Antwort What is difference between half duplex and full duplex? Weitere Antworten – What is the difference between full duplex and half-duplex
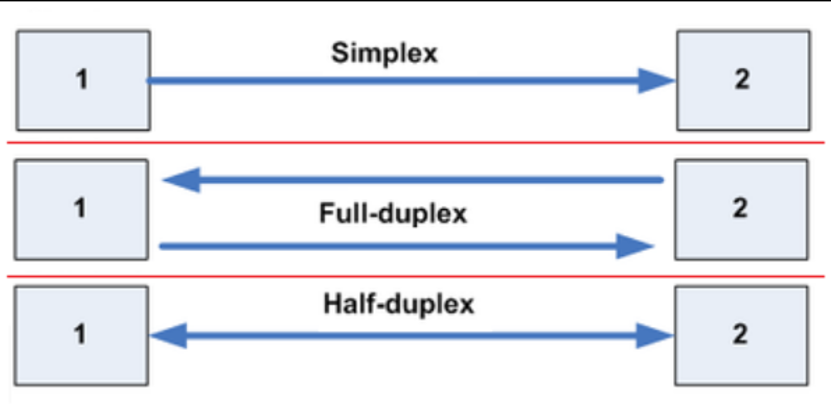
Half-duplex and full-duplex are two common methods of transmitting data. Half-duplex is when data can only go in one direction at a time. Full-duplex is when data can flow in both directions at the same time.Using the same example of moving two 150Mb files, a 100Mbps symmetrical, full duplex switch will deliver both files in 1.5 seconds. A 100Mbps asymmetrical half duplex switch with a 70/30 split will take 7.14 seconds to deliver both files.Also, some older Ethernet devices can only use half-duplex communications, even when connected to a full-duplex switch. Lastly, Wi-Fi networks are half-duplex on a per-channel basis. Each radio channel, as with walkie-talkies, can send or receive — but not both at the same time.
Is full duplex slower than half-duplex : If we compare full duplex vs half duplex, full duplex point to point is much faster, and will provide faster throughput for voice, data and video transmission.
Which is better half or full-duplex
Full-duplex Ethernet does save time when compared to half-duplex because it alleviates collisions and frame retransmissions. Sending and receiving are separate functions, creating a system where there is full data capacity in each direction. In contrast, half-duplex can be used to conserve bandwidth.
Is USB full-duplex : The USB 3.0 standard — also known as SuperSpeed USB — offers a full-duplex transfer mode, while earlier versions of USB offered only the half-duplex transfer mode. Ethernet was originally a half-duplex channel.
A one gigabit port in full duplex means that it can send and receive one gigabit per second in both directions. The back plane of your switch / router / whatever is what controls how many of your ports can be used concurrently.
Full duplex could double the capacity of wireless networks, making it a key technology for 5G.
Is Bluetooth full duplex
Bluetooth provides the effect of full duplex transmission through the use of time division duplex (TDD). In principle transmission and reception do not happen at the same time.Full-duplex Ethernet does save time when compared to half-duplex because it alleviates collisions and frame retransmissions. Sending and receiving are separate functions, creating a system where there is full data capacity in each direction. In contrast, half-duplex can be used to conserve bandwidth.Advantages. One of the notable advantages of half duplex mode is its simplicity. It allows communication in both directions using a single path for transmitting and receiving data.
USB 3.0 has transmission speeds of up to 5 Gbit/s or 5000 Mbit/s, about ten times faster than USB 2.0 (0.48 Gbit/s) even without considering that USB 3.0 is full duplex whereas USB 2.0 is half duplex. This gives USB 3.0 a potential total bidirectional bandwidth twenty times greater than USB 2.0.
Is 5G full-duplex or half-duplex : Full duplex could double the capacity of wireless networks, making it a key technology for 5G.
Is USB full-duplex or half-duplex : SuperSpeed's architecture is full-duplex; all earlier implementations, USB 1.0-2.0, are all half-duplex, arbitrated by the host.
Is 4G full-duplex or half-duplex
4G LTE and 5G NR can use both FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) and TDD (Time Division Duplex) and operate in full and half-duplex modes. The FDD and TDD support makes 4G migration easier for 3G technologies on FDD or TDD.
Wi-Fi is half-duplex, which means that on any channel, only one device can talk at a time.Half-duplex systems are usually used to conserve bandwidth, at the cost of reducing the overall bidirectional throughput, since only a single communication channel is needed and is shared alternately between the two directions.
Is USB 2.0 full-duplex or half-duplex : Half Duplex
Overview of USB versions and speeds:
USB 2.0: 480 Mbps (High Speed, Half Duplex) USB 3.0: USB 3.2 Gen 1, 5 Gbps (SuperSpeed, Full Duplex) USB 3.1: USB 3.2 Gen 2, 10 Gbps (SuperSpeed, Full Duplex) USB 3.2: USB 3.2 Gen 2 x 2, 20 Gbps (SuperSpeed, Full Duplex)