Antwort What are the steps in the PCR cycle? Weitere Antworten – What are the cycles of PCR
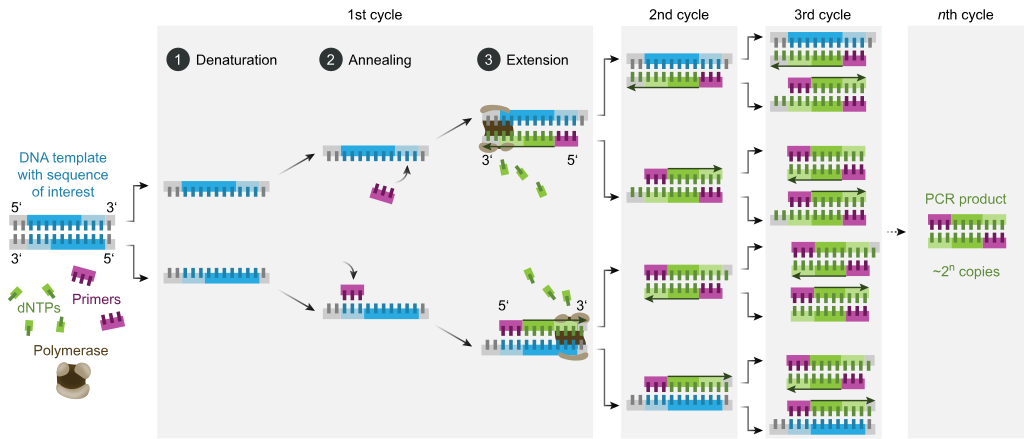
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplifies DNA and involves a series of temperature cycles critical for amplifying the DNA target. The cycling process is divided into three main stages: denaturation, annealing, and extension. These three stages are repeated for 20-40 cycles, doubling the targeted DNA amount.RT-PCR Protocol
- Experiment process.
- (1) Primer design. Design and synthesize the primers of the target gene.
- (2) RNA extraction.
- (3) Reverse transcription(RNA→cDNA)
- (4) Real-time PCR.
- (5) Result analysis.
- The factors affecting Real-time PCR results.
PCR is based on three simple steps required for any DNA synthesis reaction: (1) denaturation of the template into single strands; (2) annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis; and (3) extension of the new DNA strands from the primers.
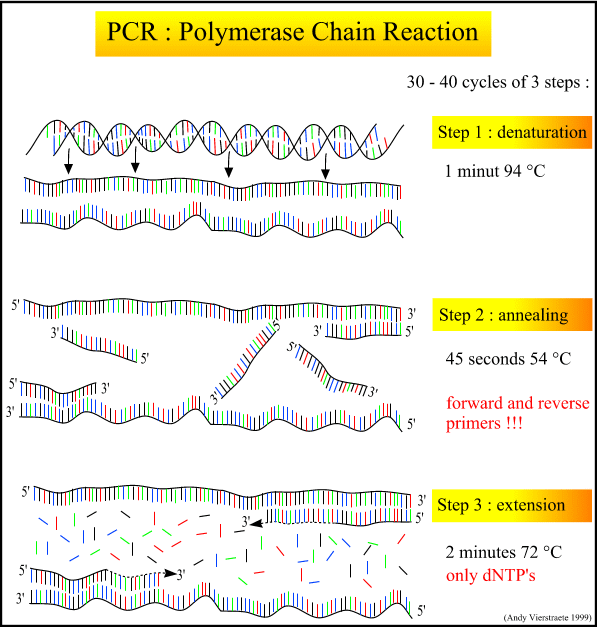
What happens in the denature step of PCR : Denaturation is the first step of PCR. In this step, heat is applied to the template to separate double-stranded DNA into two single strands. Following the denaturation step is the annealing step. The temperature is decreased so that the primers can anneal to the complementary sequences on the DNA templates.
What are the first cycles of PCR
The three temperature steps in a single cycle accomplish three tasks: the first step denatures the template (and in later cycles, the amplicons as well), the second step allows optimal annealing of primers, and the third step permits the DNA polymerase to bind to the DNA template and synthesize the PCR product.
What is 20 cycles of PCR : The number of double stranded DNA pieces is doubled in each cycle, so that after n cycles you have 2^n (2 to the n:th power) copies of DNA. For example, after 10 cycles you have 1024 copies, after 20 cycles you have about one million copies, etc.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
PCR involves using short synthetic DNA fragments called primers to select a segment of the genome to be amplified, and then multiple rounds of DNA synthesis to amplify that segment.
Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and rapid polymerase chain reaction (PCR) are two different techniques used to amplify genetic material in a cell. The main difference between RT-PCR and rapid PCR is the type of molecule that is being amplified.
What are the 3 major steps during each PCR cycle briefly describe what happens in the test tube during each of these steps
Amplification is achieved by a series of three steps: (1) denaturation, in which double-stranded DNA templates are heated to separate the strands; (2) annealing, in which short DNA molecules called primers bind to flanking regions of the target DNA; and (3) extension, in which DNA polymerase extends the 3′ end of each …Initial Denaturation for 2 minutes at 94°C. Denature for 30 seconds at 94°C. Anneal primers for 30 seconds at 55°C (or 5°C below Tm). Extend DNA for 2 minutes at 72°C.Step 2, annealing: the temperature is lowered to enable the DNA primers to attach to the template DNA. Step 3, extending: the temperature is raised again and the new strand of DNA is made by the Taq polymerase enzyme. These three stages are repeated 20-40 times, doubling the number of DNA copies each time.
Hence, the step of PCR conducted at the highest temperature causes denaturation (96°C). During denaturation, the two strands of the DNA separate due to the breaking of the hydrogen bonds present between the complementary bases.
Why 35 cycles in PCR : This is becuase; 1. DNA polymerase after 30-35 cycles is usually denatured, becuse each denaturation temp (95-94) for 30 sec to 1 min effects the protein function and it is not tolerable after 35 cycles usually.
What does 30 cycles of PCR give : After 30 cycles, as many as a billion copies of the target sequence are produced from a single starting molecule.
What are the 5 steps of PCR
For efficient endpoint PCR with fast and reliable results, here are five key steps to consider:
- Step 1DNA isolation.
- Step 2Primer design.
- Step 3Enzyme selection.
- Step 4Thermal cycling.
- Step 5Amplicon analysis.
qPCR or quantitative PCR is also known as real-time PCR. qPCR is used to quantify the nucleic acids. The amplification of the DNA molecule can be monitored during the PCR, i.e. in real time. RT-PCR is referred to as a reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.Denature for 30 seconds at 94°C. Anneal primers for 30 seconds at 55°C (or 5°C below Tm). Extend DNA for 2 minutes at 72°C. Repeat steps 8-10 for 25-30 cycles.
What are the 3 steps that occur during a PCR cycle describe each step and the temperature include an image of each : Amplification is achieved by a series of three steps: (1) denaturation, in which double-stranded DNA templates are heated to separate the strands; (2) annealing, in which short DNA molecules called primers bind to flanking regions of the target DNA; and (3) extension, in which DNA polymerase extends the 3′ end of each …