Antwort What is the gender inequality in Czech Republic? Weitere Antworten – Which country has highest gender inequality
10 countries with least gender equality
- Democratic Republic of Congo 57.5%
- Iran 57.6%
- Chad 57.9%
- Mali 60.1%
- Algeria 60.2%
- Oman 60.9%
- Benin 61.2%
- Qatar 61.7%
With 57.9 points out of 100, Czechia ranks 25th in the EU on the Gender Equality Index. Its score is 12.3 points below the score for the EU as a whole.Gender inequality is discrimination on the basis of sex or gender causing one sex or gender to be routinely privileged or prioritized over another. Gender equality is a fundamental human right and that right is violated by gender-based discrimination.
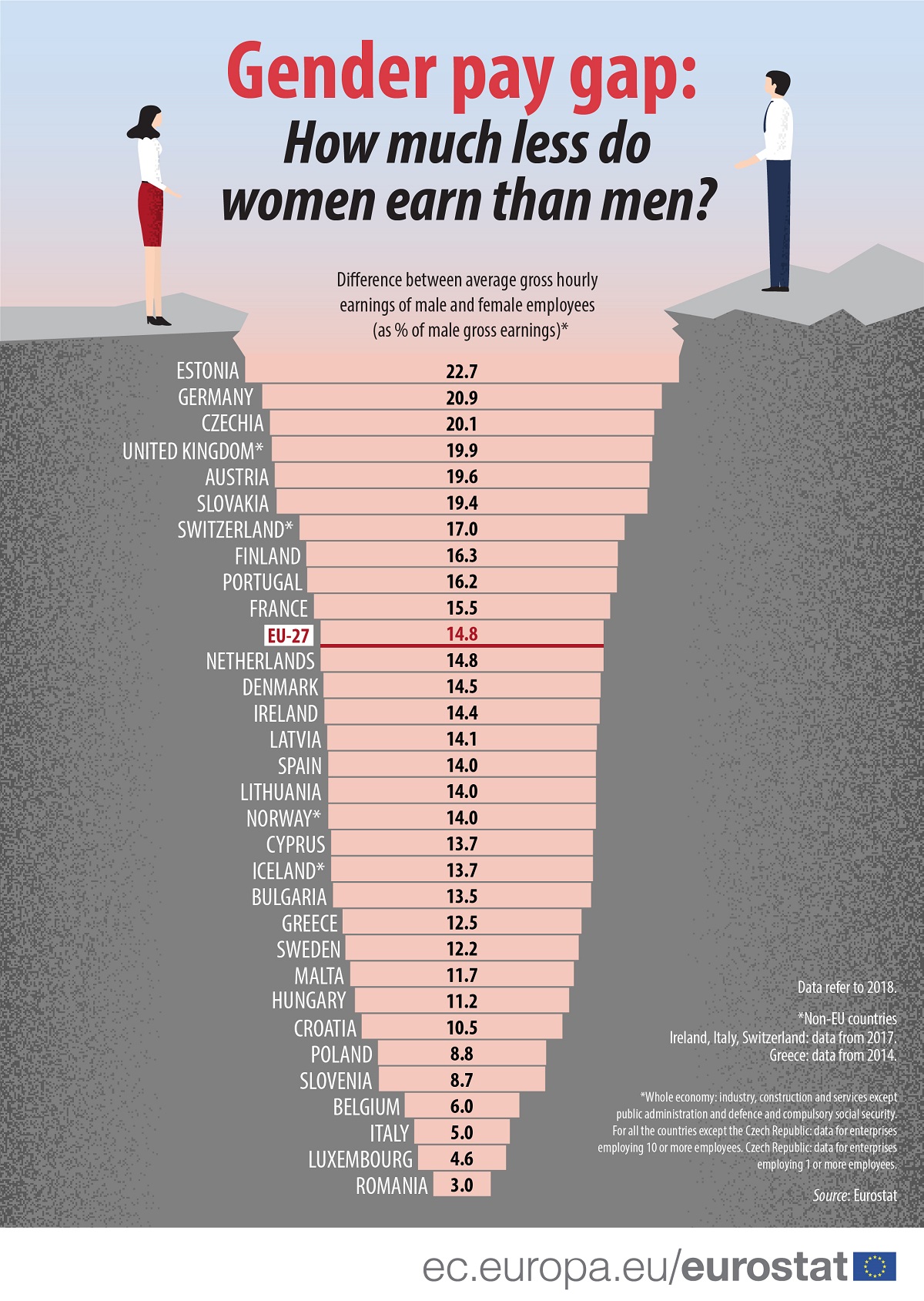
What is the wage gap in the Czech Republic : Despite Czechia's overall steady economic status, the gender wage gap in Czechia is still a prominent issue. According to EU statistics, in 2021, women in Czechia received 19.5% lower pay than men on average in private sector work and 12.2% lower in public sector work.
What is the most gender equal country in Europe
The Global Gender Gap Index
In a global perspective Iceland is considered the most gender equal country. Dominating this list is another four Nordic countries: Norway, Finland, and Sweden.
Where is gender inequality the worst : Table of Contents
- Gender Inequality.
- Kenya.
- Turkey.
- Kazakhstan.
- Iran.
- India.
- Oman.
- Bahrain.
Despite recent progress to improve gender equality in the Czech Republic, several gender gaps persist in different areas of the society and economy.
With 57.2 points out of 100 points, Czechia ranks 23rd in the EU on the Gender Equality Index. Its score is 11.4 points below the EU's score.
What are three examples of gender inequality
Examples of gender discrimination include but are not limited to:
- Misgendering or mispronouning (purposefully using the wrong gender identity or pronouns to address someone)
- Having limited access to all-gender restrooms.
- Disfavoring someone based on gender.
Every day, in every country in the world, women are confronted by discrimination and inequality. They face violence, abuse and unequal treatment at home, at work and in their wider communities – and are denied opportunities to learn, to earn and to lead. Women form the majority of those living in poverty.Six factors are generally cited as playing a role in low Czech unemployment during and after economic transformation: the low international value of the Czech crown, the human capital of the Czech work force, tripartite wage setting with a view towards maximizing employment, the efforts of Federal em- ployment offices, …
The economy of the Czech Republic is a developed export-oriented social market economy based in services, manufacturing, and innovation that maintains a high-income welfare state and the European social model.
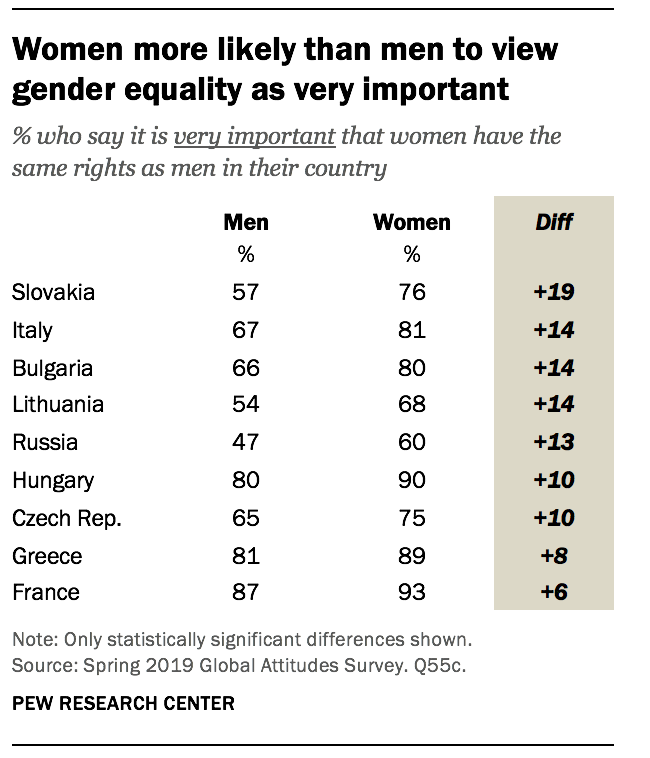
What are the least feminist countries in Europe : The former Soviet nations of Lithuania, Ukraine and Russia are the least likely to believe gender equality is very important, though more than half in each country hold this view.
Is Czech masculine feminine neutral : The subject pronouns are “on” (he), “ona” (she), and “ono” (it) for the masculine, feminine, and neuter genders, respectively. The demonstrative pronouns “ten” (that/this – masculine), “ta” (that/this – feminine), and “to” (that/this – neuter) designate gender by utilizing different endings.
What is the gender ratio in Czech Republic
The Gender Ratio of Czech Republic (2020 – 2028, males per 100 females)
| Year | Value (males per 100 females) |
|---|---|
| 2,020 | 97.07 |
| 2,021 | 97.03 |
| 2,022 | 97.08 |
| 2,023 | 97.28 |
How Can We Stop Gender Discrimination
- Ensure equal access to education.
- Empower women in the workplace.
- Protect reproductive rights.
- Strengthen legal protections.
- Provide better medical care.
- Achieve better political representation.
- Prioritize the most marginalized.
At a time when human societies were abandoning their wanderlust in favour of agricultural settlements, the first inklings of gender inequality were taking root. That's according to a study published in the European Journal of Archaeology, which analysed 5000-to-8000-year-old graves on the Iberian Peninsula.
Who is most affected by gender inequality : Women, non-binary and trans people are confronted by discrimination and inequality. They face violence, abuse and unequal treatment at home, at work,in their wider communities –and are denied opportunities to learn, to earn and to lead. Women form the majority of those living in poverty.