Antwort What is a swap example? Weitere Antworten – What is swap in simple words
A swap is an agreement or a derivative contract between two parties for a financial exchange so that they can exchange cash flows or liabilities. Through a swap, one party promises to make a series of payments in exchange for receiving another set of payments from the second party.For example, a company paying a variable rate of interest may swap its interest payments with another company that will then pay the first company a fixed rate. Swaps can also be used to exchange other kinds of value or risk like the potential for a credit default in a bond.A swap is an agreement for a financial exchange in which one of the two parties promises to make, with an established frequency, a series of payments, in exchange for receiving another set of payments from the other party. These flows normally respond to interest payments based on the nominal amount of the swap.
What are the types of swaps : Types of Swaps Derivatives
- Interest Rate Swaps. Interest rate swaps are powerful financial instruments that effectively mitigate financial risk and optimise business cash flow.
- Currency Swaps.
- Credit Default Swaps.
- Commodity Swaps.
- Equity Swaps.
What is an example of a currency swap
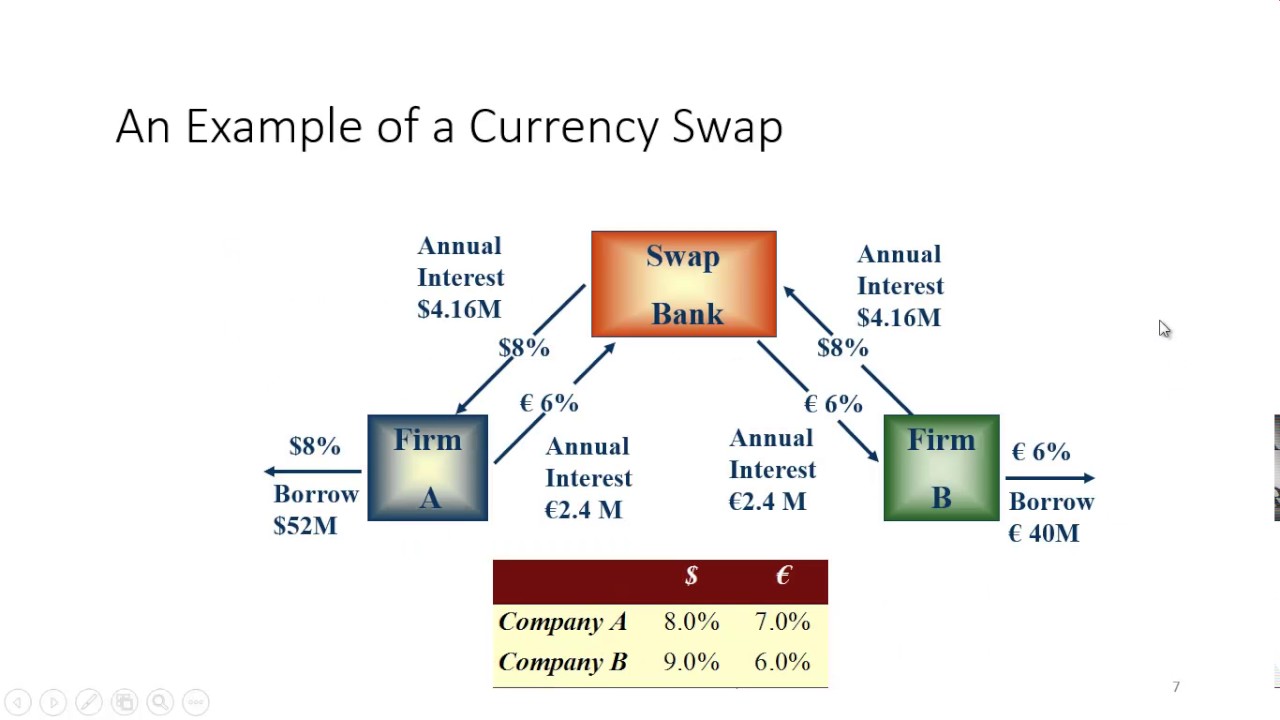
In a currency swap, or FX swap, the counterparties exchange given amounts in the two currencies. For example, one party might receive 100 million British pounds (GBP), while the other receives $125 million. This implies a GBP/USD exchange rate of 1.25.
Why is swap used : Swap memory facilitates memory management by temporarily storing inactive data on the disk. This mechanism ensures uninterrupted system performance even when RAM is fully utilized.
Swaps are customized contracts traded in the over-the-counter market privately, versus options and futures traded on a public exchange. The plain vanilla interest rate and currency swaps are the two most common and basic types of swaps.
As commodity prices fluctuate, one party exchanges the floating rate for a fixed rate. For example, a producer can swap the spot price of Brent Crude oil for a predetermined price over an agreed period, helping to lock in prices and hedge against future fluctuations.
How risky are swaps
What are the risks. Like most non-government fixed income investments, interest-rate swaps involve two primary risks: interest rate risk and credit risk, which is known in the swaps market as counterparty risk. Because actual interest rate movements do not always match expectations, swaps entail interest-rate risk.Understanding Swap Banks
A swap is a derivative contract through which two parties exchange financial instruments. These instruments can be almost anything, but most swaps involve cash flows based on a notional principal amount to which both parties agree. Usually, the principal does not change hands.interest rate swap
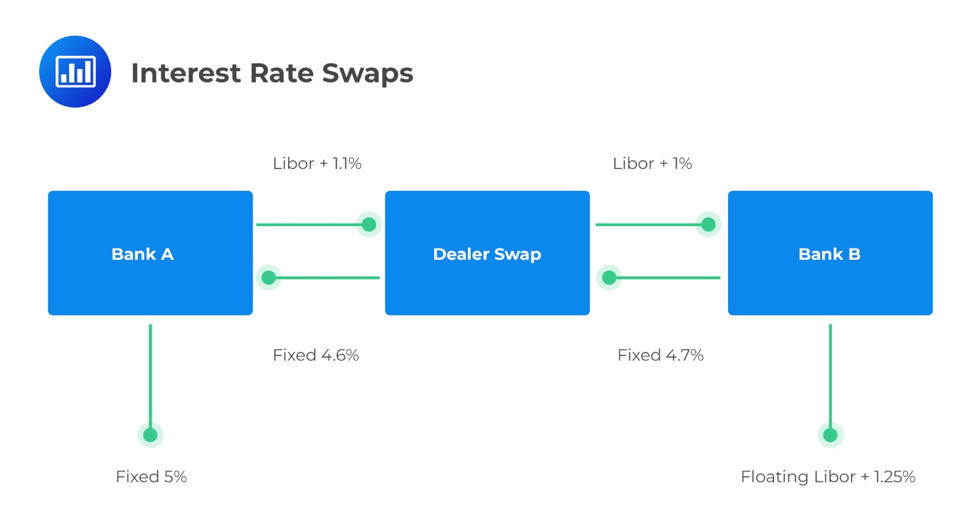
The most common type of swap is an interest rate swap. Some companies may have comparative advantage in fixed rate markets, while other companies have a comparative advantage in floating rate markets.
Investment bankers sometimes make money with swaps. Swaps create profit opportunities through a complicated form of arbitrage, where the investment bank brokers a deal between two parties that are trading their respective cash flows.
Is swap still useful : I think that's a mistake, both because swap is still useful in maximising the usefullness of RAM, but more importantly because it will cause trouble if someone creates their Discourse on a large-RAM machine, for speed or convenience, and then downsizes it to small-RAM.
Why do banks use swaps : Offers an economic benefit – Executing a swap will generate non-interest income for the bank. This fee income is recognized in the period the swap is executed and is NOT amortized over the life of the loan.
Why do swaps fail
The main reason why your swap might have failed is likely to be slippage. When you perform a swap, you are agreeing to a price quote. If the price of the swap goes outside of the allowed slippage set (typically 2-3%), it will fail, in order to prevent you from seeing a huge variance in value when completed.
Negative Swap Spreads
Another explanation for the 30-year negative rate is that traders have reduced their holdings of long-term interest-rate assets and, therefore, require less compensation for exposure to fixed-term swap rates.This is how banks that provide swaps routinely shed the risk, or interest rate exposure, associated with them. Initially, interest rate swaps helped corporations manage their floating-rate debt liabilities by allowing them to pay fixed rates, and receive floating-rate payments.
What are the two commonly used swaps : Swaps are customized contracts traded in the over-the-counter market privately, versus options and futures traded on a public exchange. The plain vanilla interest rate and currency swaps are the two most common and basic types of swaps.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/DifferentTypesofSwaps2-4de5ab58b9854ca6b325de77810c3b16.png)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_final_Currency_Swap_vs_Interest_Rate_Swap_Whats_the_Difference_Jan_2021-01-d0d9bf99a16c467daeab2fd073b67051.jpg)