Antwort What is the difference between 1 2 duplex and full-duplex? Weitere Antworten – What is the difference between half-duplex and full duplex
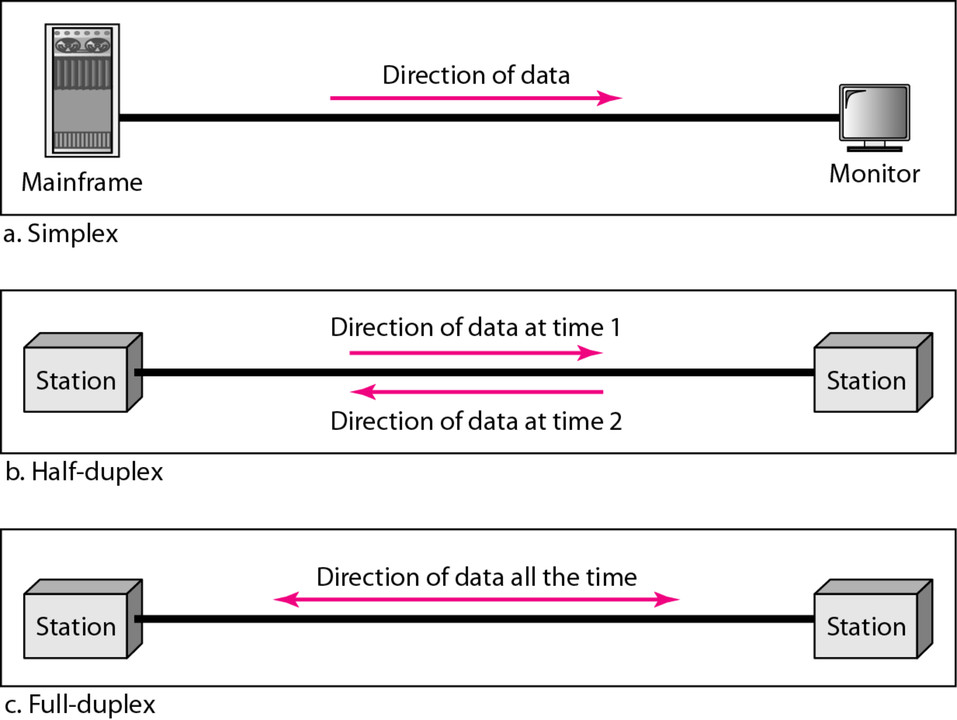
A half-duplex transmission could be considered a one-way street between sender and receiver. Full-duplex, on the other hand, enables two-way traffic at the same time. A communications channel can be used to communicate one way at a time or in both directions at once.Using the same example of moving two 150Mb files, a 100Mbps symmetrical, full duplex switch will deliver both files in 1.5 seconds. A 100Mbps asymmetrical half duplex switch with a 70/30 split will take 7.14 seconds to deliver both files.Full duplex means that data flowing up to the internet runs at the same time as data down from the internet (using your computer as point of view) Most of the transport within the internet is full duplex, but there are links that are half duplex – which means UL request occurs, then down link response occurs after.
Is full duplex slower than half-duplex : If we compare full duplex vs half duplex, full duplex point to point is much faster, and will provide faster throughput for voice, data and video transmission.
Which is better half or full-duplex
Full-duplex Ethernet does save time when compared to half-duplex because it alleviates collisions and frame retransmissions. Sending and receiving are separate functions, creating a system where there is full data capacity in each direction. In contrast, half-duplex can be used to conserve bandwidth.
Is half-duplex good : Half-duplex has limited throughput since data can only be sent one way at a time. This dramatically impedes a network's speed and reliability.
Quick Definition: Full-duplex enables simultaneous two-way communication, which allows data to flow freely bidirectionally. Half-duplex enables two-way communication, but not simultaneously. Half-duplex requires switching between a sending and receiving mode.
Full duplex could double the capacity of wireless networks, making it a key technology for 5G.
Is Wi-Fi only half-duplex
99.9% of the time Wireless is half duplex. There are experiments that can result in a "full duplex" wireless network but that's all lab-based and not real-world. With Wireless the devices cannot send and receive simultaneously and they cannot sense collisions.Full-duplex Ethernet does save time when compared to half-duplex because it alleviates collisions and frame retransmissions. Sending and receiving are separate functions, creating a system where there is full data capacity in each direction. In contrast, half-duplex can be used to conserve bandwidth.Advantages. One of the notable advantages of half duplex mode is its simplicity. It allows communication in both directions using a single path for transmitting and receiving data.
Full-duplex communication allows for faster data transfer as devices can both send and receive information simultaneously. This increases data transfer speeds compared to half-duplex or simplex communication. (Simplex communication is unidirectional data transmission, like a keyboard.)
Which is better, half or full-duplex : Full-duplex Ethernet does save time when compared to half-duplex because it alleviates collisions and frame retransmissions. Sending and receiving are separate functions, creating a system where there is full data capacity in each direction. In contrast, half-duplex can be used to conserve bandwidth.
Why would you want half-duplex : One of the notable advantages of half duplex mode is its simplicity. It allows communication in both directions using a single path for transmitting and receiving data.
Is LTE half-duplex or full-duplex
LTE can be either full duplex (meaning that transmitting and receiving can happen simulataneously), or half duplex (meaning that transmitting and receiving can happen, but not at the same time).
Full duplex could double the capacity of wireless networks, making it a key technology for 5G.The 802.11 family consists of a series of half-duplex over-the-air modulation techniques that use the same basic protocol.
Why is half-duplex still used : Half-duplex systems are usually used to conserve bandwidth, at the cost of reducing the overall bidirectional throughput, since only a single communication channel is needed and is shared alternately between the two directions.