Antwort What are the steps for amplification in PCR? Weitere Antworten – What are the steps in PCR amplification
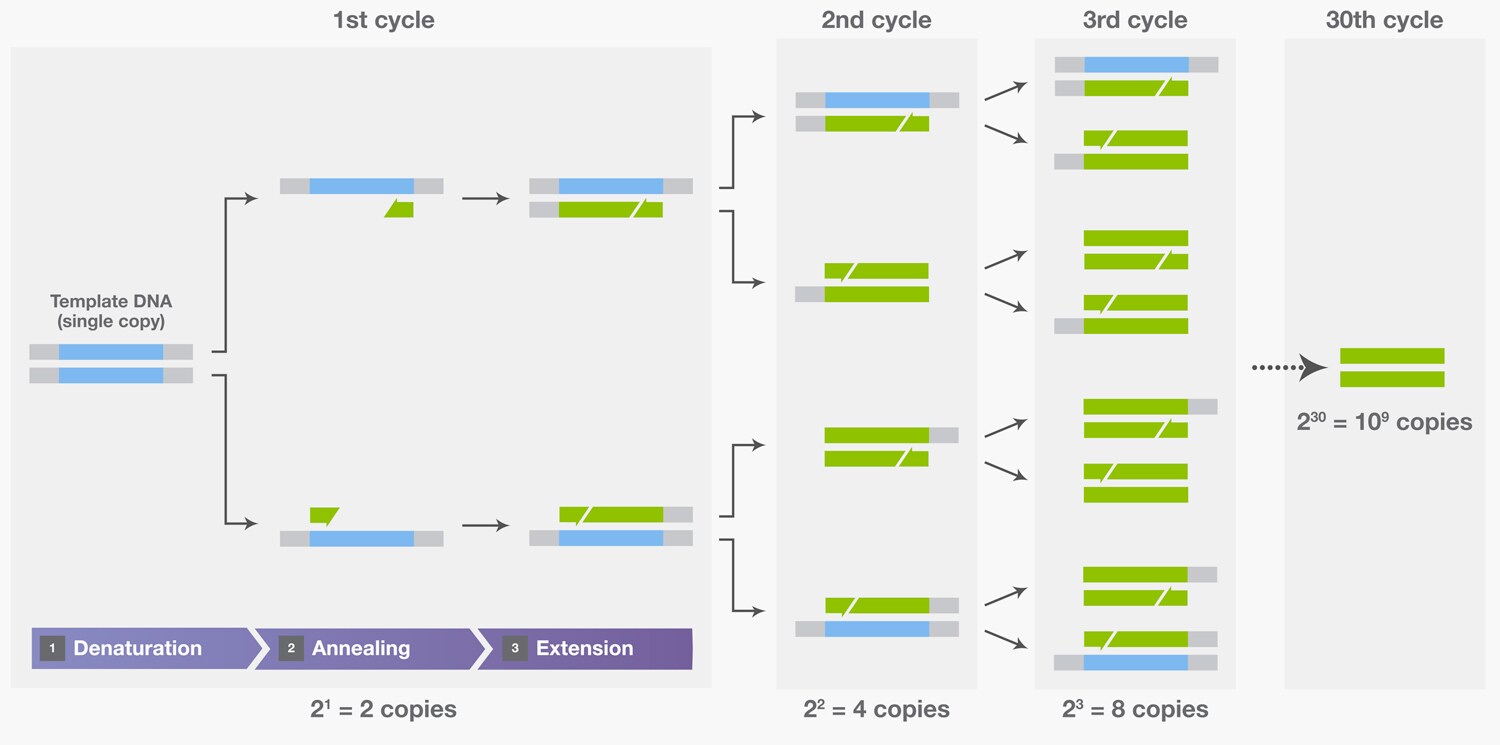
Amplification is achieved by a series of three steps: (1) denaturation, in which double-stranded DNA templates are heated to separate the strands; (2) annealing, in which short DNA molecules called primers bind to flanking regions of the target DNA; and (3) extension, in which DNA polymerase extends the 3′ end of each …The amplification plot shows two phases, an exponential phase followed by a non-exponential plateau phase. During the exponential phase, the amount of PCR product approximately doubles in each cycle.Amplification
- The two DNA strands are denatured by heat.
- The sample is then cooled to allow the primers to anneal to the DNA segments.
- The temperature is raised to allow the DNA polymerase to add nucleotides to extend the primers to produce a copy of each DNA template strand.
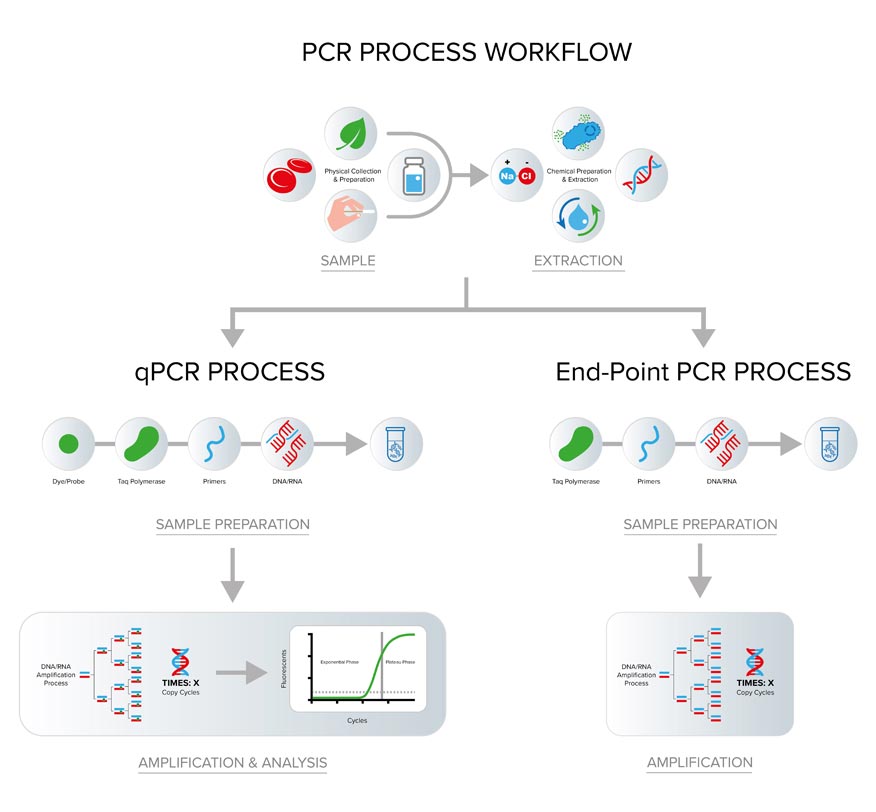
How is amplification done by PCR : The PCR process was originally developed to amplify short segments of a longer DNA molecule (Saiki et al. 1985). A typical amplification reaction includes target DNA, a thermostable DNA polymerase, two oligonucleotide primers, deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs), reaction buffer and magnesium.
What are the methods of PCR amplification
The majority of PCR methods rely on thermal cycling. Thermal cycling exposes reagents to repeated cycles of heating and cooling to permit different temperature-dependent reactions—specifically, DNA melting and enzyme-driven DNA replication.
What are the 4 steps of PCR : PCR machine steps
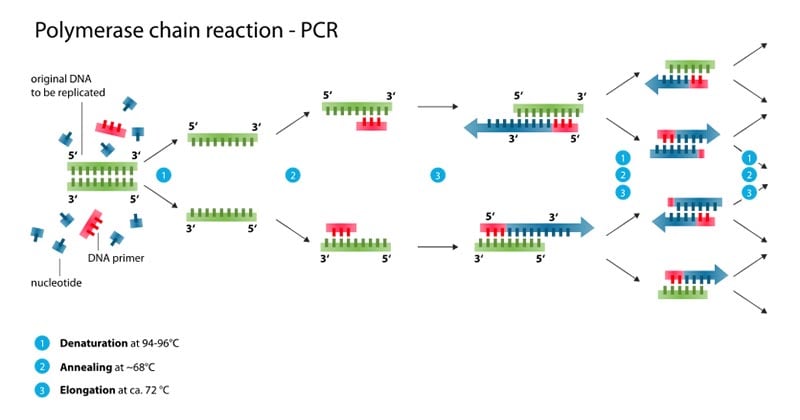
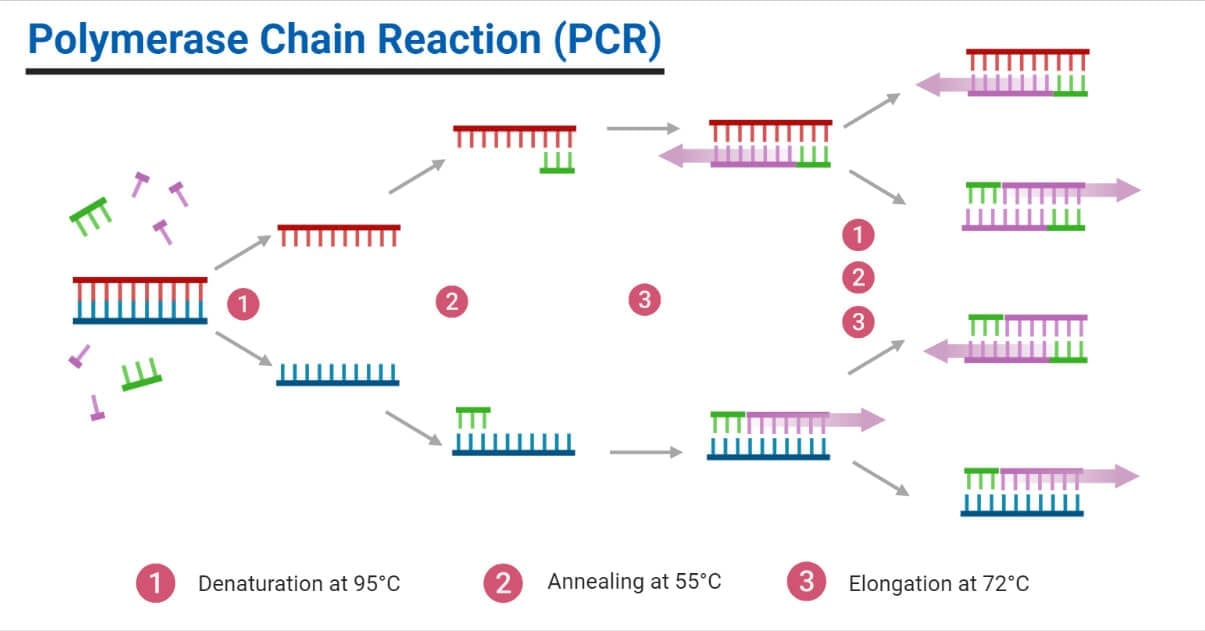
- Step 1 – Denaturation. The solution contained in the tube is heated to at least 94°C (201.2°F) using a thermal cycler.
- Step 2 – Annealing.
- Step 3 – Extension.
- Step 4 – Analysis with Electrophoresis.
The PCR amplification curve charts the accumulation of fluorescent emission at each reaction cycle. The curve can be broken into four different phases: the linear ground, early exponential, log-linear, and plateau phases.
Amplification is the process of adding power to the existing signal or wave without distorting the signal or wave shape. The power can be either added by a voltage amplification or current amplification or both simultaneously. Since Power=Voltage*Current ,increasing anyone parameter or both increases the power.
What are the four phases of real time PCR amplification
The PCR amplification curve charts the accumula- tion of fluorescent emission at each reaction cycle. The curve can be broken into four different phases: the linear ground, early exponential, log-linear, and plateau phases.How does PCR work To amplify a segment of DNA using PCR, the sample is first heated so the DNA denatures, or separates into two pieces of single-stranded DNA. Next, an enzyme called "Taq polymerase" synthesizes – builds – two new strands of DNA, using the original strands as templates.A standard polymerase chain reaction (PCR) setup consists of four steps:
- Add required reagents or mastermix and template to PCR tubes.
- Mix and centrifuge.
- Amplify per thermo cycler and primer parameters.
- Evaluate amplified DNA by agarose gel electrophoresis followed by ethidium bromide staining.
The polymerase chain reaction is a nucleic acid amplification testing procedure that consists of denaturing, renaturing, elongating, and amplifying a short segment of DNA or RNA.
What are the steps in the PCR procedure in the correct order : The correct option is C Denaturation, Annealing, Extension. Polymerase chain reaction or PCR consists of the following three steps: Denaturation- The two DNA strands of template DNA separate from each other when heated to 92℃.
What are the 4 phases in qPCR amplification curve : qPCR has four distinct phases ( Figure 1); (1) during the background phase, the target DNA is too low in concentration, and the background noise covers the signal; (2) once the target DNA becomes detectable, the output signal enters the exponential phase, in which the DNA is doubled at every cycle; (3) in the …
What are the stages of amplification
Building-block amplifier stages:
- Inverting voltage amplifier (also called Common emitter or Common source amplifier)
- Current Follower (also called Common base or Common gate or cascode)
- Voltage Follower (also called Common collector or Common drain amplifier)
- Series feedback (more commonly: emitter/source degeneration)
The cycling process is divided into three main stages: denaturation, annealing, and extension. These three stages are repeated for 20-40 cycles, doubling the targeted DNA amount.PCR is a very sensitive technique that allows rapid amplification of a specific segment of DNA. PCR makes billions of copies of a specific DNA fragment or gene, which allows detection and identification of gene sequences using visual techniques based on size and charge.
How does PCR amplify DNA explain the 3 steps : PCR is based on three simple steps required for any DNA synthesis reaction: (1) denaturation of the template into single strands; (2) annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis; and (3) extension of the new DNA strands from the primers.