Antwort What is the difference between 2 step and 3 step PCR? Weitere Antworten – When to use 2 step PCR

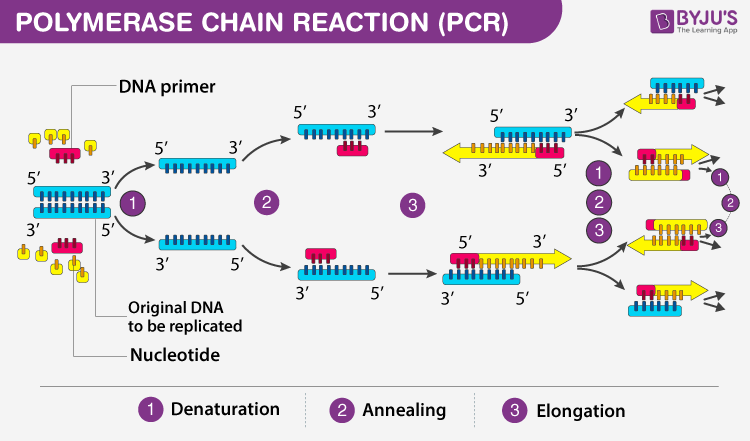
2-step PCR: When primers with annealing temperatures ≥ 72°C are used, a 2-step thermocycling protocol (combining annealing and extension into one step) is possible. Amplification of long products: When amplifying products > 6 kb, it is often helpful to increase the extension time to 40–50 seconds/kb.RT-PCR can be performed by a one-step method, in which the cDNA synthesis (RT reaction) and PCR are carried out in one tube as a single reaction, or by a two-step reaction, in which the RT reaction is run first, followed by the PCR reaction in a separate tube.Three steps of PCR─denaturation, annealing, and extension─as shown in the first cycle, and the exponential amplification of target DNA with repeated cycling.
What is the protocol for two-step RT-PCR : Two-step RT-PCR entails two separate reactions, beginning with first-strand cDNA synthesis (RT), followed by amplification of a portion of the resulting cDNA by PCR in a separate tube. Therefore, two-step RT-PCR is useful for detecting multiple genes in a single RNA sample.
What is the third step in PCR
PCR is based on three simple steps required for any DNA synthesis reaction: (1) denaturation of the template into single strands; (2) annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis; and (3) extension of the new DNA strands from the primers.
What are the disadvantages of two-step RT-PCR : The drawback of two-step RT-qPCR is that it requires an extra open-tube step, more pipetting manipulations, and longer hands-on time. This can lead to greater variability and risk of contamination, and makes two-step RT-qPCR less amenable to high-throughput applications.
The advantages
Two-step RT-qPCR is best suited for applications requiring flexibility and sensitivity. The two-tube protocol makes it possible to optimize the RT and qPCR steps separately, ensuring maximum specificity and efficiency. This approach works best with workflows analyzing many targets in fewer samples.
PCR is based on three simple steps required for any DNA synthesis reaction: (1) denaturation of the template into single strands; (2) annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis; and (3) extension of the new DNA strands from the primers.
Why does PCR need 3 cycles
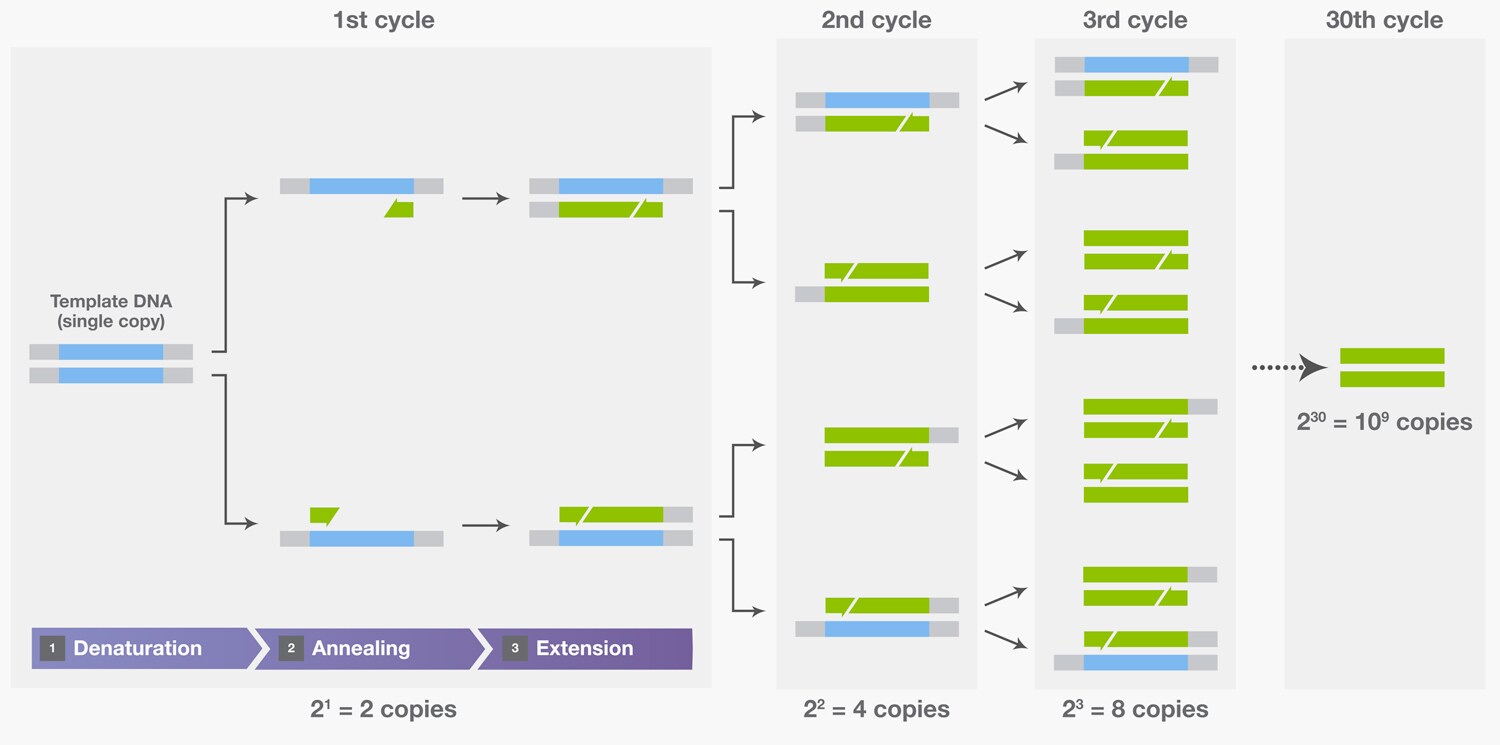
The three steps are repeated for multiple cycles, with each cycle doubling the amount of DNA in the sample. The number of cycles is determined by the amount of target DNA in the initial sample and the sensitivity required for the experiment.three
PCR is based on three simple steps required for any DNA synthesis reaction: (1) denaturation of the template into single strands; (2) annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis; and (3) extension of the new DNA strands from the primers.RT-PCR Protocol
- Experiment process.
- (1) Primer design. Design and synthesize the primers of the target gene.
- (2) RNA extraction.
- (3) Reverse transcription(RNA→cDNA)
- (4) Real-time PCR.
- (5) Result analysis.
- The factors affecting Real-time PCR results.
Step 3, extending: the temperature is raised again and the new strand of DNA is made by the Taq polymerase enzyme. These three stages are repeated 20-40 times, doubling the number of DNA copies each time. This is called thermal cycling, carried out by a machine. It's carried out by a machine called a thermal cycler.
Why is the third cycle of PCR special : In the third cycle, the newly synthesized target region DNA resulting from the second cycle comprises only the amplicon and therefore becomes the specific template. Cycling is repeated continuously, resulting in exponential amplification of the copied sequences (Figure 2.2).
What are the advantages of one-step RT-PCR : There are advantages and disadvantages to both systems. The advantages to one-step real-time RT-PCR is that it is quicker to set up, less expensive to use, and involves less handling of samples, thereby reducing pipetting errors, contamination, and other sources of error.
What are the disadvantages of one-step PCR
Disadvantages
- Impossible to optimize the two reactions separately.
- Less sensitive than two-step because the reaction conditions are a compromise between the two combined reactions.
- Detection of fewer targets per sample.
The drawback of two-step RT-qPCR is that it requires an extra open-tube step, more pipetting manipulations, and longer hands-on time. This can lead to greater variability and risk of contamination, and makes two-step RT-qPCR less amenable to high-throughput applications.PCR is a method used to amplify DNA from a small amount of DNA template. RT-PCR uses reverse transcription to produce a DNA template from an RNA source that can then be amplified.
What is the second step of PCR : The process starts with Denaturation. The second step in polymerase is annealing or hybridization. Lastly, the elongation process is followed.