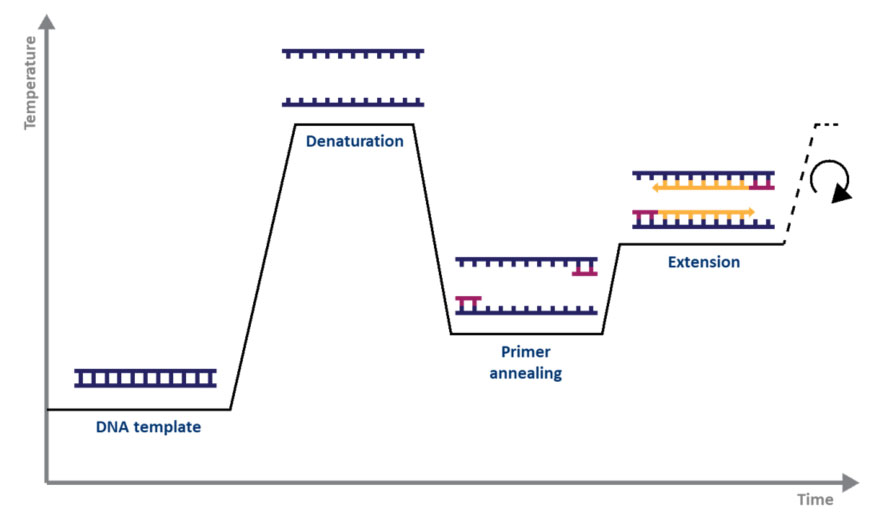
As in standard PCR, DNA is amplified by three repeating steps: denaturation, annealing, and elongation. However, in qPCR, fluorescent labeling enables the collection of data as PCR progresses. This technique has many benefits due to the range of methods and chemistries available.
What is the difference between CT and qPCR : A qPCR curve has typically an exponential phase followed by a plateau phase. The Ct measure is a determined PCR cycle and represents the basic result of a qPCR experience. It's taken in the exponential phase, where the curve is linear.
Compare and contrast: qPCR vs dPCR
In such applications, dPCR outperforms qPCR by not only measuring the absolute copy number but also overcoming the limits of detection, i.e., detecting small fold-change differences expressed as 10% precision and mutation rates <1%.
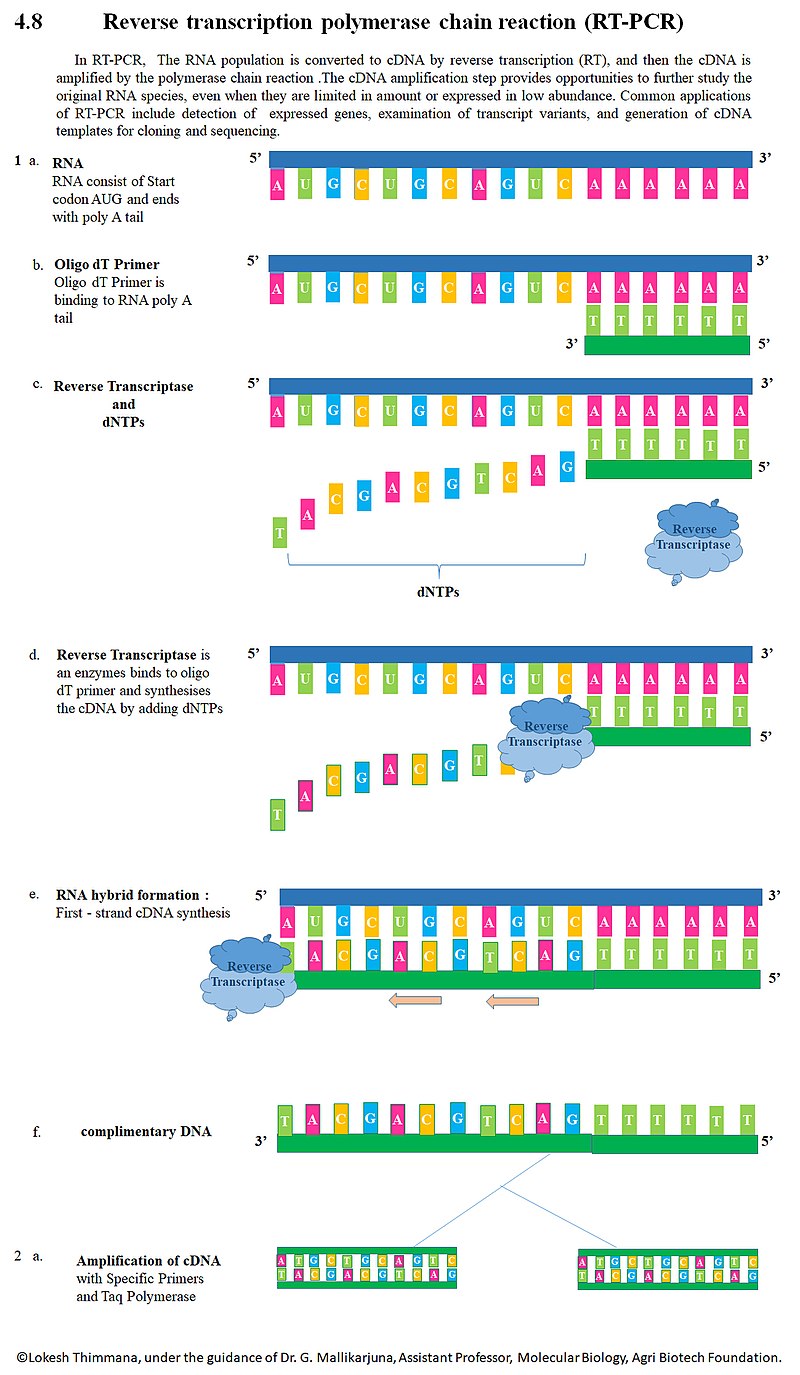
Real-time PCR, also known as quantitative PCR (qPCR), combines PCR amplification and detection in a single step. Another technique known as reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) uses RNA as the nucleic acid starting template.
Why is real time PCR better than PCR
Traditional PCR methods use Agarose gels or other post PCR detection methods, which are not as precise. As mentioned earlier, the exponential phase is the optimal point for analyzing data. Real-Time PCR makes quantitation of DNA and RNA easier and more precise than past methods.Real-time PCR is quite different from normal PCR but the fundamental principles are the same for both. However, in qPCR, we can quantify the amount transcript present after each PCR round. This is done by measuring the intensity of a fluorescent probe or dye which binds to double-stranded DNA and emits fluorescence.dPCR is recommended for analysis of copy number variation, since it can accurately detect copy changes with fewer replicates than qPCR. With qPCR, as the difference between copy numbers decreases, the number of replicates required increases rapidly.
qPCR is suitable for screening a large number of samples with higher throughput and larger dynamic range. dPCR systems offer more precisions and are ideal for measurement of fractional abundance, or the mutant vs wild type ratio.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative RNA PCR : Explanation of test results:
If a qualitative RNA test is positive (detected), then it is confirmed that the patient has chronic hepatitis C. The "qualitative" test is more accurate than the "quantitative" test because qualitative tests are able to detect very low levels of the virus.
What is the difference between qualitative PCR and real-time PCR : To sum up, RT-PCR and qPCR are the advanced methods of PCR or polymerase chain reaction. qPCR gives faster, more detailed real-time results and is used to quantify nucleic acids. RT-PCR is used to detect and amplify cDNA.
Why is PCR test more accurate
Because the PCR test is so sensitive, it can detect very small amounts of virus material. This means that the test can continue to detect fragments of SARS-CoV-2 virus even after you've recovered from COVID-19 and are no longer contagious.
The PCR test takes a sample of ribonucleic acid (RNA) and “amplifies” it with the help of lab technologies. Amplifying RNA helps to make even small traces of the COVID-19 virus visible in the test sample. Even if you have a small trace of the virus in your system, the PCR test will detect it.Although RT-qPCR can provide quantitative results using Ct values and a standard curve [3], it is mainly used for qualitative analysis in clinical COVID-19 detection.
What’s the difference between a PCR and rapid test : “Unlike the PCR test, the antigen test can only determine if you have an active virus in your body. The rapid test can't detect small amounts of the virus or asymptomatic cases as accurately as the PCR test can,” Heather said. So how accurate are home COVID-19 tests