Antwort What are the 4 steps of real time PCR? Weitere Antworten – What are the 4 phases of real-time PCR
The curve can be broken into four different phases: the linear ground, early exponential, log-linear, and plateau phases. Data gathered from these phases are important for calculating background signal, cycle threshold (Ct), and amplification efficiency.Real-time PCR steps
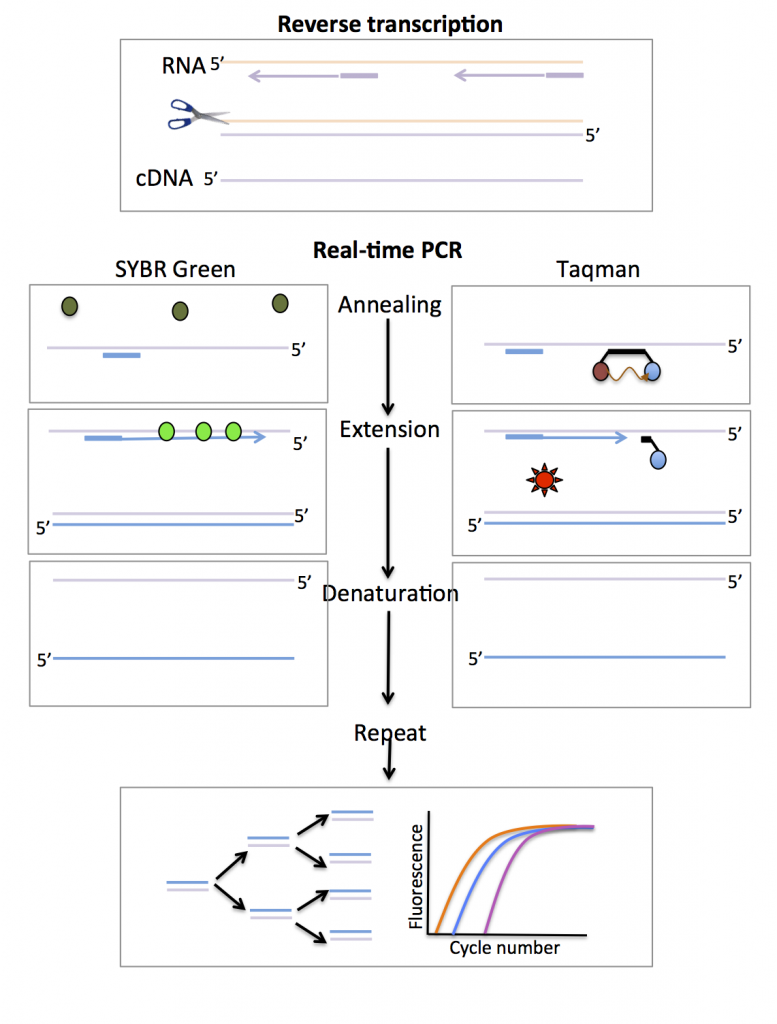
The first step in a real-time PCR reaction is the conversion of RNA to complementary DNA (cDNA) – this process is known as reverse transcription (Figure 1). The next step uses fluorescent reporters and a PCR reaction to amplify and detect specific genes (Figure 1).RT-PCR Protocol
- Experiment process.
- (1) Primer design. Design and synthesize the primers of the target gene.
- (2) RNA extraction.
- (3) Reverse transcription(RNA→cDNA)
- (4) Real-time PCR.
- (5) Result analysis.
- The factors affecting Real-time PCR results.
What are the 3 real-time PCR steps also used in PCR : Three steps of PCR─denaturation, annealing, and extension─as shown in the first cycle, and the exponential amplification of target DNA with repeated cycling.
What are the 4 steps of PCR quizlet
- double-stranded DNA sample.
- heat to 95℃ – strands separated.
- add primers and reduce temp to 55℃ to allow primers to anneal.
- raise temp to 72℃ so DNA polymerase binds and extends primers using free nucleotides.
How many cycles are in real-time PCR : 40 cycles
Typically, in a qPCR experiment, there are 40 cycles (40 rounds of amplification). At the beginning of a PCR run, the amount of PCR product is low, indicating very little fluorescence since amplification is just beginning.
Quantitative PCR (qPCR), also called real-time PCR or quantitative real-time PCR, is a PCR-based technique that couples amplification of a target DNA sequence with quantification of the concentration of that DNA species in the reaction.
Reverse transcription (RT)-PCR is used to amplify RNA targets. The RNA template is converted into complementary (c)DNA by the enzyme reverse transcriptase. The cDNA serves later as a template for exponential amplification using PCR. RT-PCR can be undertaken in one or two steps.
What is the 2 step RT-PCR procedure
Two-step RT-PCR entails two separate reactions, beginning with first-strand cDNA synthesis (RT), followed by amplification of a portion of the resulting cDNA by PCR in a separate tube. Therefore, two-step RT-PCR is useful for detecting multiple genes in a single RNA sample.PCR is based on three simple steps required for any DNA synthesis reaction: (1) denaturation of the template into single strands; (2) annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis; and (3) extension of the new DNA strands from the primers.The three steps are repeated for multiple cycles, with each cycle doubling the amount of DNA in the sample. The number of cycles is determined by the amount of target DNA in the initial sample and the sensitivity required for the experiment.
For efficient endpoint PCR with fast and reliable results, here are five key steps to consider:
- Step 1DNA isolation.
- Step 2Primer design.
- Step 3Enzyme selection.
- Step 4Thermal cycling.
- Step 5Amplicon analysis.
What are the stages of PCR quizlet :
- PCR. Polymerase chain reaction.
- Three steps. Denaturation.
- Denaturation. 94 c for 30 sec separates DNA from being double stranded to single stranded.
- Primer annealing. 55 c for 45 sec oligonucleotide primers are able to bind on DNA strands.
- Primer extension. 72 c for 2 min uses thermophiles.
- Paul berg. Discovered cloning.
Why 40 cycles for qPCR : The number of reaction cycles, 40 in most cases, means that the reagents become exhausted and additional amplification slows or stops, hence the term 'end-point' PCR. The DNA of interest, or target DNA, might be a gene identifying Streptococcus equi subsp.
What is the difference between qPCR and RT-PCR
qPCR or quantitative PCR is also known as real-time PCR. qPCR is used to quantify the nucleic acids. The amplification of the DNA molecule can be monitored during the PCR, i.e. in real time. RT-PCR is referred to as a reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.
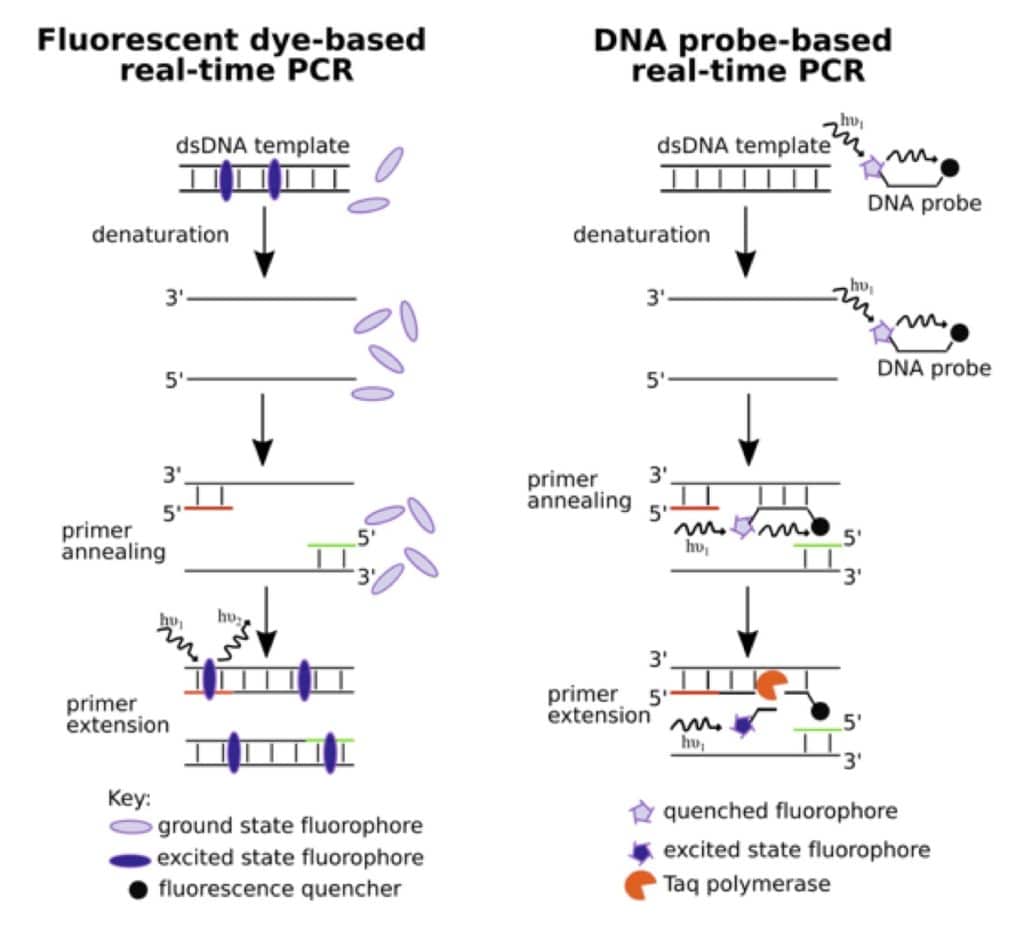
RT-PCR as a relatively simple, inexpensive, extremely sensitive and specific tool to determine the expression level of target genes. Real-time PCR is a quantitative method for determining copy number of PCR templates, such as DNA or cDNA, and consists of two types: probe-based and intercalator-based.Compared to other available virus isolation methods, real time RT–PCR is significantly faster and has a lower potential for contamination or errors, as the entire process can be carried out within a closed tube. It continues to be the most accurate method available for the detection of the COVID-19 virus.
What is RT-PCR in simple words : (Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR) is a major development of PCR technology that enables reliable detection and measurement of products generated during each cycle of PCR process.