Antwort Is RT-PCR more sensitive than antigen? Weitere Antworten – Is PCR more sensitive than antigen
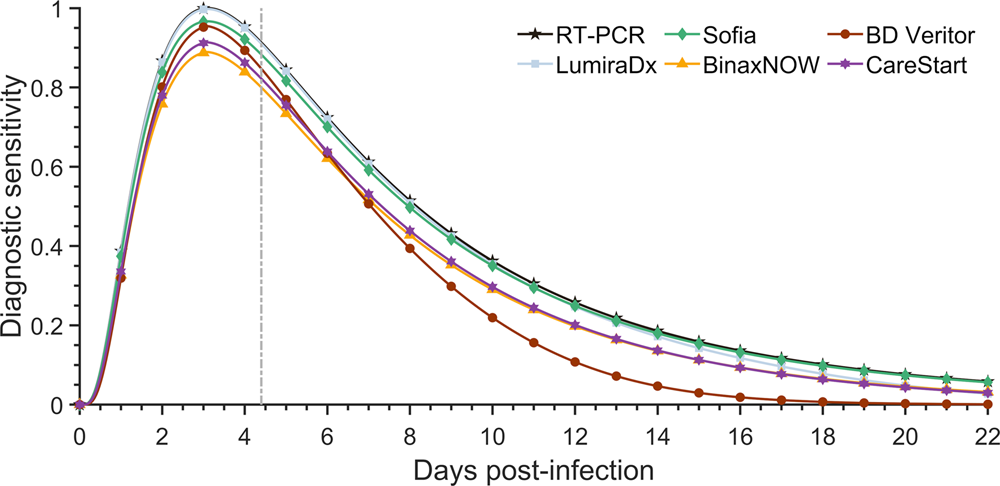
Antigen tests for SARS-CoV-2 are generally less sensitive than real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and other nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), which detect and amplify the presence of viral nucleic acid.RT-PCR tests are the most accurate of the three, and typically do not need to be repeated.The sensitivity of the rapid antigen test compared with the PCR test was 0.63 (95% CI: 0.53 to 0.73) and the specificity was 0.998 (95% CI: 0.995 to 1.000).
Is PCR an antigen detection : Molecular tests, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and other nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) tests, which detect genetic material called RNA from the virus. Antigen tests, often referred to as rapid tests or, for some, at-home or self tests, which detect proteins called antigens from the virus.
What is the difference between PCR and RT-PCR
PCR is a method used to amplify DNA from a small amount of DNA template. RT-PCR uses reverse transcription to produce a DNA template from an RNA source that can then be amplified.
Is PCR more sensitive than culture : Polymerase chain reaction is more sensitive than viral culture and antigen testing for the detection of respiratory viruses in adults with hematological cancer and pneumonia.
A systematic review, performed on pooled data for 8136 clinical specimens tested for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR, substantially confirmed results for different types of specimens: [29] specimens from the lower respiratory tract showed a positive rate of 71.3%; bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and saliva samples had the highest …
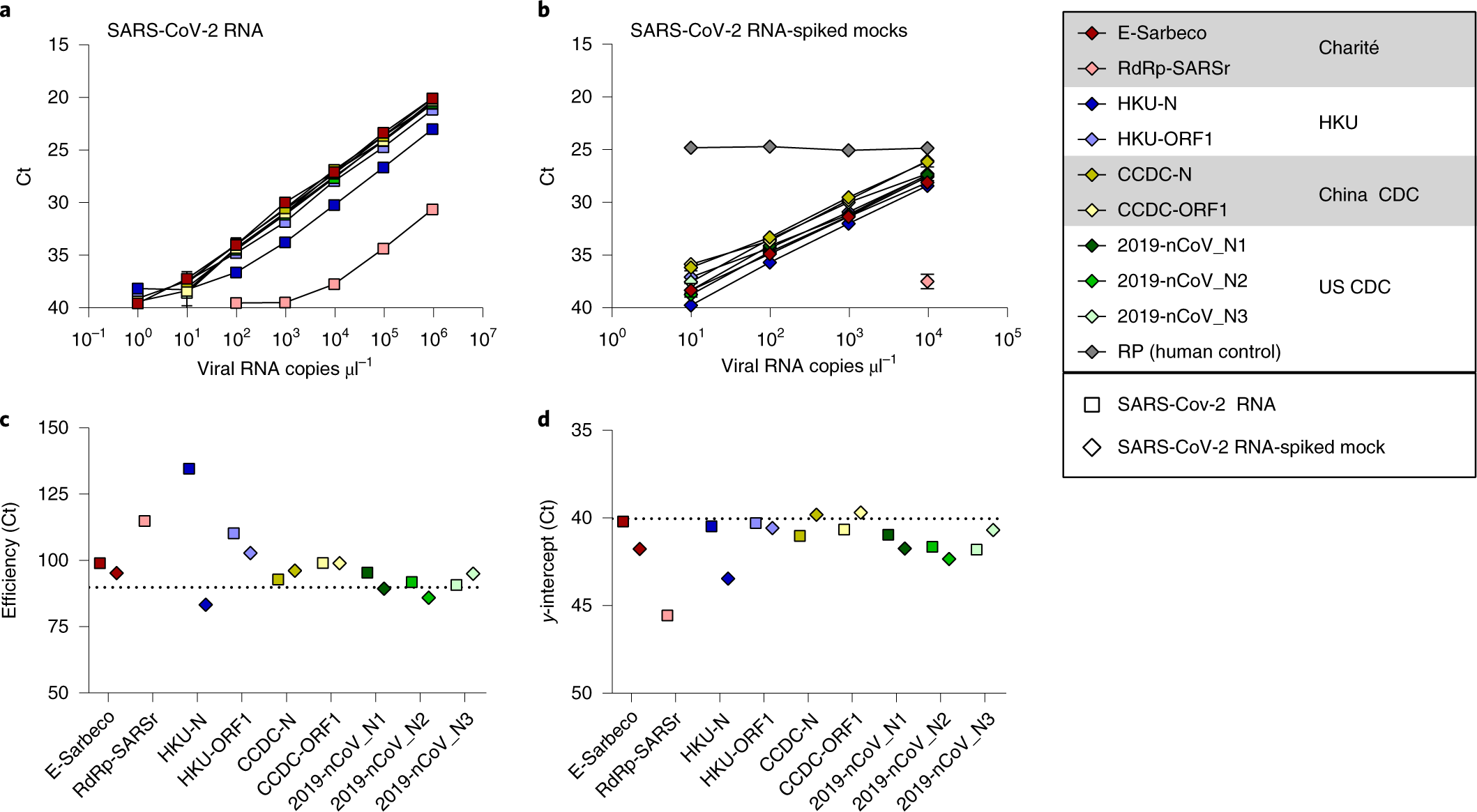
The analytic performance of PCR based tests is good, with most assays able to detect 500-5000 copies of viral RNA/mL1 near 100% of the time (analytical sensitivity) and most tests do not cross react with other viruses, so the analytical specificity is near 100% also.
What is the advantage of a molecular test like RT-PCR over a rapid antigen test
“Unlike the PCR test, the antigen test can only determine if you have an active virus in your body. The rapid test can't detect small amounts of the virus or asymptomatic cases as accurately as the PCR test can,” Heather said.PCR is a method used to amplify DNA from a small amount of DNA template. RT-PCR uses reverse transcription to produce a DNA template from an RNA source that can then be amplified.An antigen test is quicker but less reliable than a PCR test. In some cases, it may not detect the virus.
With more accurate results, PCR tests are the preferred way to go, but antigen tests work for rapid results, as well.
How sensitive is COVID RT-PCR : This systematic review and meta-analysis suggests that RT-PCR assays on nasopharyngeal specimens achieve a pooled sensitivity of 89% (95 % CI, 85.4 to 91.8%) for diagnosing SARS-CoV-2 infection.
What is the sensitivity of a PCR : The analytic performance of PCR based tests is good, with most assays able to detect 500-5000 copies of viral RNA/mL1 near 100% of the time (analytical sensitivity) and most tests do not cross react with other viruses, so the analytical specificity is near 100% also.
Is PCR more sensitive than Elisa
When both tests were compared on the basis of their analytical sensitivities, the maximum detection titer of the ELISA test using the PCEV as cutoff value was 1:320. The RT-PCR showed a higher analytical sensitivity of 1:10,240.
With respect to RT-PCR, the proposed criteria had 98.5% (95% confidence interval [95% CI] 97.5–99.5%) sensitivity, 70% (95% CI 65.8–74.2%) specificity, 85.5% (95% CI 83.4–87.7%) accuracy, PPV of 79.7% (95% CI 76.6–82.7%) and NPV of 97.6% (95% CI 95.9–99.2%).With more accurate results, PCR tests are the preferred way to go, but antigen tests work for rapid results, as well.
Which COVID test is more sensitive : PCR tests are far more sensitive than antigen tests and can pick up COVID-19 earlier and stay positive for longer. While they're considered the gold standard for a COVID-19 diagnosis, PCR tests are unnecessary for those who have already tested positive on an antigen test.