Antwort Is USB full-duplex or half-duplex? Weitere Antworten – Is USB full duplex
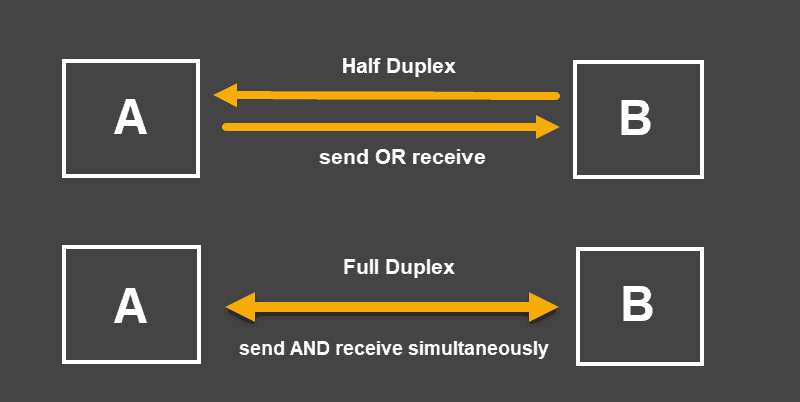
The USB 3.0 standard — also known as SuperSpeed USB — offers a full-duplex transfer mode, while earlier versions of USB offered only the half-duplex transfer mode. Ethernet was originally a half-duplex channel.USB 2.0. USB 2.0 was released in April 2000, adding a higher maximum signaling rate of 480 Mbit/s (maximum theoretical data throughput 53 MByte/s) named High Speed or High Bandwidth, in addition to the USB 1.x Full Speed signaling rate of 12 Mbit/s (maximum theoretical data throughput 1.2 MByte/s).The USB 2.0 specification allows Hosts to deliver 5V at 500 mA, for a total power output of 2.5 watts. USB 3.0 and 3.1 allow 5V at 900 mA (4.5W).
Is USB 3.0 half-duplex : USB 3.0 has transmission speeds of up to 5 Gbit/s or 5000 Mbit/s, about ten times faster than USB 2.0 (0.48 Gbit/s) even without considering that USB 3.0 is full duplex whereas USB 2.0 is half duplex. This gives USB 3.0 a potential total bidirectional bandwidth twenty times greater than USB 2.0.
Why is USB half-duplex
USB has deferential protocol for communication. Basically, for full duplex communication in differential fashion, minimum 1 pair for Tx data line and minimum 1 pair for Rx data lines are must. While USB has only 1 pair of data lines (D+, D-), so USB would be half duplex protocol.
Is USB 2.0 or 3.2 better : USB 2.0 –A widely used standard that offers a maximum transfer speed of 480 Mbps. USB 3.0/3.1/3.2 –Offer transfer speeds of up to 5 Gbps (USB 3.0), 10 Gbps (USB 3.1), and 20 Gbps (USB 3.2). These are backward compatible with USB 2.0 devices but might reduce the overall transfer speed when a USB 2.0 device is connected.
Currently, a standard USB 2.0 connection offers up to 2.5W of power (which is just about enough to charge your phone at a snail's pace), while the USB PD standard supported by USB-C can deliver a massive 100W of power, which is more than enough to charge a laptop.
USB connectors were originally developed to deliver dc power and digital signals.
Can I plug USB-C into PD
The USB-C PD standard is compatible with the USB4 and USB Power Delivery 3.1 specifications. The USB-C PD specification defines how devices can use the USB-C connector to supply power and how these devices are identified and managed.Full-featured USB-C cables that implement USB 3.1 Gen 2 can provide 10 Gbit/s (full duplex) signalling rate. They are marked with a SuperSpeed USB 10 Gbps (previously marketed as SuperSpeed+) logo.Full-featured USB-C cables that implement USB 3.1 Gen 2 can provide 10 Gbit/s (full duplex) signalling rate.
With the arrival of USB 3.2, the industry dominant USB-A connection was beginning to phase out in favor of USB-C. Since USB-C supports higher data transfer speeds and could charge other peripheral devices faster, it has naturally become the main USB connector in utilizing USB 3.2 Gen 2.
Can a 2.0 USB work on 3.2 port : USB 3.2 is completely backward compatible, but when utilized in a USB 2.0 connection, data speeds and power utilization are limited to USB 2.0 levels. USB 2.0 is compatible with USB 3.2 ports, except for USB 3.2 type-B connectors which utilize a new design, but again only utilize USB 2.0 functionality.
Is USB 3.2 Gen 2 Type-C the same as USB-C : Confusion often arises when discussing the relationship between USB Type C connectors and say for example USB 3.2 Gen 2 (previously USB 3.1 Gen 2). The USB Type C standard defines only the physical connector while the USB 3.2 standard applies only to the electrical signal.
How do I know if my USB is A or C
USB-C ports are oval in shape and USB-C cables can fit in either way; there isn't a “right side up” like there is with USB 2.0 and 3.0 cables. USB-A ports are rectangular and USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 cables have a “right side up” – cables only fit in one way.
USB-A connectors are only compatible with USB-A ports, so they are not reversible and can only be inserted in one way. On the other hand, USB-C (or "Type-C") is a smaller, oval-shaped connector that is reversible.That's why most electronic devices have a converter built into the plug. You may not realize it but every time you're charging a device such as your smartphone, the plug is actually converting AC power to DC.
Is USB-C PD bidirectional : First, USB-C is fully bi-directional. At the simplest level, this means that both ends of the cable are physically the same, so there is no distinction between host and receptor.