Antwort What are the 4 concepts of bioethics? Weitere Antworten – What are the 4 main principles of bioethics
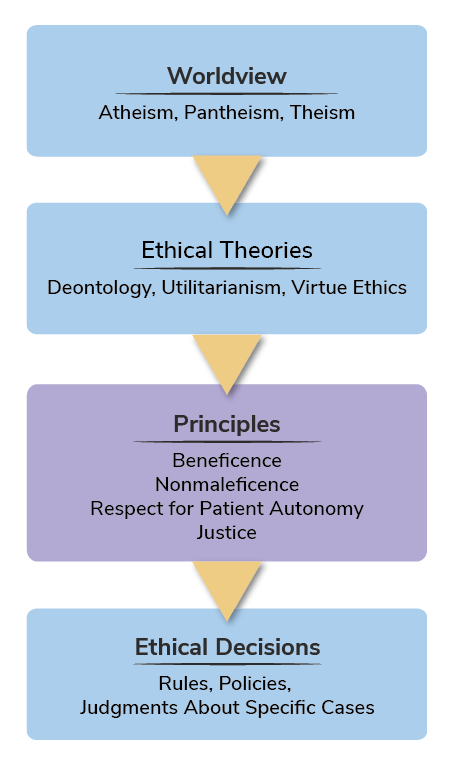
For several decades, a popular approach to understanding Western bioethics has involved the 4 principles. These principles—respect for autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, and justice—initially were described by Beauchamp and Childress in 1979.An overview of ethics and clinical ethics is presented in this review. The 4 main ethical principles, that is beneficence, nonmaleficence, autonomy, and justice, are defined and explained. Informed consent, truth-telling, and confidentiality spring from the principle of autonomy, and each of them is discussed.There are four principles of bioethics, which are all underwritten by a respect for the sanctity of life and human dignity. These four principles include autonomy, beneficence, justice, and non-maleficence.
What are the 4 basic concepts of medical ethics : Four Pillars of Medical Ethics
Beneficence (doing good) Non-maleficence (to do no harm) Autonomy (giving the patient the freedom to choose freely, where they are able) Justice (ensuring fairness)
What are the 4 pillars of ethics
Beneficence, nonmaleficence, autonomy, and justice constitute the 4 principles of ethics. The first 2 can be traced back to the time of Hippocrates “to help and do no harm,” while the latter 2 evolved later.
What are the 4 bioethical principles of Beauchamp : The four principles of Beauchamp and Childress – autonomy, non-maleficence, beneficence and justice – have been extremely influential in the field of medical ethics, and are fundamental for understanding the current approach to ethical assessment in health care.
Doing nothing (an omission), when one could or should have done something, can be deemed just as unethical as doing something (an act). With these basic concepts in mind, let's look at how some ethical considerations could be considered under the classic four 'Ps' of product, price, place and promotion.
The four principles (or principles) of medical ethics are defined as:
- Autonomy – respect for the patient's right to self-determination.
- Beneficence – the duty to 'do good'
- Non-Maleficence – the duty to 'not do bad'
- Justice – to treat all people equally and equitably.
What are the four basic categories of ethics
Four broad categories of ethical theory include deontology, utilitarianism, rights, and virtues.The 4 basic ethical principles that apply to forensic activities are respect for autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, and justice.Nonmaleficence (do no harm) Obligation not to inflict harm intentionally; In medical ethics, the physician's guiding maxim is “First, do no harm.” Beneficence (do good) Provide benefits to persons and contribute to their welfare. Refers to an action done for the benefit of others.
The model involves four ethical levels: conduct level, fair level, integrity level and avoidable harm level.
What is the most basic foundation principle of bioethics : The principles of bioethics
- Principle of autonomy. These are the rights of an individual to self-determination and the respect for their ability to make informed decisions about personal matters in freedom.
- Principle of beneficence.
- Principle of non-maleficence.
- Principle of justice.
What is an example of a non-maleficence : For example, if a diabetic patient asked a healthcare professional for a coke and the healthcare professional denied the request in order to prevent the patient from drinking something that could harm them, that would be an act of nonmaleficence.
What is the golden rule of bioethics
Four commonly accepted principles of health care ethics, excerpted from Beauchamp and Childress (2008), include the: Principle of respect for autonomy, Principle of nonmaleficence, Principle of beneficence, and.
Beneficence in nursing relates to ensuring that the patient's best interest is considered, regardless of the nurse's personal opinion. Examples of beneficence in nursing include providing comfort to a dying patient or assisting with tasks a patient cannot perform independently.Beneficence means performing a deed that benefits someone, while nonmaleficence means refraining from doing something that harms or injures someone. Feeding people at a soup kitchen is an example of beneficence. Preventing a patient from taking a harmful medication is an example of nonmaleficence.
Which bioethical principle is the most important : Principle of non-maleficence
Principle of non-maleficence
It is embodied in the phrase "first, do no harm" — from the Latin, primum non nocere —. Not harming the patient, which is part of the Hippocratic Oath, is considered to be of the highest importance.