Antwort What is 100 Mbps full-duplex? Weitere Antworten – What is the difference between 100mb half-duplex and full-duplex
Using the same example of moving two 150Mb files, a 100Mbps symmetrical, full duplex switch will deliver both files in 1.5 seconds. A 100Mbps asymmetrical half duplex switch with a 70/30 split will take 7.14 seconds to deliver both files.10 to 1000Mbps
Full duplex offers the connection speed 10 to 1000Mbps, and newer point to point wireless bridges can transmit up to 6Gbps! Full duplex Ethernet bridge links are similar to having a two land highway where traffic can be sent and received at the same time, without any collisions, or slow down in traffic.A one gigabit port in full duplex means that it can send and receive one gigabit per second in both directions. The back plane of your switch / router / whatever is what controls how many of your ports can be used concurrently.
What is 10 Mbps half-duplex : This means that 10Mb/s half duplex is only 10Mb/s in one direction assuming no collisions (almost impossible as most protocols acknowledge transmission).
What is 100mbps half-duplex
100BASE-T (fast ethernet over 2 wire pairs) is full duplex, meaning 100Mbit per direction, simultaneously. It is possible to configure a 100Mbit network interface in half duplex, meaning that the total bandwidth available for send+receive is 100Mbit (as opposed to 200Mbit for full duplex)
Why is full-duplex faster : Full-duplex communication allows for faster data transfer as devices can both send and receive information simultaneously. This increases data transfer speeds compared to half-duplex or simplex communication. (Simplex communication is unidirectional data transmission, like a keyboard.)
Full-duplex Ethernet does save time when compared to half-duplex because it alleviates collisions and frame retransmissions. Sending and receiving are separate functions, creating a system where there is full data capacity in each direction. In contrast, half-duplex can be used to conserve bandwidth.
In-band full duplex communication has a rich set of potential applications – it is defined in the NGMN Whitepaper as a Technology Building Block for 5G. In the 5G network architecture, it can enable efficient implementation of new radio features to achieve greater spectral efficiency and boost network capacity.
What is 100Mbps half-duplex
100BASE-T (fast ethernet over 2 wire pairs) is full duplex, meaning 100Mbit per direction, simultaneously. It is possible to configure a 100Mbit network interface in half duplex, meaning that the total bandwidth available for send+receive is 100Mbit (as opposed to 200Mbit for full duplex)The 802.11 family consists of a series of half-duplex over-the-air modulation techniques that use the same basic protocol.Also, some older Ethernet devices can only use half-duplex communications, even when connected to a full-duplex switch. Lastly, Wi-Fi networks are half-duplex on a per-channel basis. Each radio channel, as with walkie-talkies, can send or receive — but not both at the same time.
The 802.11 family consists of a series of half-duplex over-the-air modulation techniques that use the same basic protocol.
Should I enable full duplex : Enabling channels to be full-duplex in networking helps avoid performance issues related to contention over bandwidth between senders and increased transmission collisions. Simplex connections transmit in only one direction; half-duplex transmissions are bidirectional but can go in only one direction at a time.
Should I use full duplex : Full-duplex Ethernet does save time when compared to half-duplex because it alleviates collisions and frame retransmissions. Sending and receiving are separate functions, creating a system where there is full data capacity in each direction. In contrast, half-duplex can be used to conserve bandwidth.
Why is full duplex faster
Full-duplex communication allows for faster data transfer as devices can both send and receive information simultaneously. This increases data transfer speeds compared to half-duplex or simplex communication. (Simplex communication is unidirectional data transmission, like a keyboard.)
Effects of Full-Duplex Operation
While full-duplex operation has the potential to double the bandwidth of an Ethernet link segment, it usually won't result in a large increase in performance on a link that connects to a user's computer.Lastly, Wi-Fi networks are half-duplex on a per-channel basis. Each radio channel, as with walkie-talkies, can send or receive — but not both at the same time.
Is LTE full-duplex : Duplex refers to the ability for a communication channel to transmit and receive data. LTE can be either full duplex (meaning that transmitting and receiving can happen simulataneously), or half duplex (meaning that transmitting and receiving can happen, but not at the same time).



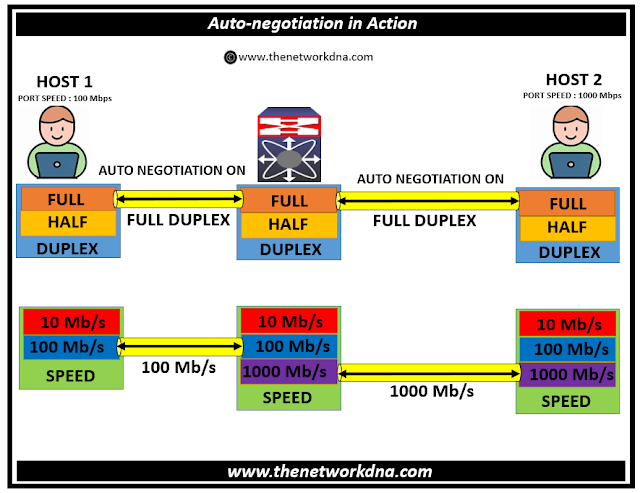

.jpeg-1080x1080.jpg)