Antwort What are the 3 types of PCR? Weitere Antworten – What are the three main types of PCR
Assembly PCR – longer DNA fragments are aplified by using overlapping primers. Asymmetric PCR – only one strand of the target DNA is amplified. In situ PCR – PCR that takes place in cells, or in fixed tissue on a slide.Many types of PCR process with slight modifications can be used to produce better results such as multiplex-PCR, RT-PCR, Nested PCR,inverse PCR, colony PCR, asymmetric PCR helicase PCR, ligation-mediated PCR etc5.qPCR or quantitative PCR is also known as real-time PCR. qPCR is used to quantify the nucleic acids. The amplification of the DNA molecule can be monitored during the PCR, i.e. in real time. RT-PCR is referred to as a reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.
What is the difference between conventional PCR and RT-PCR : Although both conventional PCR and Real-time PCR (RT-PCR) follow a similar procedure, there are many advantages to RT-PCR including the following: The ability to monitor the progress of the PCR reaction (amplification) as it occurs in real time.
What are the 3 PCR steps
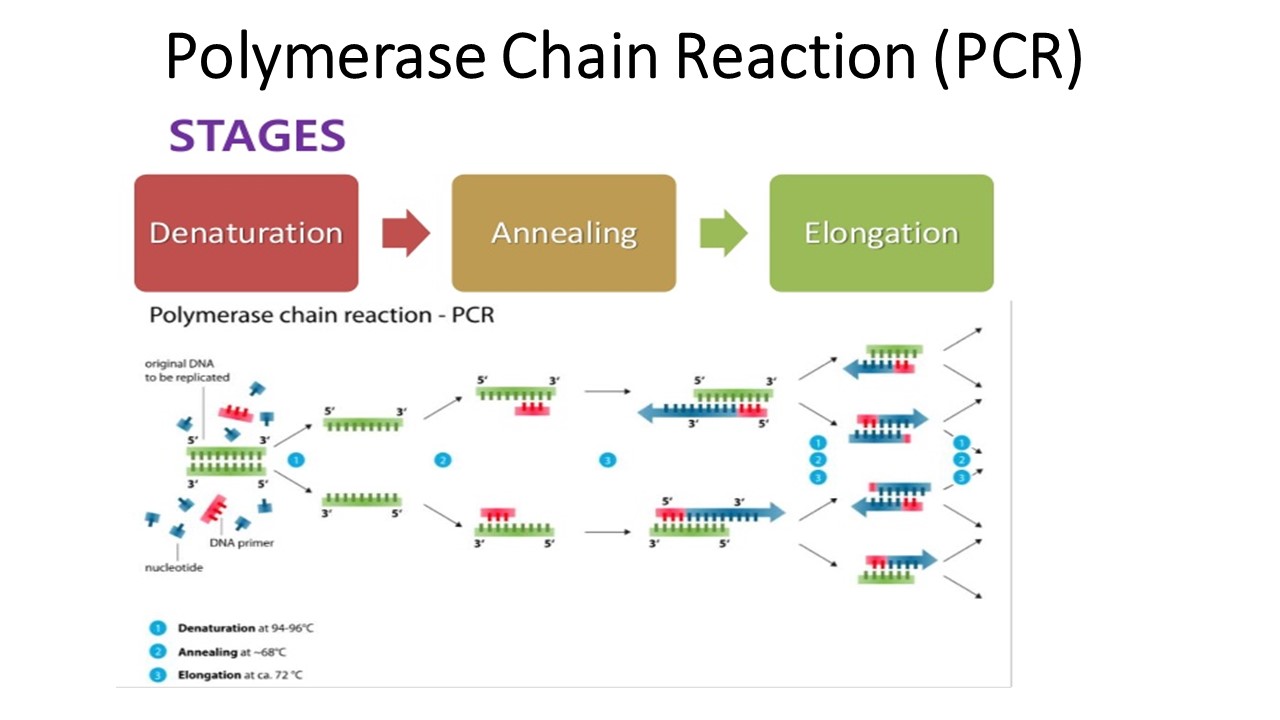
PCR is based on three simple steps required for any DNA synthesis reaction: (1) denaturation of the template into single strands; (2) annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis; and (3) extension of the new DNA strands from the primers.
What is PCR and its type : What is PCR PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is a technique used in a lab to make millions of copies in a different section of DNA. It was developed in 1980 by American biochemist “Kary Mullis”.
A simple PCR reaction consists of target DNA, a set of synthetic oligonucleotide primers that flank the target DNA sequence, a thermostable DNA polymerase (usually Taq polymerase), and nucleotides. The three steps to each amplification cycle include denaturation, annealing and extension.
qPCR is an established technique for gene analysis used in a broad range of applications. qPCR measures amplification as it occurs, whereas endpoint, conventional or traditional PCR collects results after each reaction is complete.
Is digital PCR better than qPCR
dPCR is recommended for analysis of copy number variation, since it can accurately detect copy changes with fewer replicates than qPCR. With qPCR, as the difference between copy numbers decreases, the number of replicates required increases rapidly.The rapid test can't detect small amounts of the virus or asymptomatic cases as accurately as the PCR test can,” Heather said. So how accurate are home COVID-19 tests The rapid test is less accurate and there is a greater chance for a false negative, not a false positive.RT-PCR tests are the most accurate of the three, and typically do not need to be repeated.
The three steps are repeated for multiple cycles, with each cycle doubling the amount of DNA in the sample. The number of cycles is determined by the amount of target DNA in the initial sample and the sensitivity required for the experiment.
What are the 3 real time PCR steps also used in PCR : Three steps of PCR─denaturation, annealing, and extension─as shown in the first cycle, and the exponential amplification of target DNA with repeated cycling.
What type of testing is PCR : Molecular tests, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and other nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) tests, which detect genetic material called RNA from the virus. Antigen tests, often referred to as rapid tests or, for some, at-home or self tests, which detect proteins called antigens from the virus.
What is the PCR method
PCR is a very sensitive technique that allows rapid amplification of a specific segment of DNA. PCR makes billions of copies of a specific DNA fragment or gene, which allows detection and identification of gene sequences using visual techniques based on size and charge.
PCR machine steps
- Step 1 – Denaturation. The solution contained in the tube is heated to at least 94°C (201.2°F) using a thermal cycler.
- Step 2 – Annealing.
- Step 3 – Extension.
- Step 4 – Analysis with Electrophoresis.
A standard Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is an in vitro method that allows a single, short region of a DNA molecule (single gene perhaps) to be copied multiple times by Taq Polymerase.
Is qPCR better than PCR : Both PCR and qPCR are polymerase chain reaction techniques used to amplify specific sections of DNA. The main difference between the two is that qPCR is a real-time method, while PCR is not. This means that with qPCR, you can monitor the amplification of your target DNA in real-time as it is happening.