Antwort What are the three steps of PCR and temperatures? Weitere Antworten – What is the temperature of the PCR steps
13. Representative Results
| 2-step PCR Cycling | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cycle step | Temperature | Time |
| Initial Denaturation | 94 °C to 98 °C | 1 minute |
| Denaturation Annealing/Extension | 94 °C 70 °C to 80 °C | 10 to 60 seconds Amplicon and DNA polymerase dependent |
| Final Extension | 70 °C to 80 °C | 5 minutes |
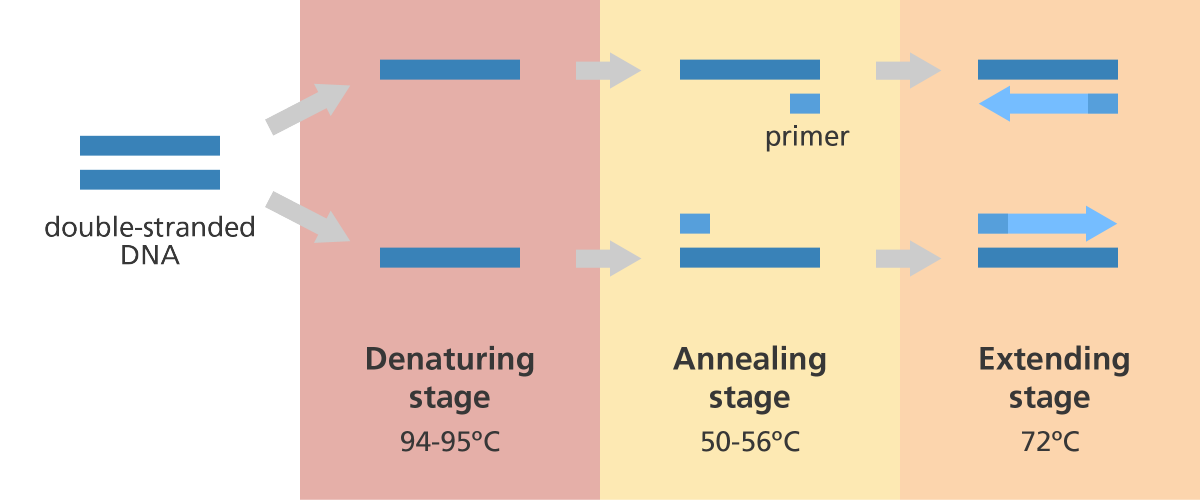
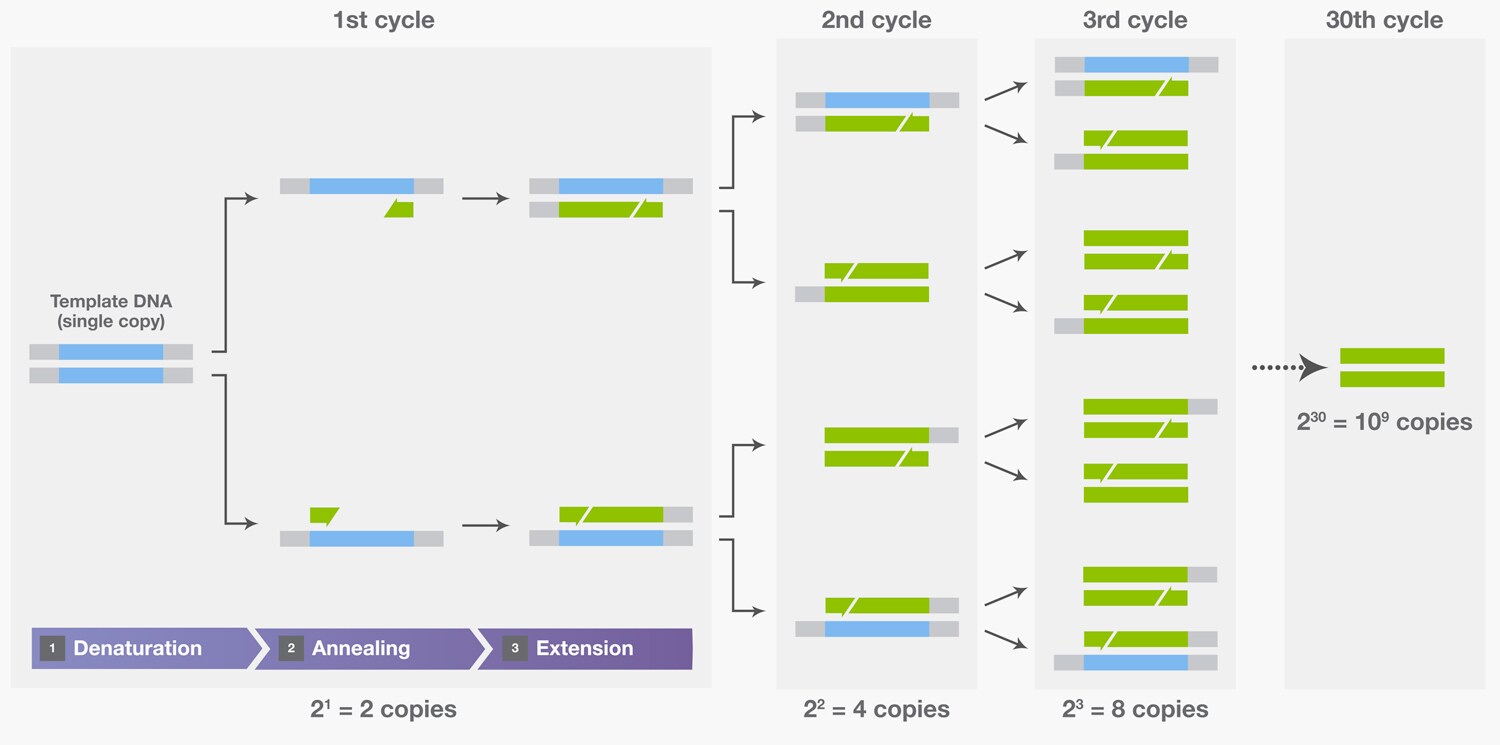
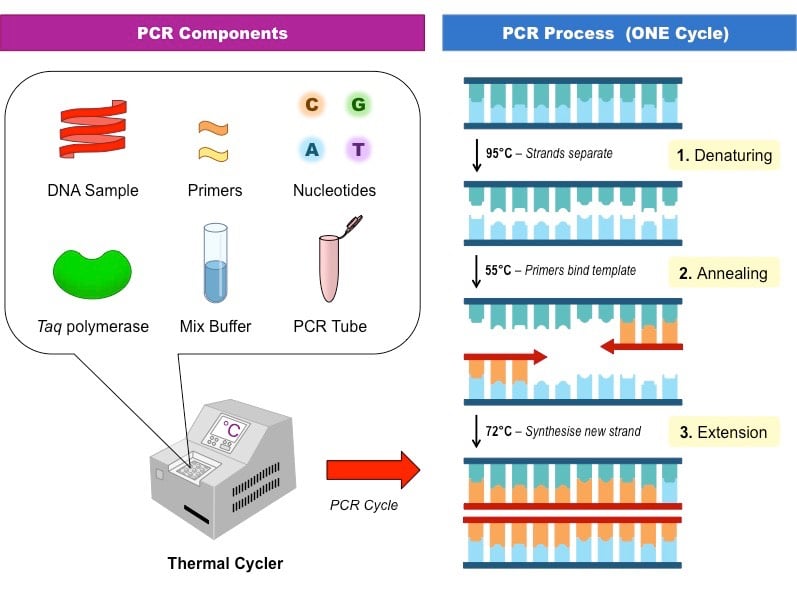
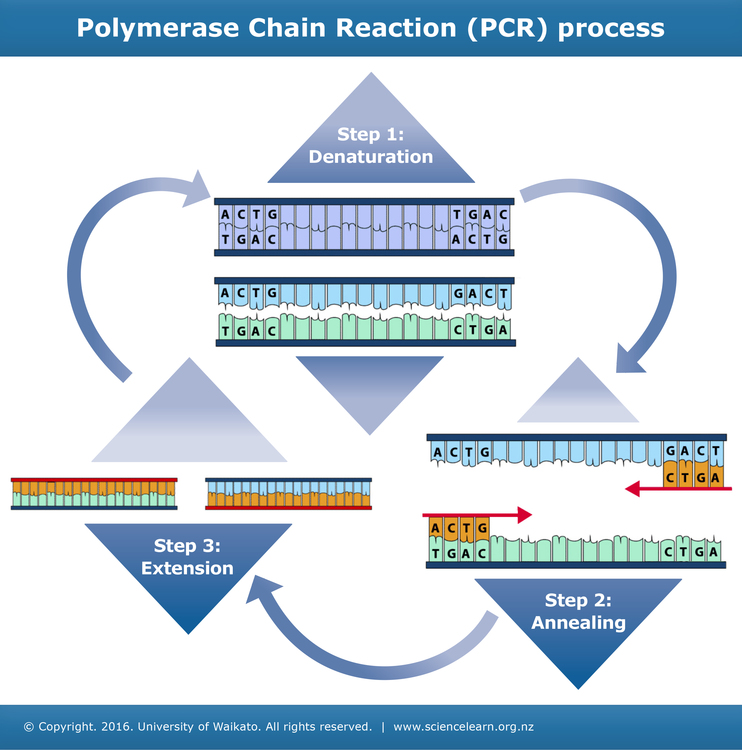
22. 5. 2012PCR is based on three simple steps required for any DNA synthesis reaction: (1) denaturation of the template into single strands; (2) annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis; and (3) extension of the new DNA strands from the primers.72°C
A typical PCR cycle includes an extension step at 72°C after denaturation of double-stranded DNA and annealing of oligonucleotide primers. At this temperature the thermostable poly-merase replicates the DNA at an optimal rate that depends on the buffer and nature of the DNA template ( 1 ).
What is the temperature for annealing in PCR : In general, the annealing temperatures usually range between 55°C and 72°C.
How is temperature used in PCR
PCR consists of cycles of reaction heating and cooling. Each temperature plateau is used to control a defined stage of the reaction and the incubation times are dependent on the instrument, reaction plates or tubes and reagents.
What happens at each temperature in PCR : Annealing: The temperature is lowered to approximately 5 °C below the melting temperature (Tm) of the primers (often 45–60 °C) to promote primer binding to the template. Extension: The temperature is increased to 72 °C, which is optimum for DNA polymerase activity to allow the hybridized primers to be extended.
Amplification is achieved by a series of three steps: (1) denaturation, in which double-stranded DNA templates are heated to separate the strands; (2) annealing, in which short DNA molecules called primers bind to flanking regions of the target DNA; and (3) extension, in which DNA polymerase extends the 3′ end of each …
The high temperature breaks the hydrogen bonds between the bases in two strands of template DNA. This causes the two strands to separate, resulting in two single strands of DNA. These single DNA strands act as templates for the production of the new DNA strands.
Why is PCR done at different temperatures
PCR consists of cycles of reaction heating and cooling. Each temperature plateau is used to control a defined stage of the reaction and the incubation times are dependent on the instrument, reaction plates or tubes and reagents.The initial denaturation step is commonly performed at 94–98°C for 1–3 minutes. The time and temperature of this step can vary depending on the nature of the template DNA and salt concentrations of buffer.45–68°C.
Annealing: The annealing step is typically 15–60 seconds. Annealing temperature is based on the Tm of the primer pair and is typically 45–68°C.
During the annealing phase of PCR, the reaction temperature needs to be sufficiently low to allow both forward and reverse primers to bind to the template, but not so low as to enable the formation of undesired, non-specific duplexes or intramolecular hairpins, both of which reduce reaction efficiency.
Why is PCR done at high temperatures : The high temperature causes the hydrogen bonds between the bases in two strands of template DNA to break and the two strands to separate. This results in two single strands of DNA, which will act as templates to produce the new copies of each strand of DNA.
Why are the temperatures used in PCR : During the annealing phase of PCR, the reaction temperature needs to be sufficiently low to allow both forward and reverse primers to bind to the template, but not so low as to enable the formation of undesired, non-specific duplexes or intramolecular hairpins, both of which reduce reaction efficiency.
What are the steps of the PCR process
A standard polymerase chain reaction (PCR) setup consists of four steps:
- Add required reagents or mastermix and template to PCR tubes.
- Mix and centrifuge.
- Amplify per thermo cycler and primer parameters.
- Evaluate amplified DNA by agarose gel electrophoresis followed by ethidium bromide staining.
3 Stages of the PCR Cycling Process
- Denaturation. During this step, the temperature increases to around 95-98°C for 15-30 seconds.
- Annealing. This step involves lowering the temperature to around 50-56°C for specific amplification and 36°C for aspecific amplification.
- Extension.
initial denaturation phase
The initial denaturation phase consists of a period at high temperature, during which the secondary structure of the complex double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) is melted to become single-stranded DNA (ssDNA).
What happens if annealing temperature is too high in PCR : Typically, the optimum annealing temperature is 3-5 degrees Celsius below the melting temperature. Too high of an annealing temperature prevents optimal binding of the primers to the templates while too low of an annealing temperature can lead to non-specific binding and, subsequently, non-specific PCR products.