Antwort What are main theories of motivation? Weitere Antworten – What are the five major theories of motivation
Let's get into five of the most common and frequently referenced theories.
- Maslow's hierarchy of needs.
- Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory (AKA dual-factor or two-factor theory)
- Vroom's expectancy theory.
- Reinforcement theory.
- Self-determination theory.
There are four major theories in the need-based category: Maslow's hierarchy of needs, ERG theory, Herzberg's dual factor theory, and McClelland's acquired needs theory.Top 3 Motivation Theories in Management
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs.
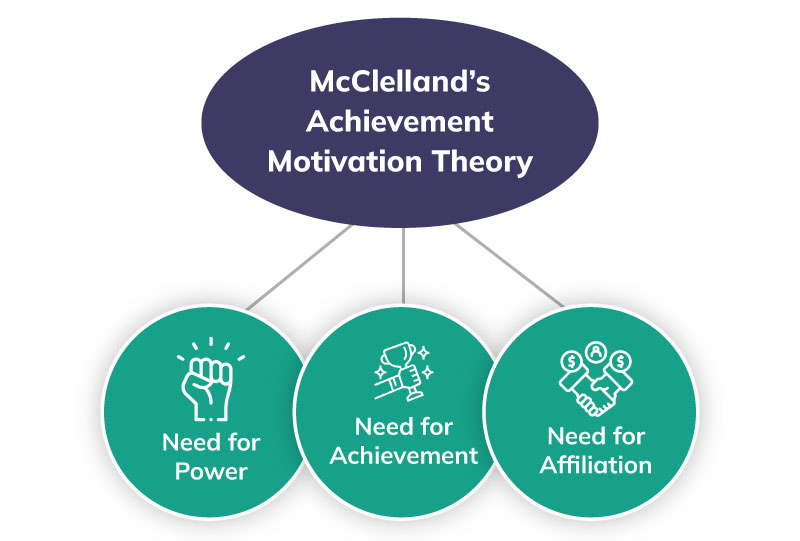
- McClelland's Three Needs Theory.
- Herzberg's Motivation Theory.
How many motivational theories are there : Four theories may be placed under this category: Maslow's hierarchy of needs, ERG theory, Herzberg's two-factor theory, and McClelland's acquired-needs theory.
What are the big five motivation theory
It is the most commonly accepted and used model of personality in academic research and psychology. The five personality traits are openness to experience, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism.
What is the 5 factor theory of motivation : The five major groups of traits called factors in the five factor model as openness to experience, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism.
Daniel Goleman, who developed the concept of emotional intelligence in the mid '90s, identified four elements that make up motivation: our personal drive to improve and achieve, commitment to our goals, initiative, or readiness to act on opportunities, as well as optimism, and resilience.
The four-drive theory of motivation was developed by Paul Lawrence and Nitin Nohria in their 2002 book Driven: How Human Nature Shapes Our Choices. It consists of four parts: the drive to acquire and achieve, the drive to bond and belong, the drive to challenge and comprehend, and the drive to define and defend.
What are the 3 biological theories of motivation
Biological theories of motivation include: Instinct Theory, Arousal Theory, and Drive Reduction Theory. Motivation is the underlying drive that prompts a behavior and can be categorized as either intrinsic (derived within oneself) or extrinsic (derived from external rewards or punishments).McClelland's human motives model distinguishes three major motives: the need for achievement, affiliation, and power.Process theories of motivation try to explain why behaviors are initiated. These theories focus on the mechanism by which we choose a target, and the effort that we exert to “hit” the target. There are four major process theories: (1) operant conditioning, (2) equity, (3) goal, and (4) expectancy.
The five major psychological perspectives are the Behavioral, Cognitive, Humanistic, Psychodynamic, and Biological viewpoints.
What are the 5 C’s of motivation : The 5 Cs – Curiosity, Commitment, Consistency, Clarity, and Collaboration – form a framework that can guide individuals toward achieving their goals and aspirations. Let's delve into each of these vital components and understand how they contribute to success.
What are the 4 major motivating factors : These four factors are:
- leadership style.
- reward system.
- organizational climate.
- structure of the work.
What are the 3 process based theories of motivation
In this section we will discuss three process-based theories of motivation: equity theory, expectancy theory, and reinforcement theory.
There are three major approaches to employee motivation that are need-based: Maslow's hierarchy of needs, McClelland's need theory, and Herzberg's two-factor theory. These theories are focused on the psychological needs that motivate employees and the behaviors that they choose.People are motivated in three ways: material, social and ideological.
What are the 5 pillars of motivation : Probably here is the place to mention the five pillars of a motivating teacher according to Dr. Wlodkowski: expertise, enthusiasm, empathy, clarity, and cultural responsiveness.