Antwort What happens during cycle 3 of PCR? Weitere Antworten – Why does PCR take 3 cycles
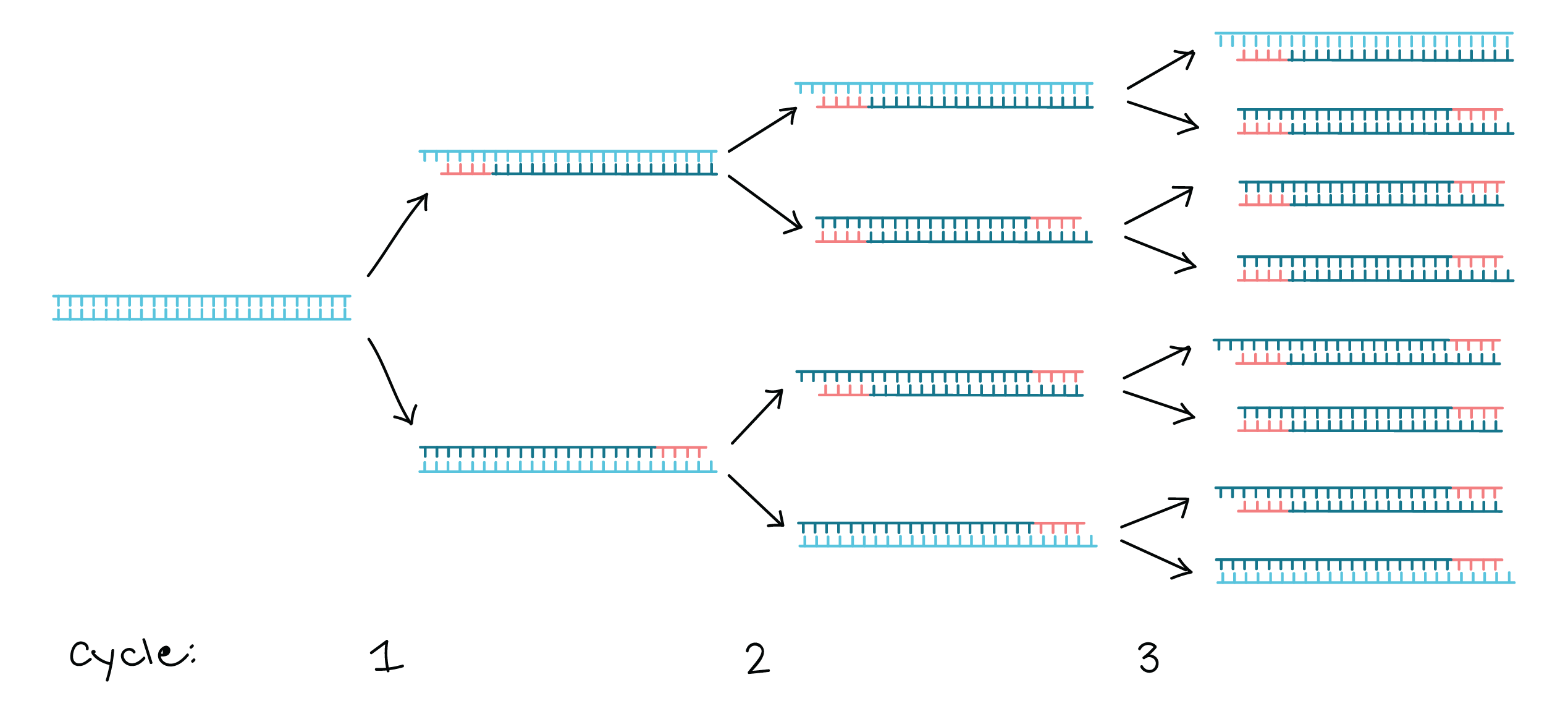
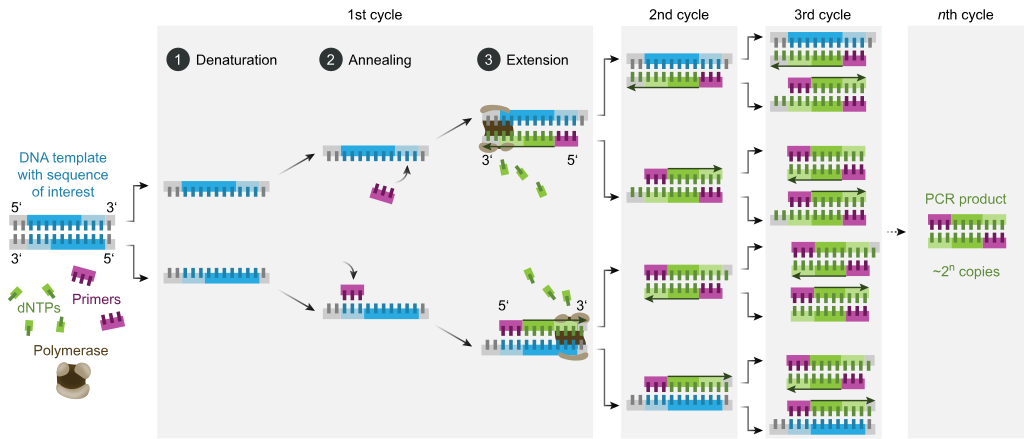
The three steps are repeated for multiple cycles, with each cycle doubling the amount of DNA in the sample. The number of cycles is determined by the amount of target DNA in the initial sample and the sensitivity required for the experiment.Step 3, extending: the temperature is raised again and the new strand of DNA is made by the Taq polymerase enzyme. These three stages are repeated 20-40 times, doubling the number of DNA copies each time. This is called thermal cycling, carried out by a machine.PCR is based on three simple steps required for any DNA synthesis reaction: (1) denaturation of the template into single strands; (2) annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis; and (3) extension of the new DNA strands from the primers.
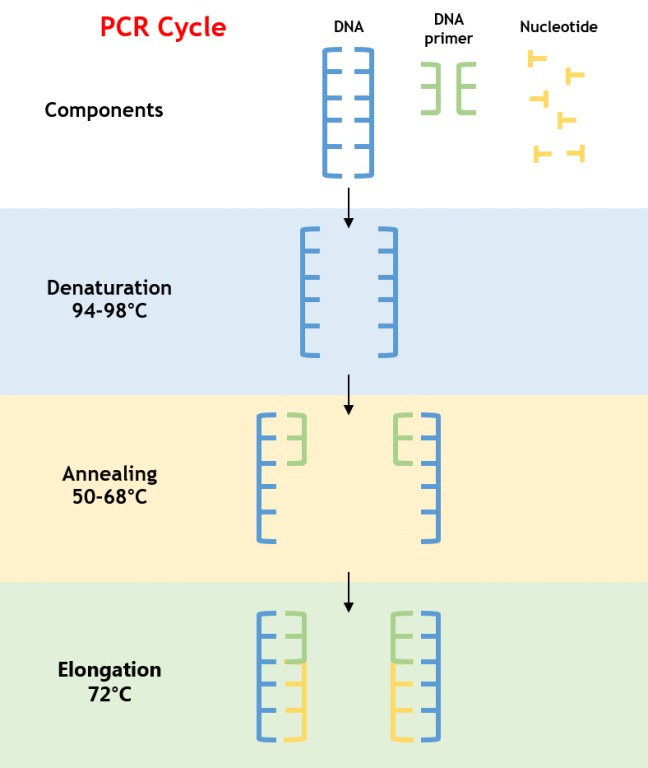
What are the stages of the PCR cycle : Each PCR cycle consists of template denaturation, primer annealing and primer extension. If the temperatures for annealing and extension are similar, these two processes can be combined. Each stage of the cycle must be optimized in terms of time and temperature for each template and primer pair combination.
How many copies of DNA after 3 cycles of PCR
8 copies
So, that means after the second cycle, it will produce 4 copies of DNA sample, then after the third cycle, 8 copies are produced, after the fourth cycle, 16 copies are produced, after the fifth cycle, 32 copies are produced, and lastly, after the sixth cycle, 64 copies of DNA samples are produced.
How many copies after 3 cycles of PCR : Thus the number of copies of DNA produced is 8.
13. Representative Results
| Standard 3-step PCR Cycling | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cycle step | Temperature | Time |
| Initial Denaturation | 94 °C to 98 °C | 1 minute |
| Denaturation Annealing Extension | 94 °C 5 °C below Tm 70 °C to 80 °C | 10 to 60 seconds 30 seconds Amplicon and DNA polymerase dependent |
| Final Extension | 70 °C to 80 °C | 5 minutes |
Initial Denaturation for 2 minutes at 94°C. Denature for 30 seconds at 94°C. Anneal primers for 30 seconds at 55°C (or 5°C below Tm). Extend DNA for 2 minutes at 72°C.
What are the 3 major steps during each PCR cycle briefly describe what happens in the test tube during each of these steps
Amplification is achieved by a series of three steps: (1) denaturation, in which double-stranded DNA templates are heated to separate the strands; (2) annealing, in which short DNA molecules called primers bind to flanking regions of the target DNA; and (3) extension, in which DNA polymerase extends the 3′ end of each …Phases of the PCR amplification curve. The PCR amplification curve charts the accumula- tion of fluorescent emission at each reaction cycle. The curve can be broken into four different phases: the linear ground, early exponential, log-linear, and plateau phases.16 copies
The number of double stranded DNA pieces is doubled in each cycle, so that after n cycles you have 2^n (2 to the n:th power) copies of DNA. For example, after 4 cycles you have 16 copies, after 20 cycles you have about one million copies, etc.
Final answer: After 5 cycles of PCR, a single double-stranded DNA molecule would become 32 double-stranded copies, as each PCR cycle doubles the amount of DNA present.
How many copies of DNA are there after 3 cycles : So after 3 cycles you have 8–6=2, after 4 cycles 16–8=8, after 20 cycles 1,048,576–40= 1,048,536 copies. What is the total number of DNA molecules present after 5 cycles of PCR starting with 3 molecules of template DNA PCR is a method used to amplify DNA.
How many DNA copies after 4 PCR cycles : 16 copies
The number of double stranded DNA pieces is doubled in each cycle, so that after n cycles you have 2^n (2 to the n:th power) copies of DNA. For example, after 4 cycles you have 16 copies, after 20 cycles you have about one million copies, etc.
What is the temperature of step 3 in PCR
PCR step3. The temperature is raised to be optimal for the DNA polymerase. The heat-stable polymerases used for PCR typically have an optical temperature in the range of 65-75 degrees C.
It used repeating cycles consisting of three steps (denaturing, annealing and extension). PCR has the ability to make millions of copies of the template DNA.Denaturation is the first step of PCR. In this step, heat is applied to the template to separate double-stranded DNA into two single strands. Following the denaturation step is the annealing step. The temperature is decreased so that the primers can anneal to the complementary sequences on the DNA templates.
What are the 3 cycles in PCR and what they do which one can you change to improve specificity : PCR steps of denaturation, annealing, and extension are repeated (or “cycled”) many times to amplify the target DNA. The number of cycles is usually carried out 25–35 times but may vary upon the amount of DNA input and the desired yield of PCR product.