Antwort What is PCR 3 steps? Weitere Antworten – What are the three steps of PCR
PCR is based on three simple steps required for any DNA synthesis reaction: (1) denaturation of the template into single strands; (2) annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis; and (3) extension of the new DNA strands from the primers.Three steps of PCR─denaturation, annealing, and extension─as shown in the first cycle, and the exponential amplification of target DNA with repeated cycling.The major differences between 2P protocol and the original 3P protocol [5] include (Tables 1 and 2): (1) a decrease in the number of PCR steps from three to two by eliminating the enrichment step but by maintaining the same total number of PCR cycles (30 cycles); (2) the use of a steady decrease in annealing …
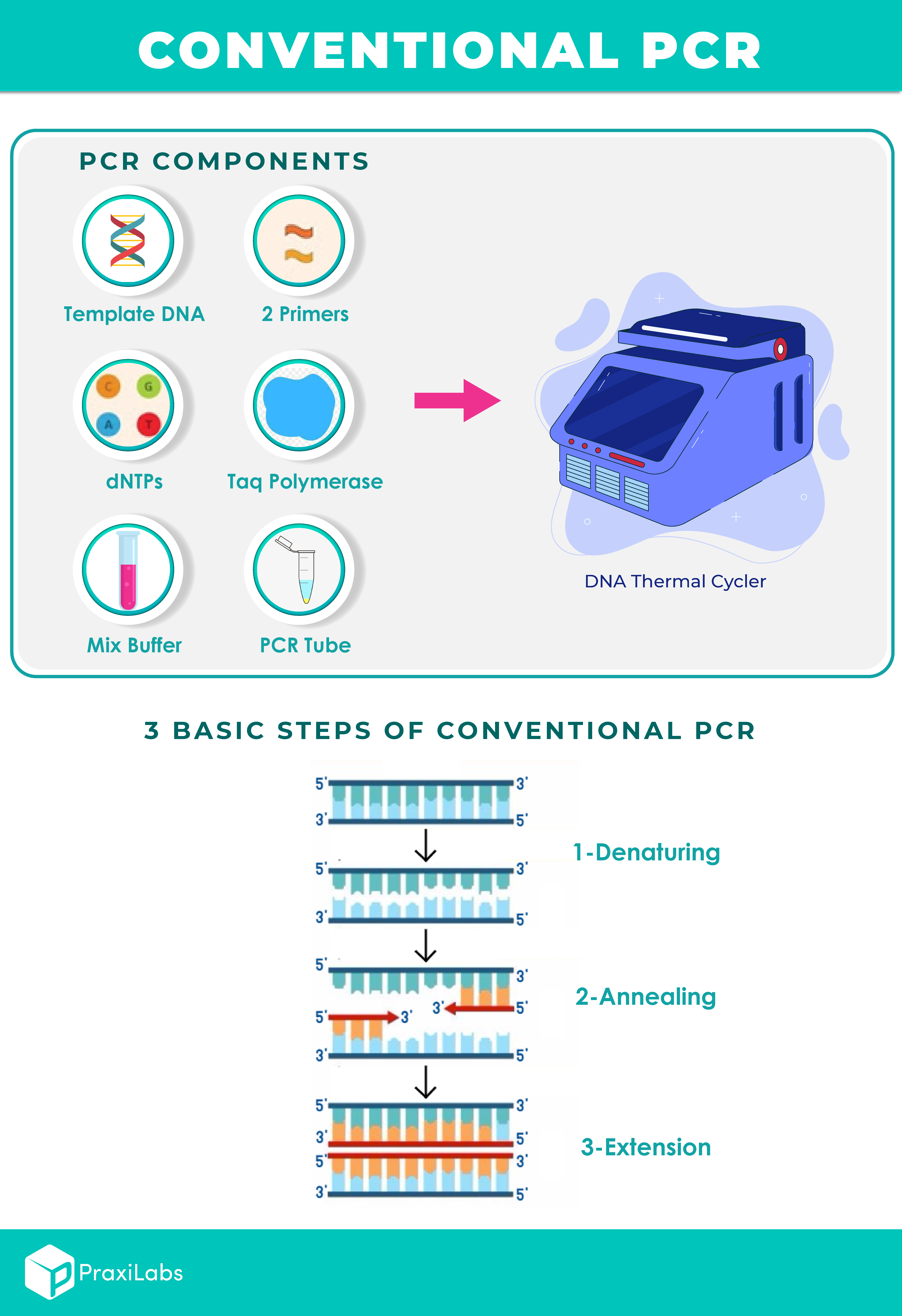
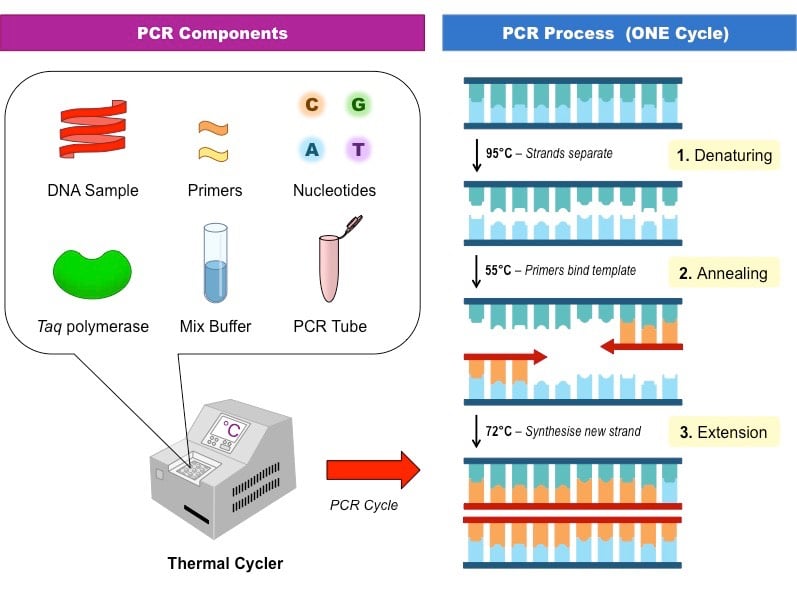
What are the steps of the PCR technique : A standard polymerase chain reaction (PCR) setup consists of four steps:
- Add required reagents or mastermix and template to PCR tubes.
- Mix and centrifuge.
- Amplify per thermo cycler and primer parameters.
- Evaluate amplified DNA by agarose gel electrophoresis followed by ethidium bromide staining.
What are the three steps of PCR quizlet
It used repeating cycles consisting of three steps (denaturing, annealing and extension). PCR has the ability to make millions of copies of the template DNA.
What is the summary of PCR : Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
PCR involves using short synthetic DNA fragments called primers to select a segment of the genome to be amplified, and then multiple rounds of DNA synthesis to amplify that segment.
The three steps are repeated for multiple cycles, with each cycle doubling the amount of DNA in the sample. The number of cycles is determined by the amount of target DNA in the initial sample and the sensitivity required for the experiment.
Two-step RT-PCR entails two separate reactions, beginning with first-strand cDNA synthesis (RT), followed by amplification of a portion of the resulting cDNA by PCR in a separate tube. Therefore, two-step RT-PCR is useful for detecting multiple genes in a single RNA sample.
What are the 4 steps of PCR
PCR machine steps
- Step 1 – Denaturation. The solution contained in the tube is heated to at least 94°C (201.2°F) using a thermal cycler.
- Step 2 – Annealing.
- Step 3 – Extension.
- Step 4 – Analysis with Electrophoresis.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
PCR involves using short synthetic DNA fragments called primers to select a segment of the genome to be amplified, and then multiple rounds of DNA synthesis to amplify that segment.Denaturation is the first step of PCR. In this step, heat is applied to the template to separate double-stranded DNA into two single strands. Following the denaturation step is the annealing step. The temperature is decreased so that the primers can anneal to the complementary sequences on the DNA templates.
- PCR. Polymerase chain reaction.
- Three steps. Denaturation.
- Denaturation. 94 c for 30 sec separates DNA from being double stranded to single stranded.
- Primer annealing. 55 c for 45 sec oligonucleotide primers are able to bind on DNA strands.
- Primer extension. 72 c for 2 min uses thermophiles.
- Paul berg. Discovered cloning.
What are the cycles of PCR : PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplifies DNA and involves a series of temperature cycles critical for amplifying the DNA target. The cycling process is divided into three main stages: denaturation, annealing, and extension. These three stages are repeated for 20-40 cycles, doubling the targeted DNA amount.
What is the end result of PCR : The result is a brand-new strand of DNA and a double-stranded molecule of DNA. The duration of this step depends on the length of DNA sequence being amplified. It usually takes around one minute to copy 1,000 DNA bases.
What are the 3 cycles in PCR and what they do which one can you change to improve specificity
PCR steps of denaturation, annealing, and extension are repeated (or “cycled”) many times to amplify the target DNA. The number of cycles is usually carried out 25–35 times but may vary upon the amount of DNA input and the desired yield of PCR product.
8 copies
So, that means after the second cycle, it will produce 4 copies of DNA sample, then after the third cycle, 8 copies are produced, after the fourth cycle, 16 copies are produced, after the fifth cycle, 32 copies are produced, and lastly, after the sixth cycle, 64 copies of DNA samples are produced.As the name implies, one-step RT-PCR combines first-strand cDNA synthesis (RT) and subsequent PCR in a single reaction tube. This reaction setup can help simplify your workflow, reduces variation, and minimizes possible contamination.
What is one-step vs 2 step PCR : Compared to one-step RT-PCR, the disadvantages of two-step RT-PCR include multiple steps for an extended workflow, additional sample handling and processing, and may increase the chance of contamination and variation in results.