Antwort What is duplex mode in Wi-Fi? Weitere Antworten – What is duplex in Wi-Fi
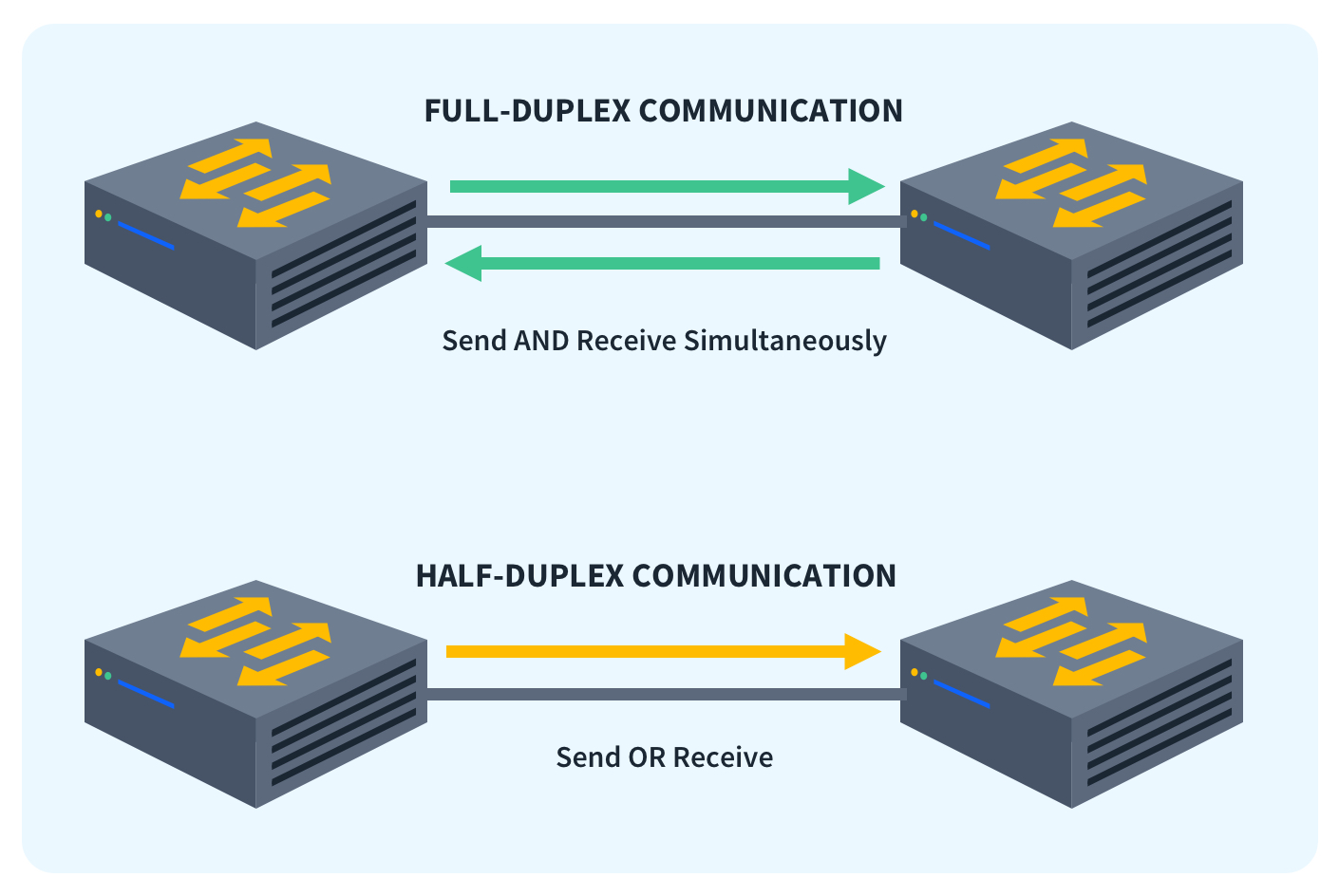
Simply put full duplex is the networking term for describing the communication between two locations or devices in both directions simultaneously. Unlike TDD the FDD method is achieved by using two different frequencies for transmit and receive.The operational underpinnings of Wi-Fi 6E are based in the IEEE 802.11 framework. As with previous Wi-Fi standards, Wi-Fi 6E is a half-duplex technology bound by the laws of physics for interference and coexistence with signals in the same unlicensed spectrum.Wireless FidelityWi-Fi / Full name
WIFI stands for Wireless Fidelity which is a wireless technology standard for wireless Internet access. It is used as a replacement for cable connections and other types of wires.
What is duplex good for : These multi-unit buildings provide alternatives to single-family homes and large apartment complexes. Since they often have enough space for more than one person, duplexes are perfect for renters looking to live with friends or for those looking to meet new housemates.
Why is duplex better
You could live on one side of the duplex and rent the other. This will reduce your monthly mortgage, insurance, and property tax. You could rent both sides, and that income can pay the mortgage, insurance, and property tax in full, and you may even have some money left over at the end of the month as a profit.
Can Wi-Fi ever be full duplex : Not only Wi-Fi cannot work as full-duplex, but also two or more devices cannot transmit or receive traffic simultaneously. Unlike 3G/4G, Wi-Fi uses unlicensed frequencies in the spectrum, which simply means you do not have to pay for using them.
As an evolution of 802.11, Wi-Fi 7 is still a shared medium, half-duplex technology.
6. Wi-Fi- 802.11be
| Version | IEEE Standard | Maximum Linkrate (Mbit/s) |
|---|---|---|
| Wi‑Fi 4 | 802.11n | 72- 600 |
| Wi-Fi 3 | 802.11g | 6- 54 |
| Wi-Fi 2 | 802.11a | 6-54 |
| Wi-Fi 1 | 802.11b | 1-11 |
What is difference between Wi-Fi and Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi can provide wireless connectivity for multiple types of internet service, such as DSL, satellite internet, and fiber optics. Wireless Internet, on the other hand, is another name for Cellular Wireless. It is produced by cell towers. Wi-Fi requires physical devices, like routers and modems, to operate.Both the units of a duplex are usually well-equipped with separate entrances, washrooms, balconies, and kitchens. Therefore, such properties are known to have an excellent resale value which also includes a faster appreciation rate.Full-duplex Ethernet does save time when compared to half-duplex because it alleviates collisions and frame retransmissions. Sending and receiving are separate functions, creating a system where there is full data capacity in each direction. In contrast, half-duplex can be used to conserve bandwidth.
Duplex Cons
Shared spaces: If you're looking to own your own property, you may find it frustrating to have a neighbor living so close to you. You'll most likely have to share a driveway and yard with the tenant renting the other unit, so you must make sure you're comfortable sharing these common areas.
Why is Wi-Fi always half-duplex : 99.9% of the time Wireless is half duplex. There are experiments that can result in a "full duplex" wireless network but that's all lab-based and not real-world. With Wireless the devices cannot send and receive simultaneously and they cannot sense collisions.
Why is Wi-Fi only half-duplex : Half duplex: Half-duplex wireless devices are those that cannot transmit and receive signals simultaneously. Most wireless devices today are half duplex. This is because the signals a wireless device transmits are more powerful than the ones it receives.
Is 802.11 n full duplex
The 802.11 family consists of a series of half-duplex over-the-air modulation techniques that use the same basic protocol.
First, the speed difference. Wi-Fi 6 maximum speed is 9.6 Gbps (which, honestly, is fast), while Wi-Fi 7 is expected to have a maximum speed of 46 Gbps. That's 46 Gbps for a single client.If you're able to use most of your devices near your router, 5 GHz is your best choice to take advantage of higher speeds. Similarly, if you're doing a lot of high-bandwidth activities online, such as gaming or videoconferencing, it's best to use this frequency and move as close as possible to the router.
Which Wi-Fi type is fastest : Wi-Fi 6
The difference between Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6 speeds per device is not so vast. Wi-Fi 6 is invariably faster, but the real speed advantage comes when multiple devices are connected to the Wi-Fi network.