Antwort What is 16S used for? Weitere Antworten – What is 16s rRNA used for
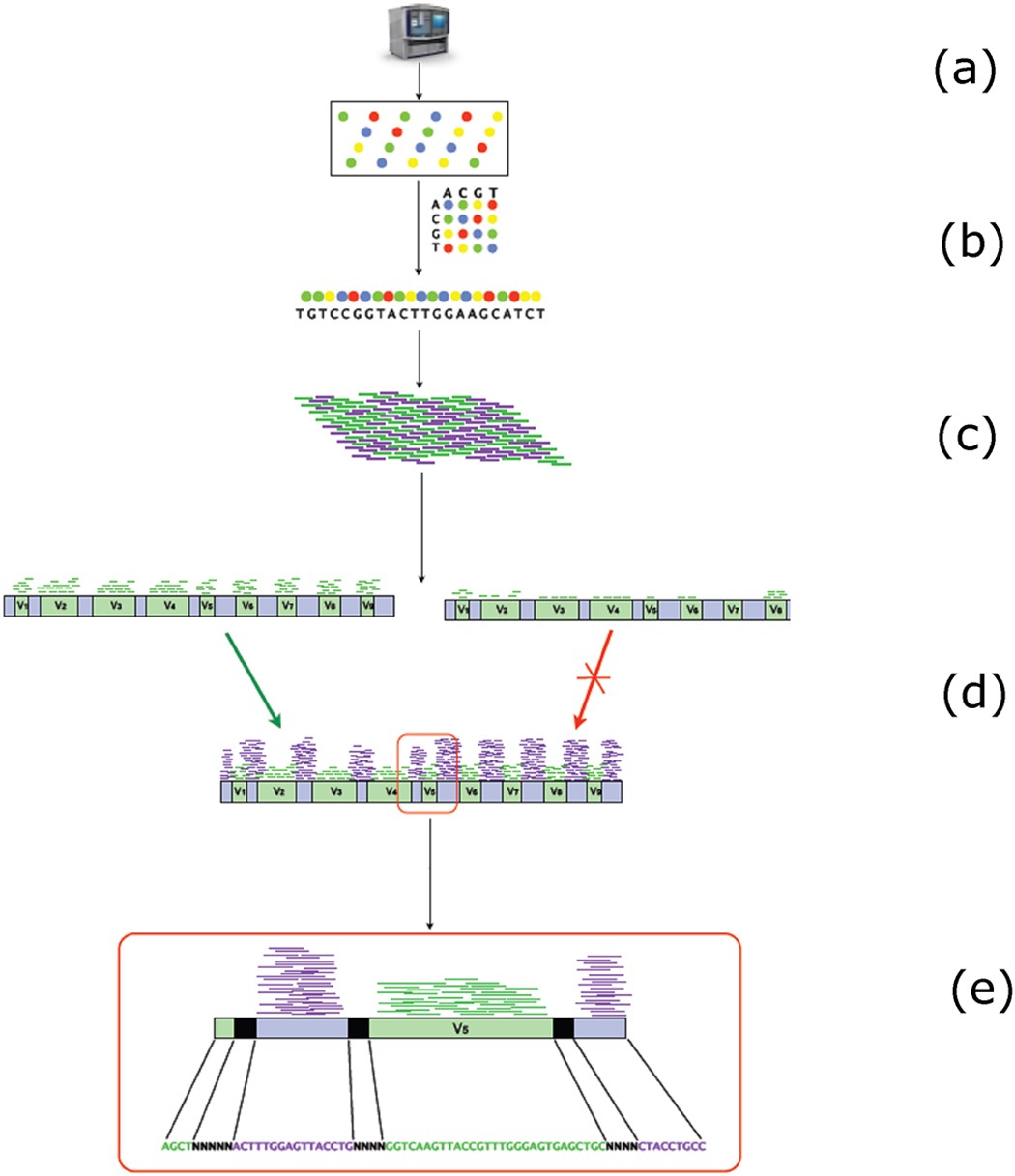
How does 16s rRNA sequencing work 16s rRNA sequencing is a culture-free method to identify and compare bacterial diversity from complex microbiomes or environments that are difficult to study. It is commonly used to identify bacteria present within a given sample down to the genus and/or species level.16S rRNA gene sequence analysis can better identify poorly described, rarely isolated, or phenotypically aberrant strains, can be routinely used for identification of mycobacteria, and can lead to the recognition of novel pathogens and noncultured bacteria.Background: Broad-range 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is used for detection and identification of bacterial pathogens in clinical specimens from patients with a high suspicion for infection.
Do humans have the 16s gene : Finally, we demonstrate that such intragenomic 16S gene copy variants are highly prevalent in taxa isolated from the human gut microbiome, suggesting they may be used to improve discrimination between species and even strains in 16S gene-based microbiome studies.
Is 16S a housekeeping gene
generally, so-called "house-keeping" genes involved in basic cellular functions are used for normalisation (16S, tus, rpoD, glyA, dnaB, gyrA, pykA/F, pfkA/B, mdoG, arcA).
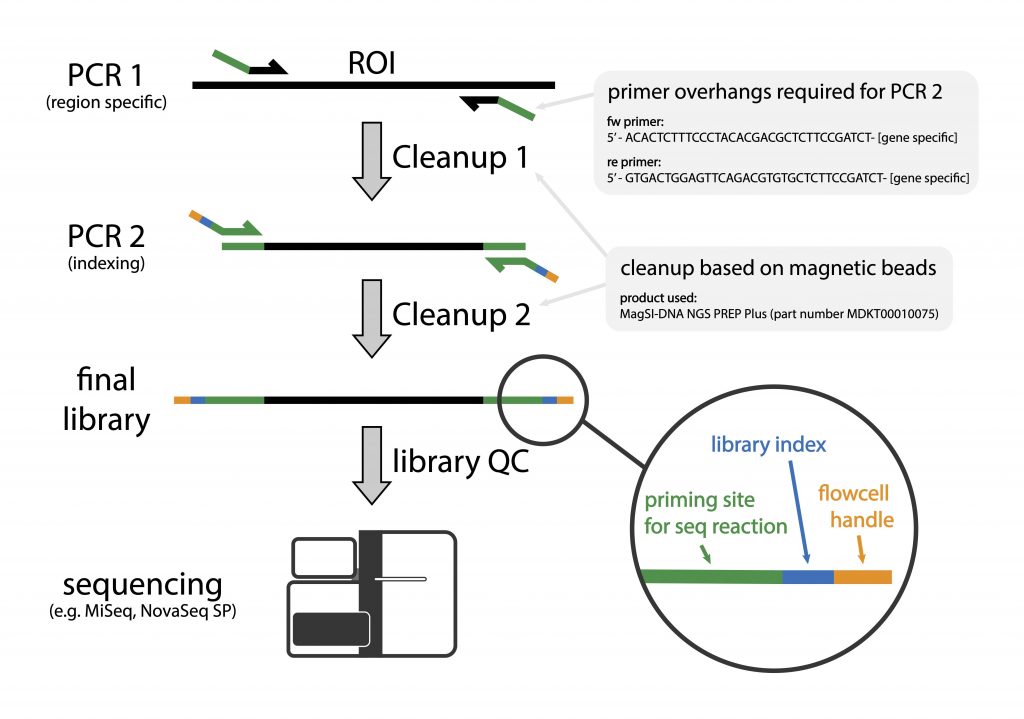
What is the purpose of amplifying 16S rRNA gene : This method should be useful for increasing the amounts of bacterial 16S ribosomal DNA sequences for the purposes of sequencing and probing. It should have a broad range of applications, including the detection and identification of known pathogens that are difficult to culture.
Profiling microbial communities using 16S rRNA genes is a straightforward and cost-effective method to profile the taxonomic composition of a microbial community, but it has limited taxonomic resolution due to the conservation of the target gene and length of amplicon product.
In research, 16S rDNA PCR will continue to be used to identify novel bacterial species, characterise species-specific pathogenicity and as a gold-standard assay to compare against when evaluating new assays. It is also used in combination with cutting-edge techniques, such as next-generation sequencing.
Why is the 16S gene used to identify bacteria
Because of the complexity of DNA–DNA hybridization, 16S rRNA gene sequencing is used as a tool to identify bacteria at the species level and assist with differentiating between closely related bacterial species [8]. Many clinical laboratories rely on this method to identify unknown pathogenic strains [19].No, viruses do not contain 16S ribosomal RNA. The 16S rRNA is a component of the small subunit (30S) of the prokaryotic ribosome, which is involved in protein synthesis. Viruses lack ribosomes and rely on the host cell's machinery for protein synthesis.Whereas, metagenomic will sequence all or most of the genes within a provided DNA sample. So, with 16s sequencing, one can get only the taxonomic information (from which bacteria does the 16s sequence came) while from metagenomics, both taxonomy and functional potential of the sample can be determined.
As 16S rRNA sequencing uses PCR to amplify a specific region of DNA, there is little chance of amplification from the 'host' DNA. Shotgun metagenomic sequencing, on the other hand, sequences all the DNA in a sample meaning that non-microbial reads may obscure the microbiome results.
What does the 16S primer do in PCR : In particular, the analysis of 16S rRNA genes, aided by using PCR to amplify target sequences in environmental samples, has enabled molecular ecologists to provide better estimates of bacterial diversity (1). PCR primers for amplification of 16S rRNA genes are widely available (6, 13).
What does the 16S gene encode : The 16S ribosomal RNA gene codes for the RNA component of the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome. It is widely present in all bacterial species. Different bacterial species have one to multiple copies of the 16S rRNA gene.
What is the difference between 16S and WGS
16S amplicon sequencing is currently used to identify dominant organisms present in a biological sample. However, WGS has been shown to detect and identify more genera of bacteria, archaea, viruses, and eukaryota compared to 16S amplicon sequencing.
All microorganisms have at least one copy of 16S, making it ubiquitous, and as it is highly conserved and evolves slowly, it is the most widely used single target for phylogenetic studies of bacteria and archaea (3, 4, 42).Principles of 16S rRNA Sequencing
The 16S rRNA gene is a small, conserved gene that codes for the 16S subunit of the ribosome. The 16S rRNA gene is found in all bacteria and archaea, and is highly conserved, making it an ideal target for identifying and characterizing these microorganisms.
Is 16S protein coding : In theory, 16S rRNA gene should not encode any protein. You have to have ribosome binding site upstream of the gene to make it able to produce proteins. As far as I know, 16S rRNA gene does not have one.