Antwort What is the difference between interest rate and swap rate? Weitere Antworten – What is the difference between a swap and an interest rate swap
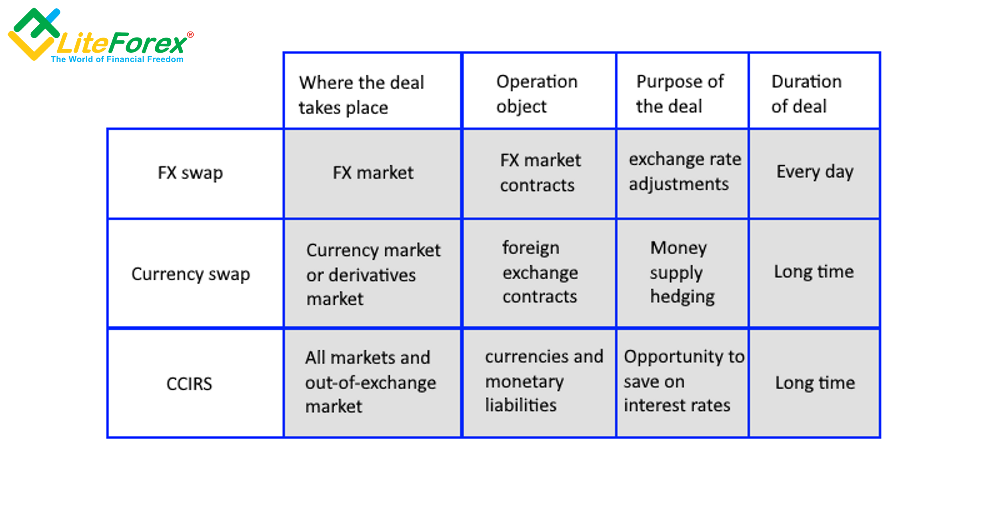
An interest rate swap is an agreement between two parties to exchange one stream of interest payments for another, over a set period of time. Swaps are derivative contracts and trade over-the-counter.While currency swaps involve two currencies, interest rate swaps only deal with one currency. For example, assume bank XYZ operates in the United States and deals only with U.S. dollars, while bank QRS operates in Russia and deals only with rubles. Suppose bank QRS has investments in the United States worth $5 million.At a high level, interest rate caps are option products that require a premium and create a synthetic upper limit for the rate on your floating-rate debt. Swaps, on the other hand, allow you to synthetically fix your floating rate at a specific level based on the current forward curve.
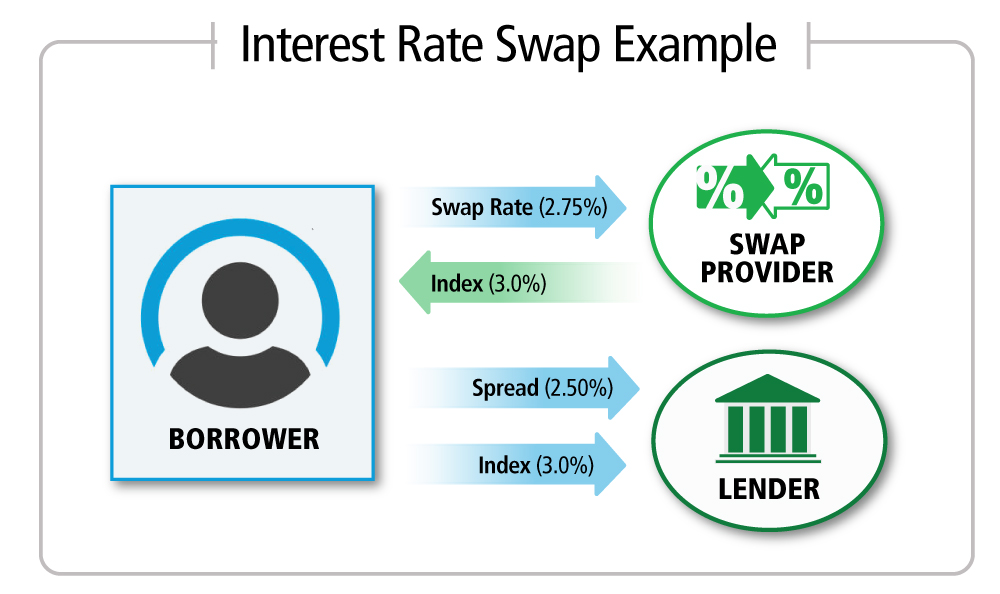
What is interest rate swap with an example : An interest rate swap is a contractual arrangement be- tween two parties, often referred to as “counterparties”. As shown in Figure 1, the counterparties (in this example, a financial institution and an issuer) agree to exchange payments based on a defined principal amount, for a fixed period of time.
What is the 3 month Euribor swap rate
Current 1 Month, 3 Month, and 6 Month EURIBOR
| Index | Rate |
|---|---|
| One Month | 3.856% |
| Three Month | 3.818% |
| Six Month | 3.789% |
What is the difference between LIBOR and swap rate : The “swap rate” is the fixed interest rate that the receiver demands in exchange for the uncertainty of having to pay the short-term LIBOR (floating) rate over time. At any given time, the market's forecast of what LIBOR will be in the future is reflected in the forward LIBOR curve.
Exchange rates and interest rates are both equally important in determining a country's economic growth, inflation, levels of foreign trade, and other economic determinants. Exchange rates and interest rates are closely related, yet in no way they represent the same thing.
Since nominal interest rates depend on expected inflation while nominal exchange rates depend on relative rates of foreign and domestic inflation, an inflation shock will affect both nominal interest rates and exchange rates.
How do swap rates affect interest rates
Swap rates allow banks, companies, and investors to manage interest rate risk by locking in a fixed interest rate for a specific period. Increasing swap rates can lead to higher floating interest rates for borrowers with floating-rate mortgages while decreasing swap rates can lead to lower floating interest rates.EURIBOR swaps are commonly used by real estate borrowers to hedge floating-rate EUR debt, structured to pay this fixed rate quarterly versus receiving 3-month EURIBOR quarterly, on an Actual/360 basis without amortization. Often used as a reference rate for fixed-rate debt.Euribor is the acronym for the Euro Interbank Offered Rate. This is the interest rate at which credit institutions lend money to each other, which is often referred to as “the price of money”. The Euribor is published daily, but does not really refer to a single interest rate.
Understanding the Euro LIBOR
The financial market industry has transitioned away from using LIBOR; it is no longer an applicable rate, and variable-term loans were transitioned to other rates, such as the Euro Short-Term Rate in Europe or the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR) in the U.S.
Is LIBOR the same as interest rate : The London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR) was a benchmark interest rate at which major global banks lent to one another in the international interbank market for short-term loans. LIBOR served as a globally accepted key benchmark interest rate that indicated borrowing costs between banks.
Is there a relationship between exchange rates and interest rates : Generally, higher interest rates increase the value of a country's currency. Higher interest rates tend to attract foreign investment, increasing the demand for and value of the home country's currency.
What is the relationship between real interest rate and exchange rate
A higher U.S. real interest rate increases the attrac- tiveness of U.S. assets, leading to an increase in the demand for dollar-denominated assets and an appreciation of the real exchange rate. Then, for given price levels at home and abroad, the nominal exchange rate also tends to rise.
So in easier terms, a swap rate is a rate based on what the markets think interest rates will be in the future. If the rates rise, then mortgage lenders will look to increase their rates so that they don't lose out. Meaning if swap rates go down, mortgage rates tend to go down. If they go up, so do mortgage rates too.Interest rate swaps (“swaps”) account for the largest share of the euro area derivatives market. Between March 2021 and September 2022, gross notional on EURIBOR swaps – the most traded and liquid derivatives used to hedge interest rate risk for euro-denominated exposures – increased by around 50% (Chart A, panel a).
What do swap rates mean : Swap rates are the fixed interest rates at which two parties agree to exchange cash flows in an interest rate swap. They represent the cost or benefit associated with swapping fixed-rate. and floating-rate payments.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_final_Currency_Swap_vs_Interest_Rate_Swap_Whats_the_Difference_Jan_2021-01-d0d9bf99a16c467daeab2fd073b67051.jpg)