Antwort What are the 8 major childhood traumas? Weitere Antworten – What are the symptoms of childhood trauma in adulthood

Signs of childhood trauma
- Reliving the event (flashbacks or nightmares)
- Avoidance.
- Anxiety.
- Depression.
- Anger.
- Problems with trust.
- Self-destructive or risky behaviors.
- Withdrawal.
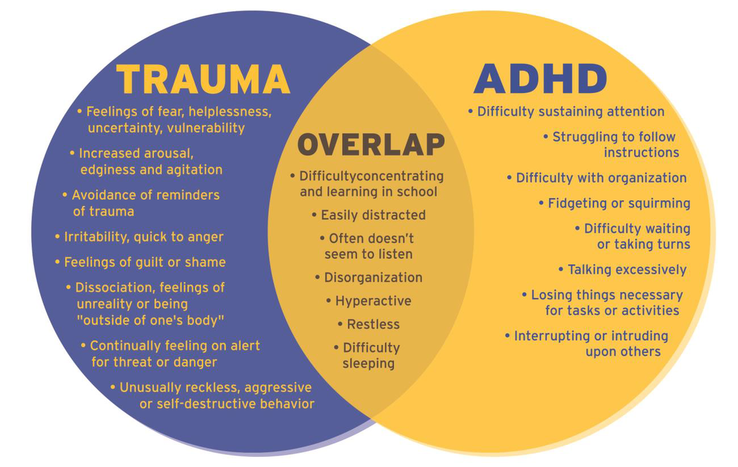
Re-experiencing or reliving unwanted memories as flashbacks or nightmares. Hyper-arousal: problems with sleep, irritability, anger, anxiety, hyper-alertness and an exaggerated startle response. Hypo-arousal: feeling numb or cut off, feeling detached from others, dissociating, or feeling flat or empty.To determine whether you or a loved one may have PTSD that stems from childhood trauma, the following are some of the more common symptoms: Reliving the event over in your mind or nightmares. Becoming upset when there's a reminder of the event. Intense and ongoing fear, sadness, and helplessness.

What are the symptoms of developmental trauma : Symptoms include behaviors such as habitual self-harm, extreme distrust, and verbal or physical aggression toward others.
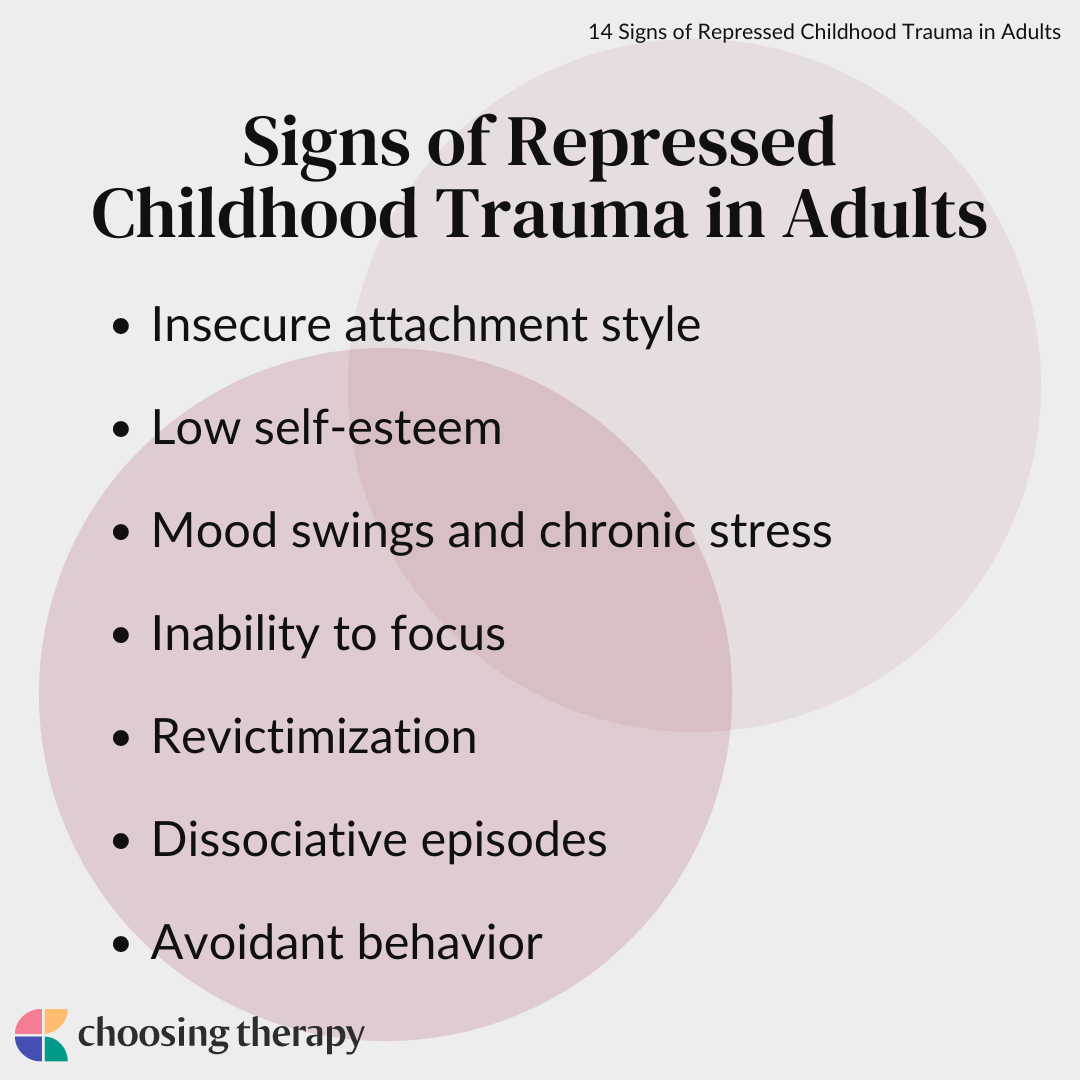
What does unhealed childhood trauma look like in adults
The effects of unhealed childhood wounds are widespread and can manifest in different ways in our adult lives. Common issues that can arise include low self-esteem, difficulty forming relationships, addiction, depression, and anxiety.
Does childhood trauma get worse with age : While flashbacks can occur in the old and young, age exacerbates these symptoms due to increased memory loss and alterations regarding context of past trauma. Age also affects the impact of physical symptoms on your body.
Let's look at the 17 most common symptoms of PTSD.
- Intrusive Thoughts.
- Nightmares.
- Avoiding Reminders of the Event.
- Memory Loss.
- Negative Thoughts About Self and the World.
- Self-Isolation; Feeling Distant.
- Anger and Irritability.
- Reduced Interest in Favorite Activities.
People can forget they were exposed to traumatic events because the brain does not process and store trauma memories like regular experiences. However, the trauma can remain in the subconscious mind for years without victims realizing they have PTSD.
How does a traumatized child act
Such a child may seem “spacey”, detached, distant, or out of touch with reality. Complexly traumatized children are more likely to engage in high-risk behaviors, such as self-harm, unsafe sexual practices, and excessive risk-taking such as operating a vehicle at high speeds.Traumatic reactions can include a variety of responses, such as intense and ongoing emotional upset, depressive symptoms or anxiety, behavioral changes, difficulties with self-regulation, problems relating to others or forming attachments, regression or loss of previously acquired skills, attention and academic …Children struggle to interpret complex events, contexts, and emotions, leaving them vulnerable to wounds that can affect them throughout their lives. However, healing from childhood trauma is possible through honesty, acceptance, and growth.
Retrospective studies have also found earlier abuse (before age 5 18, before age 12 19,20,21, or before age 17 22) or trauma (between 4–6 23 and before age 12 19,20) particularly elevates risk for depressive symptoms and major depressive disorder.
Is it too late to heal from childhood trauma : Adults who experienced childhood trauma may have a higher risk of mental health conditions and certain physical health conditions. They may also have difficulty maintaining relationships with others. It is never too late for a person to receive help for childhood trauma.
What are 100% PTSD symptoms : Finally, a 100 percent evaluation is warranted where there is total occupational and social impairment, due to such symptoms as: gross impairment in thought processes or communication; persistent delusions or hallucinations; grossly inappropriate behavior; persistent danger of hurting self or others; intermittent …
What are the 20 core PTSD symptoms
Symptoms of PTSD in Adults
- Recurring upsetting memories.
- Angry outbursts.
- Substance abuse.
- Distancing oneself from loved ones.
- Reckless or self-destructive behaviors.
- Lack of interest in favorite activities.
- Avoidance of potential triggers (certain people, events, and situations)
- Violent behavior or destruction of property.
In his 2014 book “The Body Keeps the Score,” trauma expert Bessel van der Kolk, MD, talks about how trauma affects not just our minds but our bodies, too. The body can remember trauma even if we're unaware of it. With the right support, healing is possible.Most people who go through traumatic events may have temporary difficulty adjusting and coping, but with time and good self-care, they usually get better. If the symptoms get worse, last for months or even years, and interfere with your day-to-day functioning, you may have PTSD.
At what age is trauma most impactful : Retrospective studies have also found earlier abuse (before age 5 18, before age 12 19,20,21, or before age 17 22) or trauma (between 4–6 23 and before age 12 19,20) particularly elevates risk for depressive symptoms and major depressive disorder.