Antwort What is the difference between 100mb half duplex and full duplex? Weitere Antworten – What is 100 Mbps full-duplex
A switch that can deliver 100Mbps symmetrical, full duplex can transmit and receive at a rate of 100Mbps. Even if it is full duplex, a network switch with asymmetrical bandwidth cannot send AND receive at 100Mbps. Asymmetrical switches will use an uneven split to transmit at 70Mbps and receive at 30Mbps, for example.If we compare full duplex vs half duplex, full duplex point to point is much faster, and will provide faster throughput for voice, data and video transmission.In data networking, Ethernet hubs are half-duplex devices by nature, as they create a single shared channel of communication. Ethernet switches, on the other hand, can use a connection in either half- or full-duplex mode. Most networks are built around switches now, but hubs are still used as well.
What is the difference between half duplex and full-duplex wiring : Quick Definition: Full-duplex enables simultaneous two-way communication, which allows data to flow freely bidirectionally. Half-duplex enables two-way communication, but not simultaneously. Half-duplex requires switching between a sending and receiving mode.
What is 100mbps half-duplex
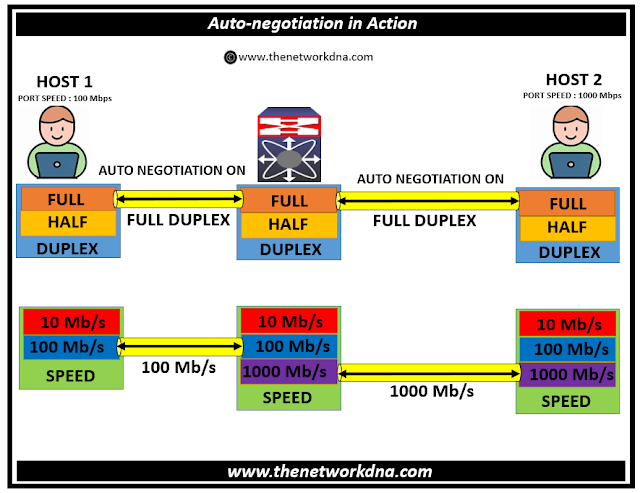
100BASE-T (fast ethernet over 2 wire pairs) is full duplex, meaning 100Mbit per direction, simultaneously. It is possible to configure a 100Mbit network interface in half duplex, meaning that the total bandwidth available for send+receive is 100Mbit (as opposed to 200Mbit for full duplex)
What does 100m half-duplex mean : Half Duplex means that a device talks then listens using 2 pairs 1/2, 3/6 in a cat x cable. So you get 100 or 1000 or 10 between talking and listening. Full Duplex means that a device can TALK and LISTEN at the same time using 1/2, 3/6 to talk but 4/5, 7/8 to listen.
100BASE-T (fast ethernet over 2 wire pairs) is full duplex, meaning 100Mbit per direction, simultaneously. It is possible to configure a 100Mbit network interface in half duplex, meaning that the total bandwidth available for send+receive is 100Mbit (as opposed to 200Mbit for full duplex)

Full-duplex Ethernet does save time when compared to half-duplex because it alleviates collisions and frame retransmissions. Sending and receiving are separate functions, creating a system where there is full data capacity in each direction. In contrast, half-duplex can be used to conserve bandwidth.
Is Wi-Fi full or half-duplex
Most wireless devices today are half duplex. This is because the signals a wireless device transmits are more powerful than the ones it receives. Owing in part to this, output signals in a half-duplex system are picked up by the device. This overwhelms the input signal and self-interference is created.Full-duplex communication over a single signal pair requires 4-to-2 wire conversions between the transceivers and the bus cable to distinguish the incoming (receive) data from the outgoing (transmit) data (Figure 2). The design of a 4-to-2 wire converter can be tricky.Basically, yes full duplex 1Gbps means 2Gbps maximum ideal transmission. Depends, as always, on all the components in the action: NIC, cabling, and switches. Practically, won't see it often. Like the others said full duplex does mean you can download a gig and upload a gig at the same time.
Full-duplex breaks one of the fundamental assumption in wireless network design; current networks are either half-duplex in time (like WiFi) and frequency (like most cellular).
Is half-duplex better than full duplex : Full-duplex Ethernet does save time when compared to half-duplex because it alleviates collisions and frame retransmissions. Sending and receiving are separate functions, creating a system where there is full data capacity in each direction. In contrast, half-duplex can be used to conserve bandwidth.
Is Wi-Fi only half-duplex : 99.9% of the time Wireless is half duplex. There are experiments that can result in a "full duplex" wireless network but that's all lab-based and not real-world. With Wireless the devices cannot send and receive simultaneously and they cannot sense collisions.
Is wifi full or half-duplex
Most wireless devices today are half duplex. This is because the signals a wireless device transmits are more powerful than the ones it receives. Owing in part to this, output signals in a half-duplex system are picked up by the device. This overwhelms the input signal and self-interference is created.
Advantages. One of the notable advantages of half duplex mode is its simplicity. It allows communication in both directions using a single path for transmitting and receiving data.Full-duplex Ethernet does save time when compared to half-duplex because it alleviates collisions and frame retransmissions. Sending and receiving are separate functions, creating a system where there is full data capacity in each direction. In contrast, half-duplex can be used to conserve bandwidth.
Is 802.11ac full duplex : As with all 802.11 standards, 802.11ac is half-duplex, shared medium radio technology that works best when employed in wireless networking environments designed by qualified professionals.