Antwort Should I use 802.11 n or G? Weitere Antworten – Which is better 802.11 n or g
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/wireless-standards-802-11a-802-11b-g-n-and-802-11ac-816553-36294250342e404eabe7dc94bc7a40f9.png)
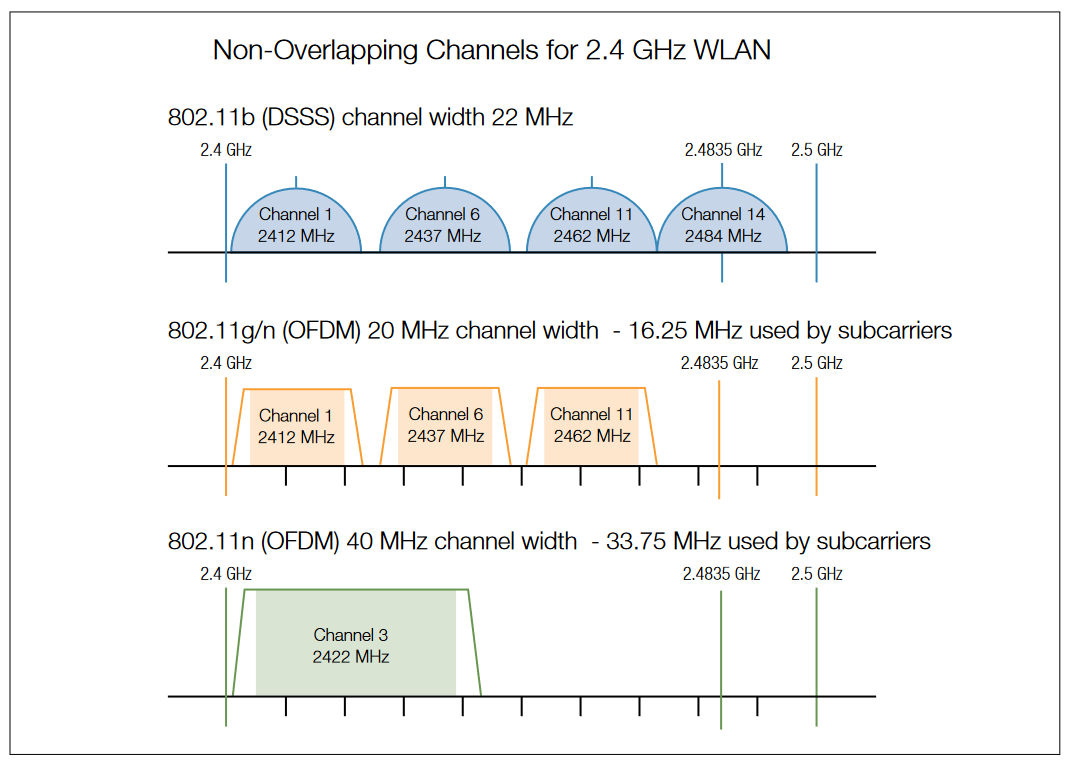
802.11b has a maximum theoretical transfer speed of 11Mbps, 802.11g has a maximum theoretical speed of 54Mbps and 802.11n has a maximum theoretical speed of up to 300Mbps (When configured correctly). If you or anyone else is still having problems then here's the answer: All WIFIs are backward compatible.Many home networks today still operate using 802.11g routers. At 54 Mbps, these routers can keep up with most high-speed home internet connections, including basic video streaming and online gaming. G-compatible routers can be found inexpensively through both retail and secondhand sales outlets.When 802.11n only mode is selected, only 802.11n wireless stations can connect to the modem router. It is strongly recommended that you select 802.11bgn mixed, and all of 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n wireless stations can connect to the modem router.
Which 802.11 mode is best : Because 802.11ac is backward compatible with 802.11n and most 802.11ac routers are dual-band (2.4 & 5 GHz) in practice, for most of us this all boils down to: 802.11ac vs 802.11ax. When you consider cost and how common support for the two standards is, 802.11ac is often the right answer today.
Is 802.11 n good for gaming
Using 802.11n as the wireless mode seems good with high speeds but for gaming not so much, ping would always spike up when someone opens up a youtube video or download somethings. 802.11g on the other hand, gives a better and stable ping for gaming. downside is the limited speed.
Is 802.11n outdated : While these features may have been an upgrade from Wireless-G, Wireless-N is mostly phased out. Luckily, new routers and wireless standards will still support Wireless-N and older wireless standards. Looking for a router that supports your Wireless-N devices
Despite its age, 802.11n is still the most popular Wi-Fi standard in use today due to the numerous low-end devices using it. Also, many low-cost smart home gadgets, such as wireless cameras and lightbulbs, still only use 2.4 GHz.
About 108 Mbps Speed
However, these products use proprietary extensions to the 802.11g standard to achieve higher performance. If a 108 Mbps product is connected to a standard 802.11g device, its performance falls back to the 54 Mbps maximum rate.
Why is my 802.11 n so slow
Most 802.11n products will knock your throughput down by up to 80% if you use WEP or WPA/TKIP security. The reason is that the 802.11n spec states that the high throughput rates (link rates above 54 Mbps) can't be enabled if either of those outdated security methods are used.Most 802.11n products will knock your throughput down by up to 80% if you use WEP or WPA/TKIP security. The reason is that the 802.11n spec states that the high throughput rates (link rates above 54 Mbps) can't be enabled if either of those outdated security methods are used.IEEE 802.11g-2003 or 802.11g is an amendment to the IEEE 802.11 specification that operates in the 2.4 GHz microwave band. The standard has extended link rate to up to 54 Mbit/s using the same 20 MHz bandwidth as 802.11b uses to achieve 11 Mbit/s.
An 802.11n Wi-Fi network connection supports up to 300 Mbps of rated theoretical bandwidth under best-case conditions. However, an 802.11n link sometimes operates at slower speeds like 150 Mbps and below.
Is 802.11n fast enough : An 802.11n Wi-Fi network connection supports up to 300 Mbps of rated theoretical bandwidth under best-case conditions. However, an 802.11n link sometimes operates at slower speeds like 150 Mbps and below.
Is 802.11 n outdated : While these features may have been an upgrade from Wireless-G, Wireless-N is mostly phased out. Luckily, new routers and wireless standards will still support Wireless-N and older wireless standards. Looking for a router that supports your Wireless-N devices
Is 802.11g slow
About 108 Mbps Speed
However, these products use proprietary extensions to the 802.11g standard to achieve higher performance. If a 108 Mbps product is connected to a standard 802.11g device, its performance falls back to the 54 Mbps maximum rate.


