Antwort What is 1 step PCR? Weitere Antworten – What is a one-step PCR
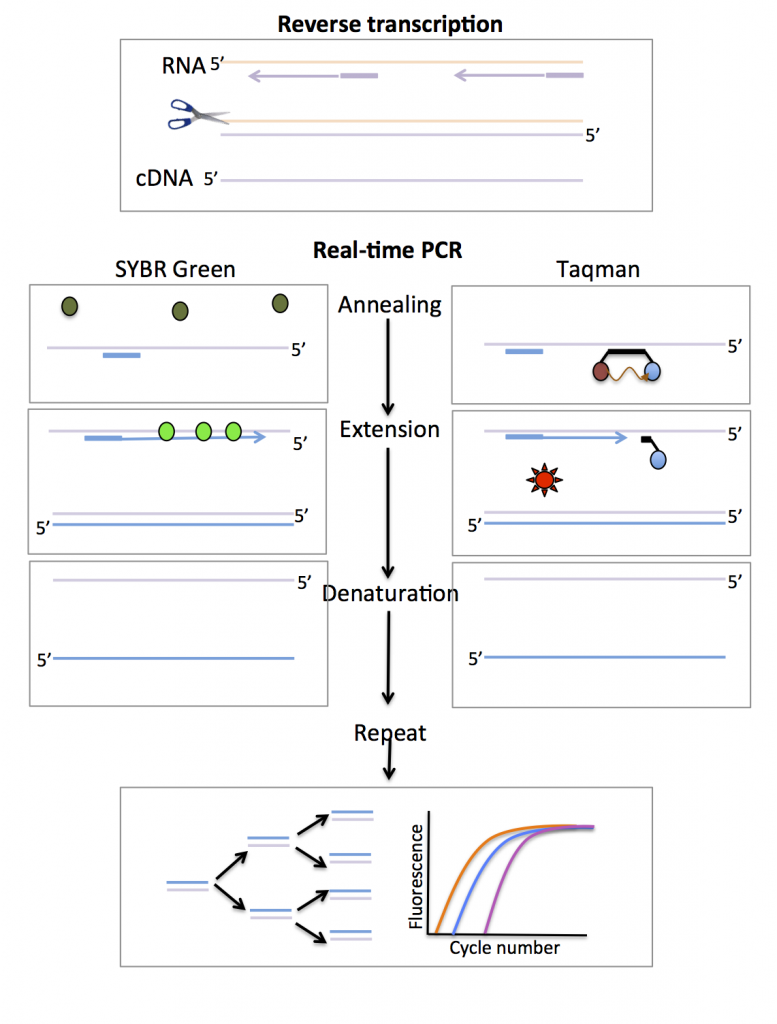
What is one-step RT-PCR As the name implies, one-step RT-PCR combines first-strand cDNA synthesis (RT) and subsequent PCR in a single reaction tube. This reaction setup can help simplify your workflow, reduces variation, and minimizes possible contamination.Two-step RT-PCR entails two separate reactions, beginning with first-strand cDNA synthesis (RT), followed by amplification of a portion of the resulting cDNA by PCR in a separate tube. Therefore, two-step RT-PCR is useful for detecting multiple genes in a single RNA sample.In one-step RT-qPCR, cDNA synthesis and qPCR are performed in a single reaction vessel in a common reaction buffer. In two-step RT-qPCR, cDNA is synthesized in one reaction, and an aliquot of the cDNA is then used for a subsequent qPCR experiment.
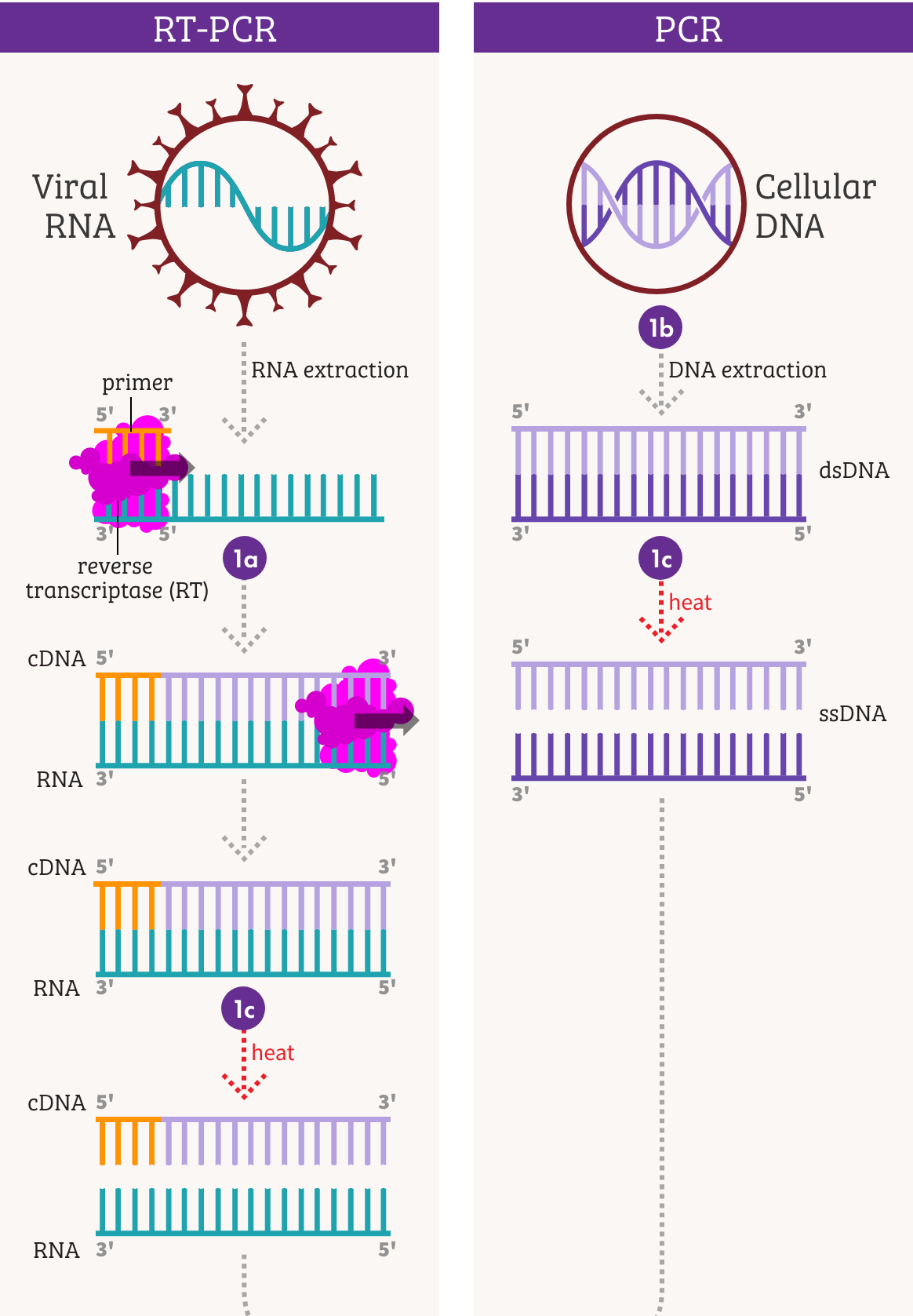
What is the first step of RT-PCR : Traditionally RT-PCR involves two steps: the RT reaction and PCR amplification. RNA is first reverse transcribed into cDNA using a reverse transcriptase as described here, the resulting cDNA is used as templates for subsequent PCR amplification using primers specific for one or more genes.
What is one-step vs two step real time PCR
The distinction between the two is fairly simple. In one-step RT-PCR, both major reactions (reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction) are carried out in a single tube. For a two-step process, the cDNA products of reverse transcription are transferred to a second tube for subsequent PCR.
What are the advantages of one-step PCR : Table 1. Comparison of one-step vs two-step RT-PCR
| One-step RT-PCR | |
|---|---|
| Advantages | Less experimental variation since both reactions take place in the same tube Fewer pipetting steps helps reduce risk of contamination Suitable for high throughput amplification/screening Fast and highly reproducible |
The distinction between the two is fairly simple. In one-step RT-PCR, both major reactions (reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction) are carried out in a single tube. For a two-step process, the cDNA products of reverse transcription are transferred to a second tube for subsequent PCR.
Two-step RT-PCR entails two separate reactions, beginning with first-strand cDNA synthesis (RT), followed by amplification of a portion of the resulting cDNA by PCR in a separate tube. Therefore, two-step RT-PCR is useful for detecting multiple genes in a single RNA sample.
What is one-step vs two-step real-time PCR
The distinction between the two is fairly simple. In one-step RT-PCR, both major reactions (reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction) are carried out in a single tube. For a two-step process, the cDNA products of reverse transcription are transferred to a second tube for subsequent PCR.RT-PCR test.
A health care professional collects a fluid sample by inserting a long nasal swab (nasopharyngeal swab) into your nostril and taking fluid from the back of your nose. A sample may be collected by using a shorter nasal swab (mid-turbinate swab) or a very short swab (anterior nares swab).One-step RT-PCR
The reaction mix includes dNTPs, primers, template RNA, necessary enzymes, and a buffer solution. The reaction mix is added to a PCR tube for each reaction, followed by template RNA. The PCR tubes are then placed in a thermal cycler to begin cycling. In the first cycle, the synthesis of cDNA occurs.
Table 1. Comparison of one-step vs two-step RT-PCR
| One-step RT-PCR | |
|---|---|
| Advantages | Less experimental variation since both reactions take place in the same tube Fewer pipetting steps helps reduce risk of contamination Suitable for high throughput amplification/screening Fast and highly reproducible |
What is the difference between 2 step and 3 step PCR : The major differences between 2P protocol and the original 3P protocol [5] include (Tables 1 and 2): (1) a decrease in the number of PCR steps from three to two by eliminating the enrichment step but by maintaining the same total number of PCR cycles (30 cycles); (2) the use of a steady decrease in annealing …
What are the disadvantages of one-step PCR : One of the limitations of one-step RT-PCR is the inability to individualize and optimize the two processes. The single, common buffer optimized for both reactions in the same tube is more likely to be suboptimal as compared to using separate buffers specifically optimized for each individual enzyme.
When to use 2 step PCR
2-step PCR: When primers with annealing temperatures ≥ 72°C are used, a 2-step thermocycling protocol (combining annealing and extension into one step) is possible. Amplification of long products: When amplifying products > 6 kb, it is often helpful to increase the extension time to 40–50 seconds/kb.
The distinction between the two is fairly simple. In one-step RT-PCR, both major reactions (reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction) are carried out in a single tube. For a two-step process, the cDNA products of reverse transcription are transferred to a second tube for subsequent PCR.Polymerase chain reaction is commonly known as PCR. It is used to produce multiple copies of a gene or DNA of interest. The steps of polymerase chain reaction are denaturation, primer annealing and extension of primers.
What is the difference between PCR and RT-PCR : PCR is a method used to amplify DNA from a small amount of DNA template. RT-PCR uses reverse transcription to produce a DNA template from an RNA source that can then be amplified.