Antwort What is half-duplex mode? Weitere Antworten – What is half-duplex vs full duplex
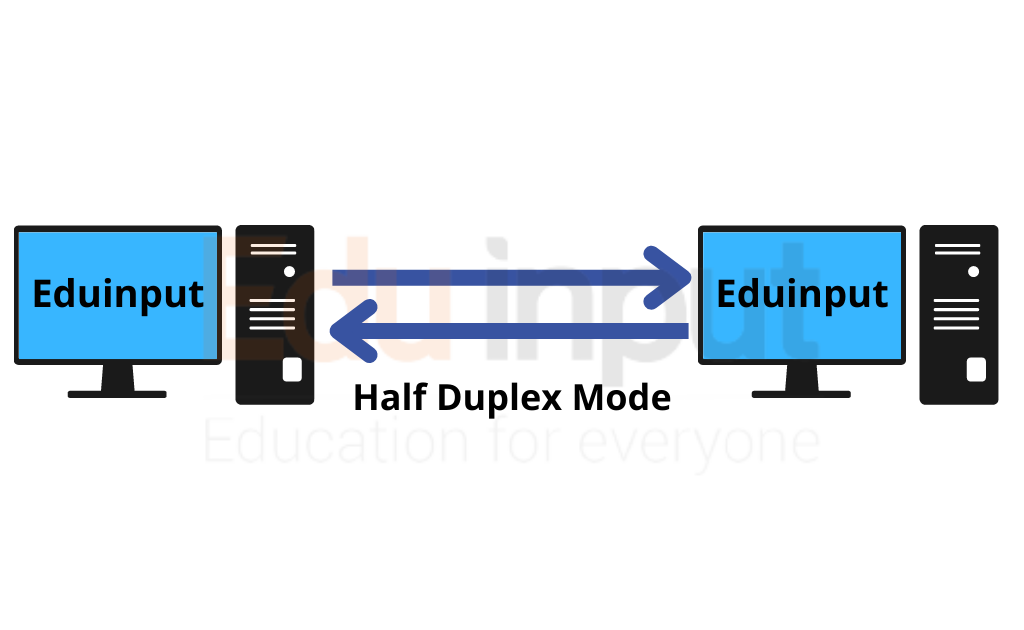
Half-duplex and full-duplex are two common methods of transmitting data. Half-duplex is when data can only go in one direction at a time. Full-duplex is when data can flow in both directions at the same time.99.9% of the time Wireless is half duplex. There are experiments that can result in a "full duplex" wireless network but that's all lab-based and not real-world. With Wireless the devices cannot send and receive simultaneously and they cannot sense collisions.A half-duplex system is a communication system that allows data transmission in both directions but not at the same time. In other words, a half-duplex system can either send or receive data at any given time.
What is duplex mode : The term duplex, on its own, refers to the capability to send and receive data. Duplex is often used when talking about conversations over a telephone or computer. A full-duplex Ethernet environment can use a pair of twisted cable for packet receiving and a pair of twisted cable for transmission.
Is half-duplex slower
In most circumstances, full-duplex is faster than half-duplex. A full-duplex medium can transfer information in both directions, simultaneously. A half-duplex medium can transfer information in either direction, but only one direction at a time.
Why choose half-duplex : Advantages. One of the notable advantages of half duplex mode is its simplicity. It allows communication in both directions using a single path for transmitting and receiving data.
The Bluetooth standard specifies the option to communicate using the wireless device protocol either as full-duplex (for example, in telephone handsets) or as half-duplex (for example, to connect to a printer).
Full duplex could double the capacity of wireless networks, making it a key technology for 5G.
What causes half-duplex
Half-Duplex
If a frame is received on the Rx line while a frame is being sent on the transmitting (Tx) line, a collision occurs. Collisions cause the collision error counter to be incremented – and the sending frame to be retransmitted – after a random back-off delay.In half-duplex mode, each station can both transmit and receive, but not at the same time. When one device is sending, the other can only receive, and vice versa. The half-duplex mode is used in cases where there is no need for communication in both directions at the same time.SuperSpeed's architecture is full-duplex; all earlier implementations, USB 1.0-2.0, are all half-duplex, arbitrated by the host.
Using the same example of moving two 150Mb files, a 100Mbps symmetrical, full duplex switch will deliver both files in 1.5 seconds. A 100Mbps asymmetrical half duplex switch with a 70/30 split will take 7.14 seconds to deliver both files.
Why is half-duplex used for WIFI : Half duplex: Half-duplex wireless devices are those that cannot transmit and receive signals simultaneously. Most wireless devices today are half duplex. This is because the signals a wireless device transmits are more powerful than the ones it receives.
Is LTE half-duplex : This means that LTE-M can be deployed both in paired FDD bands and unpaired TDD bands (see Table 5.2 for a list of supported bands), and that both full-duplex and half-duplex device implementations are possible, allowing for trade-off between device complexity and performance.
Is LTE half-duplex or full duplex
LTE can be either full duplex (meaning that transmitting and receiving can happen simulataneously), or half duplex (meaning that transmitting and receiving can happen, but not at the same time).
As with all 802.11 standards, 802.11ac is half-duplex, shared medium radio technology that works best when employed in wireless networking environments designed by qualified professionals.Half duplex: Half-duplex wireless devices are those that cannot transmit and receive signals simultaneously. Most wireless devices today are half duplex. This is because the signals a wireless device transmits are more powerful than the ones it receives.
Is USB 3.0 half-duplex : USB 3.0 has transmission speeds of up to 5 Gbit/s or 5000 Mbit/s, about ten times faster than USB 2.0 (0.48 Gbit/s) even without considering that USB 3.0 is full duplex whereas USB 2.0 is half duplex. This gives USB 3.0 a potential total bidirectional bandwidth twenty times greater than USB 2.0.