Antwort What is bus architecture with example? Weitere Antworten – What is bus architecture
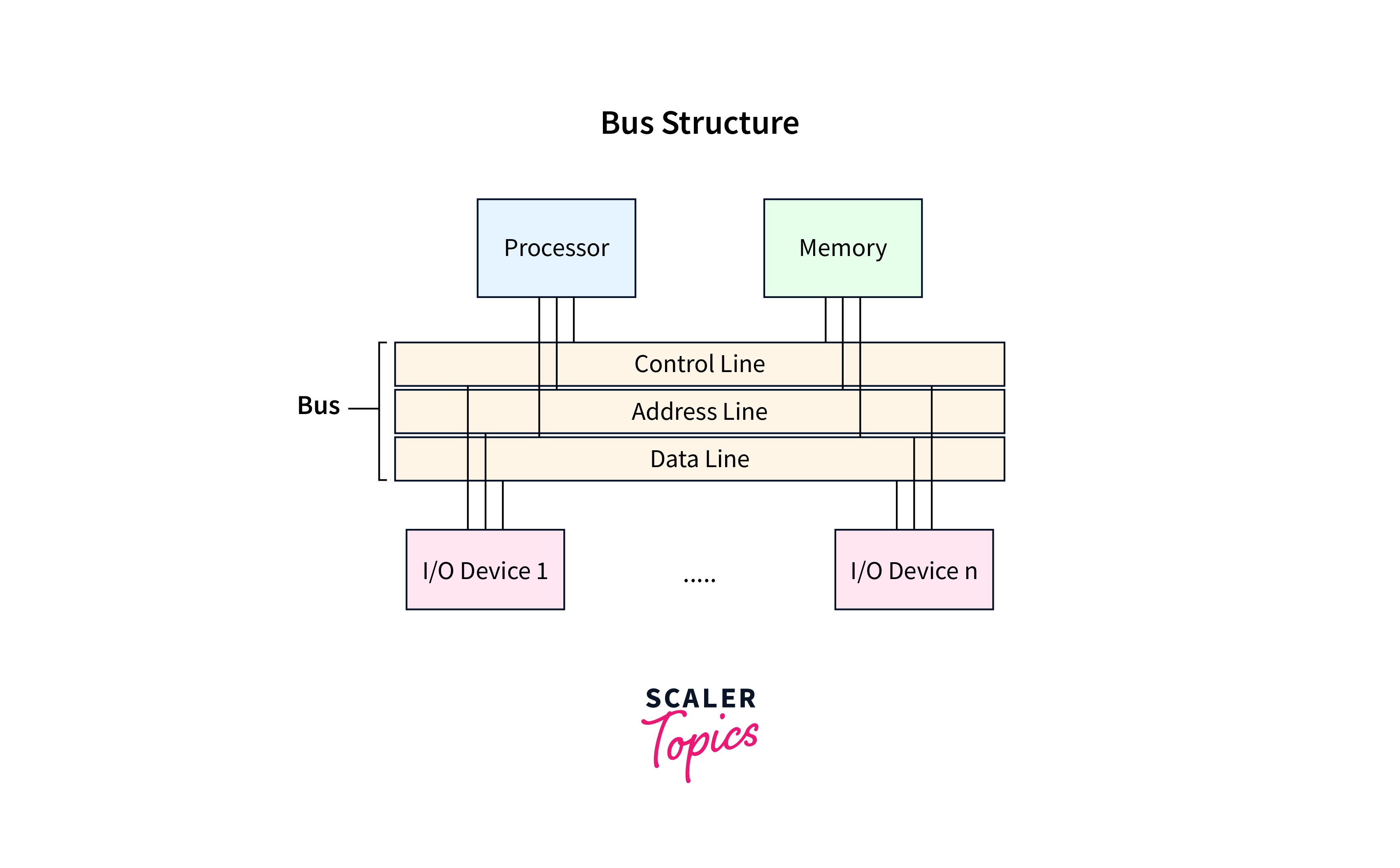
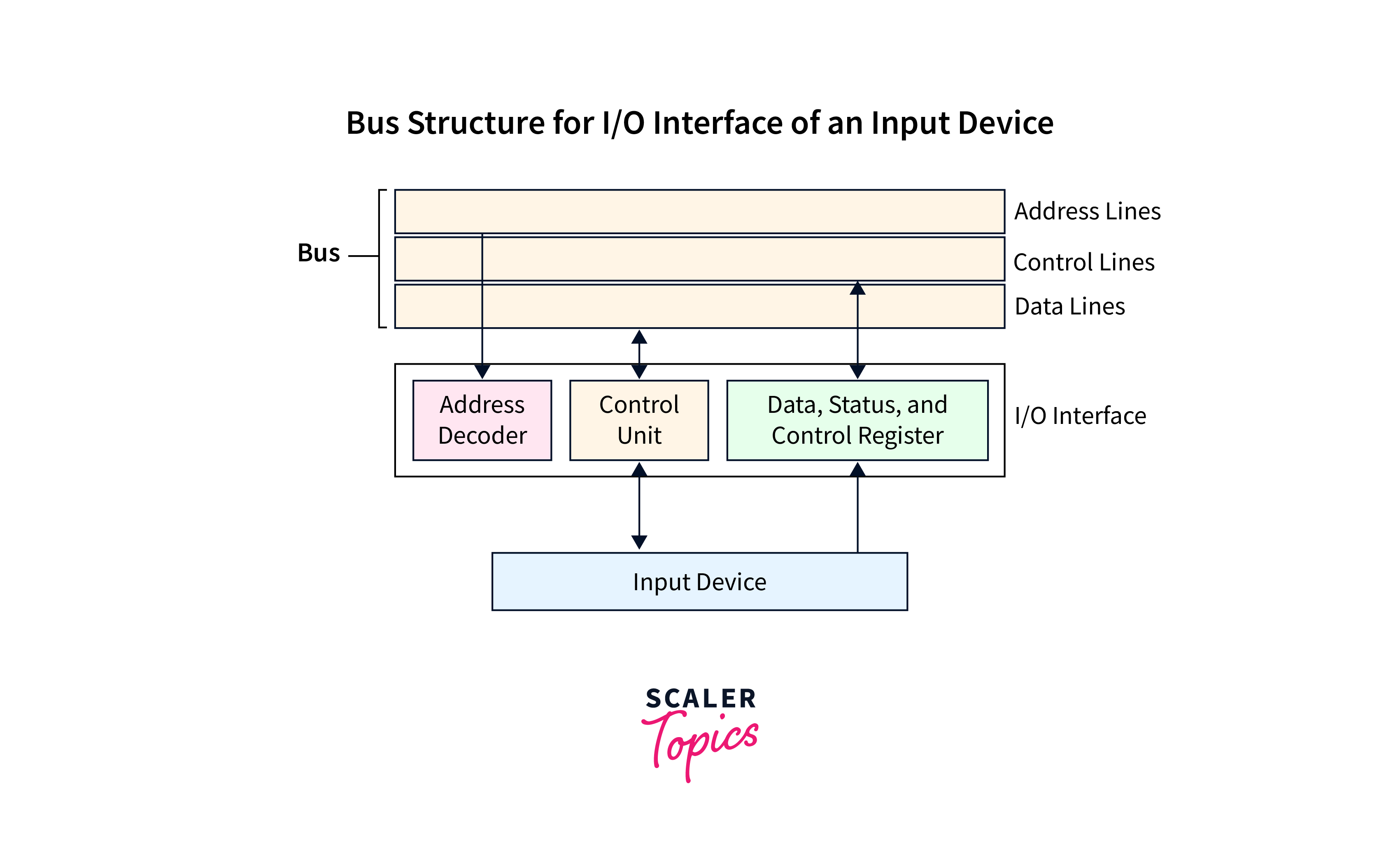
In computer architecture, a bus (historically also called data highway or databus) is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers. This expression covers all related hardware components (wire, optical fiber, etc.) and software, including communication protocols.There are three types of bus lines: Data bus, Address bus, and Control bus. Communication over each bus line is performed in cooperation with another. The data bus is a signal line for exchanging the data between the CPU and the memory, and between the CPU and I/O, and handles the data stored in the specified location.A bus, in computing and digital technology, is an electronic pathway through which data can be transferred. This pathway uses signals that move at different speeds and are sent through different channels to communicate information between components within a computer or network.
What is the role of bus in data transfer : The purpose of the data bus is to facilitate the transfer of data between the central processing unit (CPU) and other components within a computer system, such as memory and input/output devices. It serves as a communication channel, allowing data to be transmitted in parallel, thereby enhancing speed and efficiency.
What is data bus in architecture
A data bus transfers data between a computer's memory and its CPU, which operates as the device's “engine“. Bus controllers manage component information interchange speed. CPU data always travels faster than other component data. Data carried on a data bus might be parallel or serial.
What is Harvard bus architecture : Harvard architecture refers to a memory structure in which the processor is connected to two independent memory banks via two independent sets of buses.
Buses
- Address bus – carries memory addresses from the processor to other components such as primary storage and input/output devices.
- Data bus – carries the data between the processor and other components.
- Control bus – carries control signals from the processor to other components.
Yellow hazard lights (4 way caution lights) are use if I am near a road but off it in a safe area for riders to get on or off the bus. Red light stops are used on streets to halt traffic until students have boarded or gotten off the bus and are in a safe place.
What is an example of a system bus
A system bus works by sharing data and other information between various aspects of the computer's hardware. For example, if you plug a universal serial bus (USB) device or connector into your computer, the system bus recognizes that data and takes it to the computer's central processing unit.Buses may be used for scheduled bus transport, scheduled coach transport, school transport, private hire, or tourism; promotional buses may be used for political campaigns and others are privately operated for a wide range of purposes, including rock and pop band tour vehicles.A data bus transfers data between a computer's memory and its CPU, which operates as the device's “engine“. Bus controllers manage component information interchange speed. CPU data always travels faster than other component data. Data carried on a data bus might be parallel or serial.
In CAN Bus communications, data is transmitted in frames, which consist of an identifier, a data payload, and various control and error-checking bits. There are two types of frames: data frames and remote frames.
What is the bus architecture in DWH : The data warehouse bus architecture provides a rational approach to decomposing the enterprise data warehouse planning task. During the limited duration architecture phase, the team designs a master suite of standardized dimensions and facts that have uniform interpretation across the enterprise.
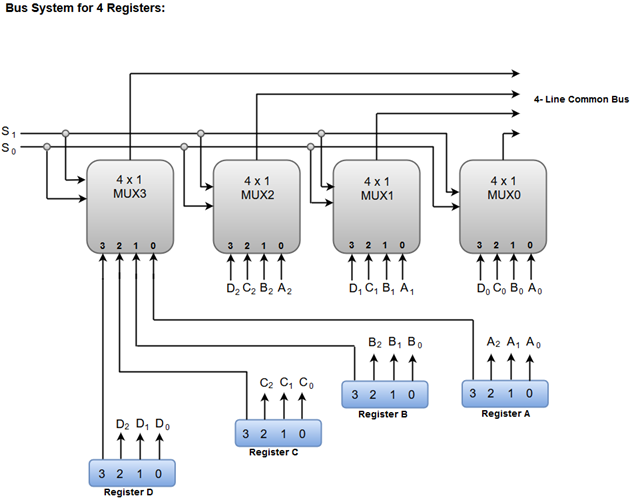
What is one bus in computer architecture : In one bus organization, a single bus is used for multiple purposes. A set of general-purpose registers, program counters, instruction registers, memory address registers (MAR), and memory data registers (MDR) are connected with the single bus. Memory read/write can be done with MAR and MDR.
Is Arm von Neumann or Harvard
Overview. With this design generation, ARM moved from a von Neumann architecture (Princeton architecture) to a (modified; meaning split cache) Harvard architecture with separate instruction and data buses (and caches), significantly increasing its potential speed.
MCs with Harvard architecture are called "RISC MCs". MCs with von- Neumann's architecture are called 'CISC microcontrollers'.Single-deck bus
The single-deck bus (also called a single decker) is the most popular bus in transit applications and has become largely synonymous with the concept of a transit bus. However, any bus could serve in a transit application and other bus types frequently show up in transit fleets.
What is the main bus concept : "Main bus" refers to an organized layout for resource transportation. The idea boils down to having several belts full of all the important materials going in one direction, with all the assembly lines to the side of it and branching resources off of the “bus” and into the assemblies, when they are needed.