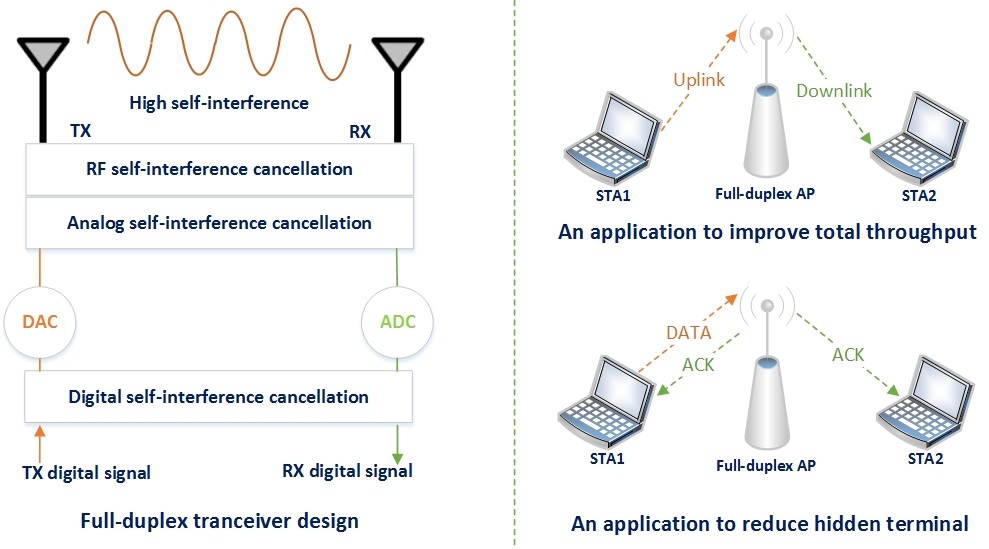
Antwort What is half-duplex Wi-Fi? Weitere Antworten – What is half-duplex full-duplex in wifi

Differences Between Full and Half-Duplex Systems
| Half-duplex | Full-duplex | Simplex |
|---|---|---|
| Used to conserve bandwidth when only single communication is needed | Used when communication is required in both directions without any delay | When maximum bandwidth is required for the transmission and only one direction is required |
A half-duplex transmission could be considered a one-way street between sender and receiver. Full-duplex, on the other hand, enables two-way traffic at the same time. A communications channel can be used to communicate one way at a time or in both directions at once.If we compare full duplex vs half duplex, full duplex point to point is much faster, and will provide faster throughput for voice, data and video transmission.

How does full duplex Ethernet work : In full-duplex Ethernet, each node is cabled to a switch with a pair of circuits: one for transmissions to the switch and the other for transmissions from the switch. In full-duplex Ethernet, simultaneous transmission is the default — but only between the Ethernet switch and each node.
Is Wi-Fi 6 half-duplex
The operational underpinnings of Wi-Fi 6E are based in the IEEE 802.11 framework. As with previous Wi-Fi standards, Wi-Fi 6E is a half-duplex technology bound by the laws of physics for interference and coexistence with signals in the same unlicensed spectrum.
Is WiFi 7 full duplex : As an evolution of 802.11, Wi-Fi 7 is still a shared medium, half-duplex technology.
A full-duplex mode is also specified and in practice, all modern networks use Ethernet switches and operate in full-duplex mode, even as legacy devices that use half duplex still exist.
Full-duplex communication allows for faster data transfer as devices can both send and receive information simultaneously. This increases data transfer speeds compared to half-duplex or simplex communication. (Simplex communication is unidirectional data transmission, like a keyboard.)
Is 100 Mbps full duplex or half-duplex
A switch that can deliver 100Mbps symmetrical, full duplex can transmit and receive at a rate of 100Mbps. Even if it is full duplex, a network switch with asymmetrical bandwidth cannot send AND receive at 100Mbps. Asymmetrical switches will use an uneven split to transmit at 70Mbps and receive at 30Mbps, for example.Half-duplex has limited throughput since data can only be sent one way at a time. This dramatically impedes a network's speed and reliability.Full-duplex: A can send to B and B can send data to A simultaneously. Since 802.11 / WiFi is CSMA/CA protocol based and since it faces collisions, its a half-duplex communication. Full Duplex is not available in Wifi at all.
The half-duplex mode comes into play in those cases where we don't need the transmission in both directions at the same moment. For Example – A walkie-talkie uses the Half-Duplex Transmission Mode. Here, we send messages in both directions, but the transmission still occurs in one direction at a time.
Does Wi-Fi 7 exist : Yes. Wi-Fi 7 is designed to maintain full backward compatibility, ensuring seamless compatibility between the latest Wi-Fi 7 devices and legacy devices from earlier generations.
Is Wi-Fi 7 full duplex : As an evolution of 802.11, Wi-Fi 7 is still a shared medium, half-duplex technology.
Is Wi-Fi 6 still half-duplex
The operational underpinnings of Wi-Fi 6E are based in the IEEE 802.11 framework. As with previous Wi-Fi standards, Wi-Fi 6E is a half-duplex technology bound by the laws of physics for interference and coexistence with signals in the same unlicensed spectrum.
As with all 802.11 standards, 802.11ac is half-duplex, shared medium radio technology that works best when employed in wireless networking environments designed by qualified professionals.You can expect problem-free, full-duplex, 4-pair Ethernet transmissions over your CAT5e UTP.
What is an example of a half-duplex : The half-duplex mode comes into play in those cases where we don't need the transmission in both directions at the same moment. For Example – A walkie-talkie uses the Half-Duplex Transmission Mode. Here, we send messages in both directions, but the transmission still occurs in one direction at a time.