Antwort What is the correct order of 3 steps of PCR? Weitere Antworten – What are the three steps of PCR
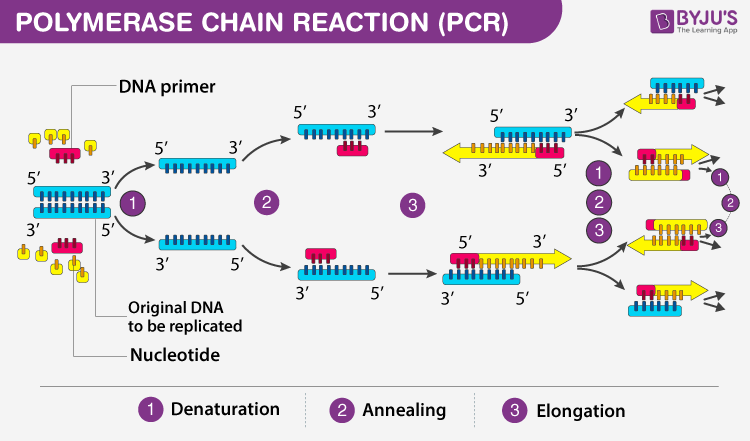
PCR is based on three simple steps required for any DNA synthesis reaction: (1) denaturation of the template into single strands; (2) annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis; and (3) extension of the new DNA strands from the primers.Hence the sequence of steps is denaturation, annealing, and extension.A standard polymerase chain reaction (PCR) setup consists of four steps:
- Add required reagents or mastermix and template to PCR tubes.
- Mix and centrifuge.
- Amplify per thermo cycler and primer parameters.
- Evaluate amplified DNA by agarose gel electrophoresis followed by ethidium bromide staining.
What is the correct order of steps during PCR amplification Quizlet :
- PCR (polymerase Chain reaction) an automated process to replicate short targeted segments of DNA into millions of copies.
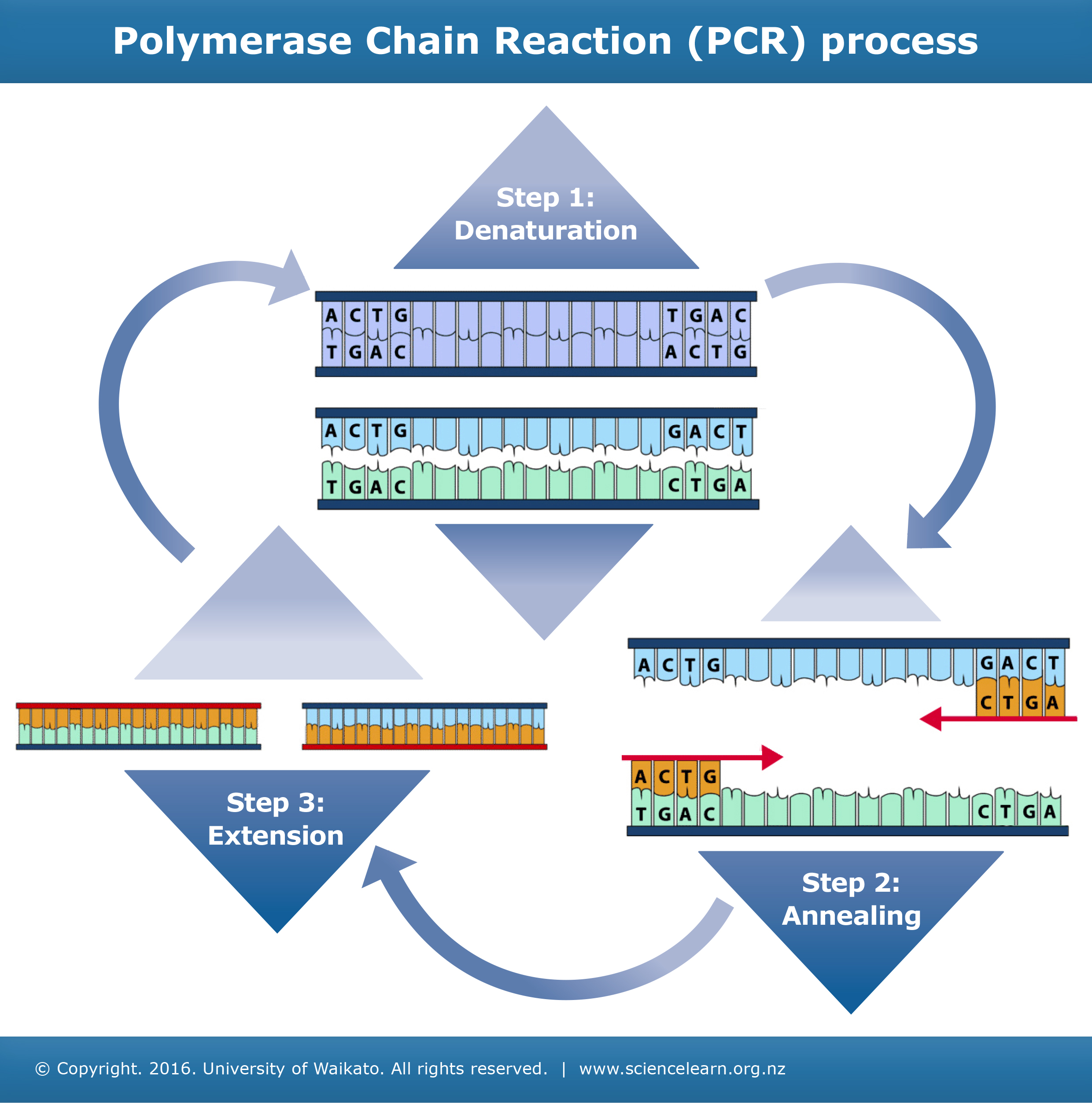
- Step 1: Denaturation. the reaction mixture is heated to 95 degress C to denature the DNA into single strands.
- Step 2: Primer Annealing.
- Step 3: Primer Extension.
- PCR requirements.
- Taq polymerase.
What are the three steps of PCR quizlet
It used repeating cycles consisting of three steps (denaturing, annealing and extension). PCR has the ability to make millions of copies of the template DNA.
What is the order of the three main steps in a PCR quizlet :
- Denaturation: hydrogen bonds are broken.
- Annealing: primers attach to DNA template.
- Elongation: polymerase binds to PCR primer and begins adding nucleotides.
The polymerase chain reaction is a nucleic acid amplification testing procedure that consists of denaturing, renaturing, elongating, and amplifying a short segment of DNA or RNA.
Denaturation
Denaturation is the first step of PCR. In this step, heat is applied to the template to separate double-stranded DNA into two single strands. Following the denaturation step is the annealing step. The temperature is decreased so that the primers can anneal to the complementary sequences on the DNA templates.
What are the cycles of PCR
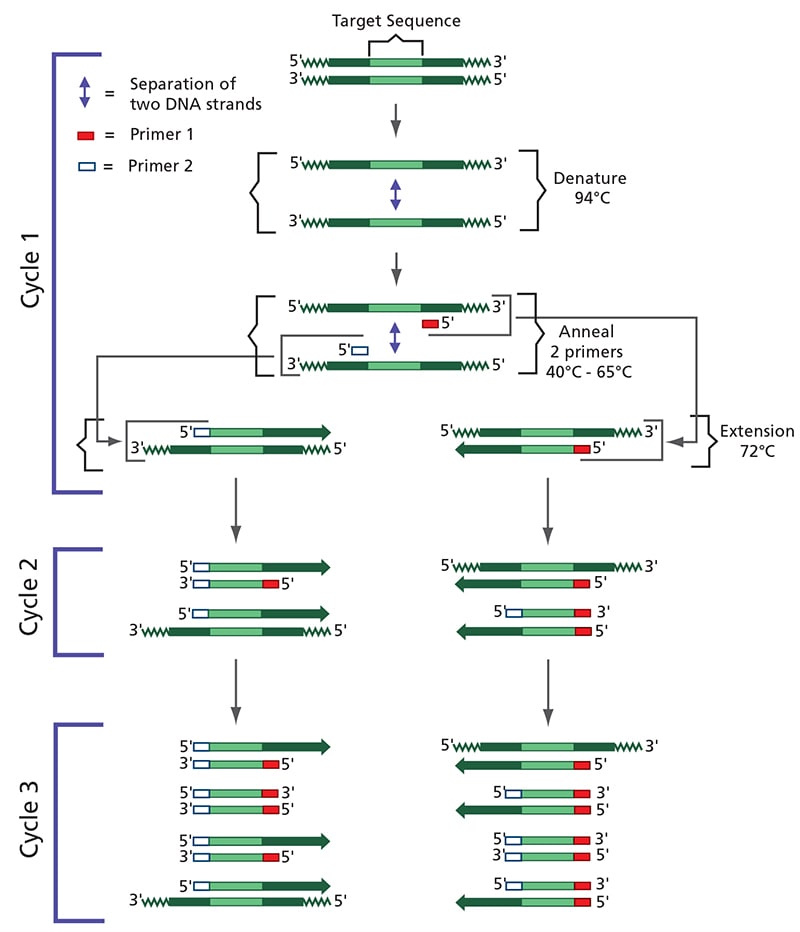
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplifies DNA and involves a series of temperature cycles critical for amplifying the DNA target. The cycling process is divided into three main stages: denaturation, annealing, and extension. These three stages are repeated for 20-40 cycles, doubling the targeted DNA amount.
- Denaturation: hydrogen bonds are broken.
- Annealing: primers attach to DNA template.
- Elongation: polymerase binds to PCR primer and begins adding nucleotides.
- PCR. Polymerase chain reaction.
- Three steps. Denaturation.
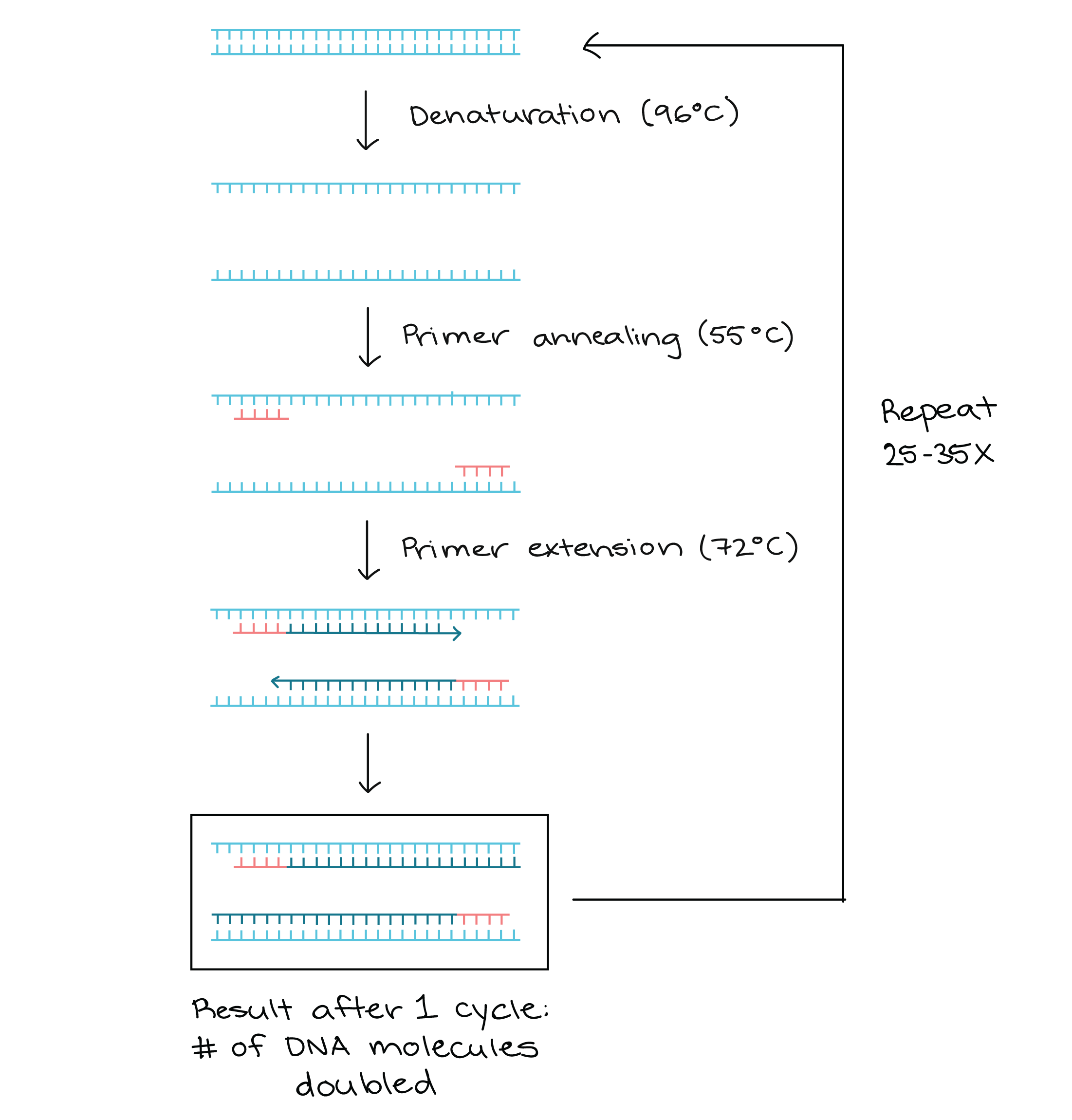
- Denaturation. 94 c for 30 sec separates DNA from being double stranded to single stranded.
- Primer annealing. 55 c for 45 sec oligonucleotide primers are able to bind on DNA strands.
- Primer extension. 72 c for 2 min uses thermophiles.
- Paul berg. Discovered cloning.
What is PCR -Process that copies a particular region of DNA using 2 primers. Each strand of DNA is used as a template to create a replicate that permits a doubling of the number of target molecules with each cycle of heating and cooling.
What are the steps of the PCR process Quizlet :
- PCR. Polymerase chain reaction.
- Three steps. Denaturation.
- Denaturation. 94 c for 30 sec separates DNA from being double stranded to single stranded.
- Primer annealing. 55 c for 45 sec oligonucleotide primers are able to bind on DNA strands.
- Primer extension. 72 c for 2 min uses thermophiles.
- Paul berg. Discovered cloning.
What is denaturation of PCR : Denaturation is the first step of PCR. In this step, heat is applied to the template to separate double-stranded DNA into two single strands. Following the denaturation step is the annealing step. The temperature is decreased so that the primers can anneal to the complementary sequences on the DNA templates.
What are the 4 steps of PCR quizlet
- double-stranded DNA sample.
- heat to 95℃ – strands separated.
- add primers and reduce temp to 55℃ to allow primers to anneal.
- raise temp to 72℃ so DNA polymerase binds and extends primers using free nucleotides.
The process starts with Denaturation. The second step in polymerase is annealing or hybridization. Lastly, the elongation process is followed.The three steps are repeated for multiple cycles, with each cycle doubling the amount of DNA in the sample. The number of cycles is determined by the amount of target DNA in the initial sample and the sensitivity required for the experiment.
What are the first cycles of PCR : The three temperature steps in a single cycle accomplish three tasks: the first step denatures the template (and in later cycles, the amplicons as well), the second step allows optimal annealing of primers, and the third step permits the DNA polymerase to bind to the DNA template and synthesize the PCR product.