Antwort What is interest rate swap in India? Weitere Antworten – What is interest rate swap in rupee
Taken together with the underlying loan/asset, this effectively converts user's floating/fixed rate liability/asset into a fixed/floating rate liability/asset. Such exchange of cashflows are known as a Rupee Interest Rate Swap (Rupee IRS). In other words, the underlying can be a liability or an asset.An interest rate swap is an agreement between two parties to exchange one stream of interest payments for another, over a set period of time. Swaps are derivative contracts and trade over-the-counter.The bank's profit is the difference between the higher fixed rate the bank receives from the customer and the lower fixed rate it pays to the market on its hedge. The bank looks in the wholesale swap market to determine what rate it can pay on a swap to hedge itself.
)
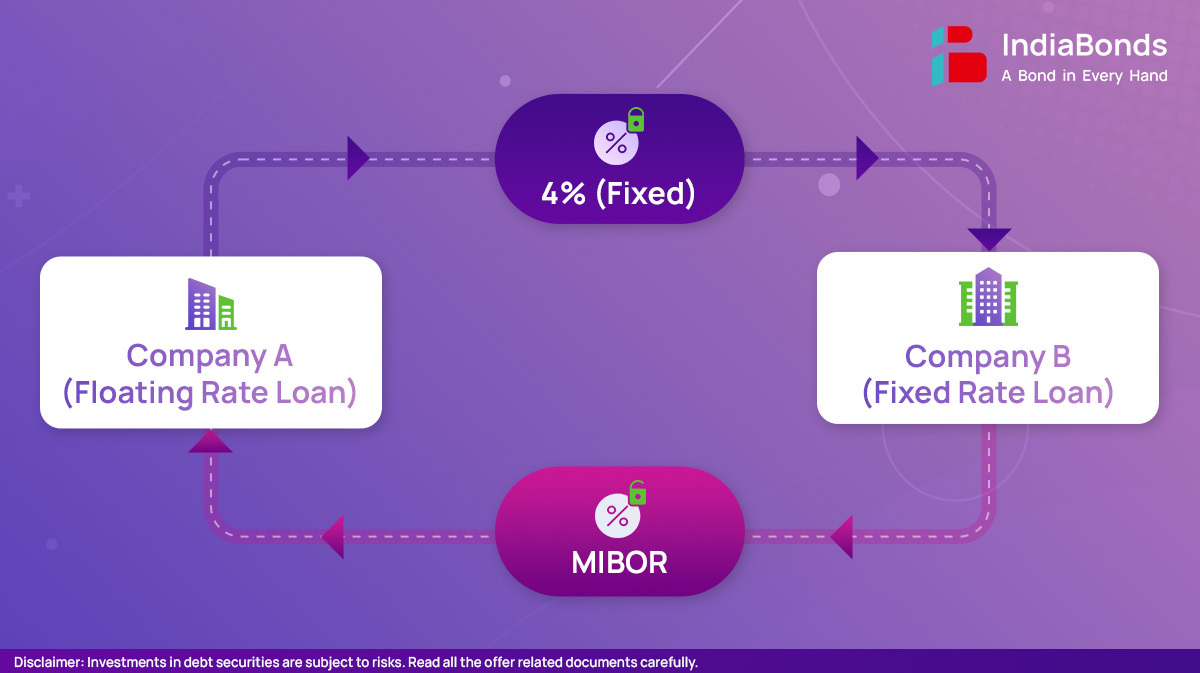
What is an example of interest swap : Since the company is worried that interest rates may rise, it finds Company B that agrees to pay Company A the LIBOR annual rate plus 1% for two years on the notional principal of $10 million. In exchange, Company A pays Company B a fixed rate of 4% on a notional value of $10 million for two years.
Why do banks use interest rate swaps
Provides competitive advantage – Separating the funding of a loan from the management of interest rate risk through derivatives provides pricing flexibility, usually allowing the bank to be more competitive.
What are the disadvantages of interest rate swaps : Unfortunately, the lack of scrutiny of the interest rate swaps by borrowers can lead to potential abuse by interest rate swap counterparties. Synthetic fixed-rate debt exposes debtors to counterparty risk that fixed-rate debt does not.
Banks and lenders use the swap rate as a reference when pricing fixed-rate mortgage products for borrowers. The swap rate represents the cost at which lenders can borrow funds on the wholesale market for the duration of the mortgage term.

The bank's profit is the difference between the higher fixed rate the bank receives from the customer and the lower fixed rate it pays to the market on its hedge. The bank looks in the wholesale swap market to determine what rate it can pay on a swap to hedge itself.
How do banks use swap rates
So in easier terms, a swap rate is a rate based on what the markets think interest rates will be in the future. If the rates rise, then mortgage lenders will look to increase their rates so that they don't lose out. Meaning if swap rates go down, mortgage rates tend to go down. If they go up, so do mortgage rates too.Interest Rate Swaps Example: Fixed-to-Floating
Take as an example two parties, Alpha and Beta. Alpha has obtained a loan with a fixed interest of 5% per annum. On the contrary, Beta has a loan of the same principal amount but with a floating interest rate(rate changes with the market), say LIBOR + 1%.Swaps also help companies hedge against interest rate exposure by reducing the uncertainty of future cash flows. Swapping allows companies to revise their debt conditions to take advantage of current or expected future market conditions.
Offers an economic benefit – Executing a swap will generate non-interest income for the bank. This fee income is recognized in the period the swap is executed and is NOT amortized over the life of the loan.

