Antwort What are the risks of swaps? Weitere Antworten – What is the credit risk of a swap
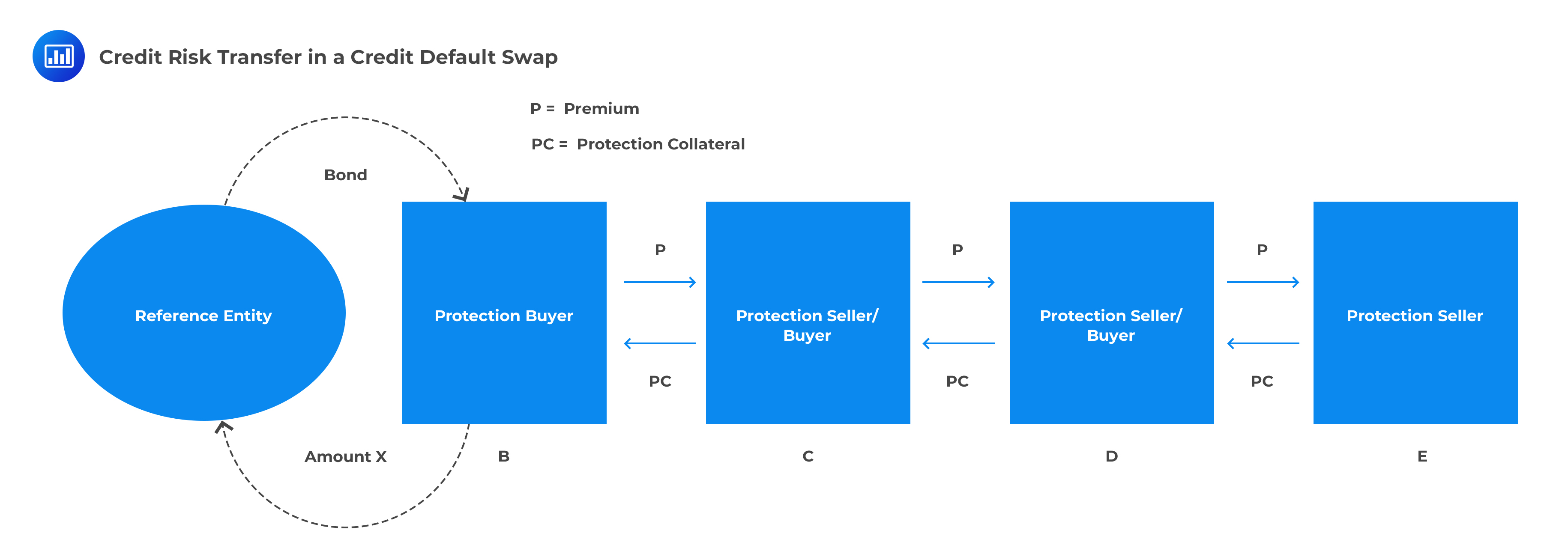
Swaps are also subject to the counterparty's credit risk: the chance that the other party in the contract will default on its responsibility. This risk has been partially mitigated since the financial crisis, with a large portion of swap contacts now clearing through central counterparties (CCPs).One of the risks of a credit default swap is that the buyer may default on the contract, thereby denying the seller the expected revenue. The seller transfers the CDS to another party as a form of protection against risk, but it may lead to default.The advantages of swaps are as follows: 1) Swap is generally cheaper. There is no upfront premium and it reduces transactions costs. 2) Swap can be used to hedge risk, and long time period hedge is possible.
How do swaps benefit investors : By entering into a swap agreement, investors can exchange fixed-rate interest payments for floating-rate interest payments or vice versa. This enables them to hedge against adverse interest rate movements, ensuring more predictable cash flows and minimizing potential losses.
Which is a disadvantage of swaps
Disadvantages of a Swap
If a swap is canceled early, there is a fee incurred. A swap is an illiquid financial instrument, and it is subject to default risk.
Do swaps have basis risk : Basis risk on a floating-to-fixed rate swap is the potential exposure of the issuer to the difference between the floating rate on the variable rate demand obligation bonds and the floating rate received from the swap counterparty.
This risk has been partially mitigated since the financial crisis, with a large portion of swap contacts now clearing through central counterparties (CCPs). However, the risk is still higher than that of investing in a “risk-free” U.S. Treasury bond.
Offers an economic benefit – Executing a swap will generate non-interest income for the bank. This fee income is recognized in the period the swap is executed and is NOT amortized over the life of the loan.
How do banks benefit from swaps
The bank's profit is the difference between the higher fixed rate the bank receives from the customer and the lower fixed rate it pays to the market on its hedge. The bank looks in the wholesale swap market to determine what rate it can pay on a swap to hedge itself.The benefit of a swap is that it helps investors to hedge their risk. Had the interest rates gone up to 8%, then Party A would be expected to pay party B a net of 2%. The downside of the swap contract is the investor could lose a lot of money.Advantages of using commodity swaps include flexibility in managing commodity exposure, customization to meet specific needs, and lower transaction costs compared to futures. Disadvantages include counterparty risk, complexity and lack of transparency, and limited liquidity in the market.
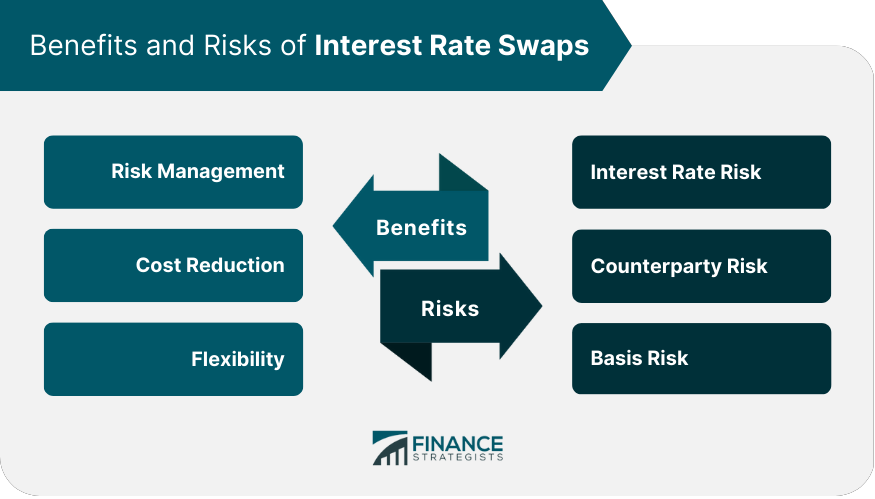
Interest rate swaps offer benefits such as risk management, cost reduction, and flexibility. However, they also expose parties to risks such as interest rate risk, counterparty risk, and basis risk.
Why are swap spreads negative : Negative Swap Spreads
Another explanation for the 30-year negative rate is that traders have reduced their holdings of long-term interest-rate assets and, therefore, require less compensation for exposure to fixed-term swap rates.
What are the pros and cons of swap loans : Interest rate swaps offer benefits such as risk management, cost reduction, and flexibility. However, they also expose parties to risks such as interest rate risk, counterparty risk, and basis risk.
What is the disadvantage of swap free
The advantage is that you will not be charged money for the trades with negative swaps. The disadvantage is that you will not be paid money for the trades with positive swaps.
By helping in hostile takeovers, a share swap can be a nightmare for the target firm's management. They can be acquired anytime if they hold on to their management. Thus, economists often criticize Share swaps for being capitalist friendly swaps for being capitalist-friendly and favoring the rich.The main reason why your swap might have failed is likely to be slippage. When you perform a swap, you are agreeing to a price quote. If the price of the swap goes outside of the allowed slippage set (typically 2-3%), it will fail, in order to prevent you from seeing a huge variance in value when completed.
Why are swap rates negative : Negative swap spreads have been alternately attributed to large increases in end-user demand for long-dated swaps or to rising balance-sheet costs at the financial intermediaries that supply swaps.