Antwort Is LAN half-duplex? Weitere Antworten – Is Ethernet full-duplex
In data networking, Ethernet hubs are half-duplex devices by nature, as they create a single shared channel of communication. Ethernet switches, on the other hand, can use a connection in either half- or full-duplex mode. Most networks are built around switches now, but hubs are still used as well.Using the same example of moving two 150Mb files, a 100Mbps symmetrical, full duplex switch will deliver both files in 1.5 seconds. A 100Mbps asymmetrical half duplex switch with a 70/30 split will take 7.14 seconds to deliver both files.Not only Wi-Fi cannot work as full-duplex, but also two or more devices cannot transmit or receive traffic simultaneously. Unlike 3G/4G, Wi-Fi uses unlicensed frequencies in the spectrum, which simply means you do not have to pay for using them.
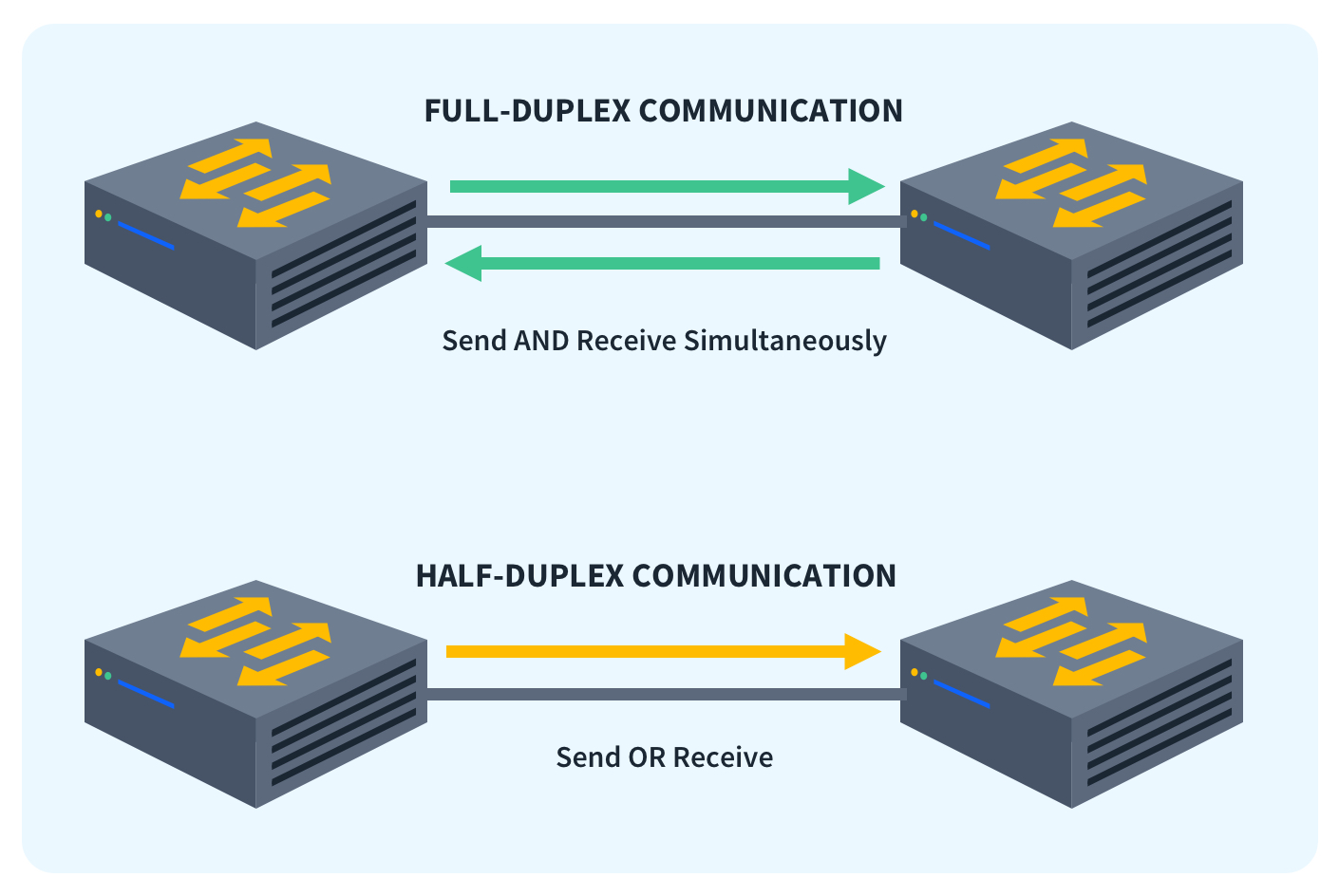
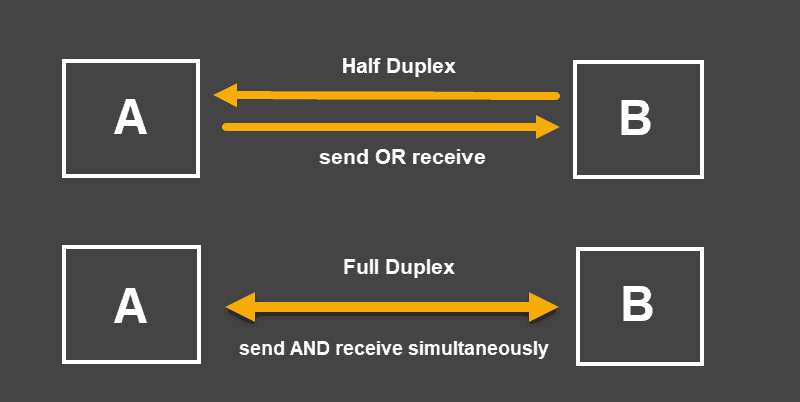
Is Ethernet simplex or duplex : In half-duplex, the device(s) (for example using Wi-Fi for connection) is transmitting or receiving at different times, never at the same time. There is also transmission overhead. In full duplex, such as over Ethernet, the device(s) is or can be transmitting and receiving at the same time.
Is half-duplex better
Full-duplex Ethernet does save time when compared to half-duplex because it alleviates collisions and frame retransmissions. Sending and receiving are separate functions, creating a system where there is full data capacity in each direction. In contrast, half-duplex can be used to conserve bandwidth.
What does 100 Mbps half-duplex mean : 100BASE-T (fast ethernet over 2 wire pairs) is full duplex, meaning 100Mbit per direction, simultaneously. It is possible to configure a 100Mbit network interface in half duplex, meaning that the total bandwidth available for send+receive is 100Mbit (as opposed to 200Mbit for full duplex)
Half-duplex devices can only transmit in one direction at one time. So although data can move in two directions, it cannot be at the same time. Both devices are capable of transmitting and receiving so when one device is sending, the other is receiving.
half duplex
99.9% of the time Wireless is half duplex. There are experiments that can result in a "full duplex" wireless network but that's all lab-based and not real-world. With Wireless the devices cannot send and receive simultaneously and they cannot sense collisions.
Is wifi half-duplex
99.9% of the time Wireless is half duplex. There are experiments that can result in a "full duplex" wireless network but that's all lab-based and not real-world. With Wireless the devices cannot send and receive simultaneously and they cannot sense collisions.An HTTP connection uses half-duplex communication; only one party can communicate at a time, and the server's message is always in response to a request from a client.All WiFi is half duplex. It's like push-to-talk radio. Each device can transmit or receive, but they can't do both at the same time. A rough rule of thumb is that when many devices are using WiFi at the same time, the data throughput is about half of the maximum data rate.
99.9% of the time Wireless is half duplex. There are experiments that can result in a "full duplex" wireless network but that's all lab-based and not real-world. With Wireless the devices cannot send and receive simultaneously and they cannot sense collisions.
Is 802.11 half or full duplex : The 802.11 family consists of a series of half-duplex over-the-air modulation techniques that use the same basic protocol.
Is Wi-Fi half-duplex : 99.9% of the time Wireless is half duplex. There are experiments that can result in a "full duplex" wireless network but that's all lab-based and not real-world. With Wireless the devices cannot send and receive simultaneously and they cannot sense collisions.
Is LTE half-duplex
This means that LTE-M can be deployed both in paired FDD bands and unpaired TDD bands (see Table 5.2 for a list of supported bands), and that both full-duplex and half-duplex device implementations are possible, allowing for trade-off between device complexity and performance.
Full duplex means that data flowing up to the internet runs at the same time as data down from the internet (using your computer as point of view) Most of the transport within the internet is full duplex, but there are links that are half duplex – which means UL request occurs, then down link response occurs after.Full duplex means that data flowing up to the internet runs at the same time as data down from the internet (using your computer as point of view) Most of the transport within the internet is full duplex, but there are links that are half duplex – which means UL request occurs, then down link response occurs after.
Is LTE half-duplex or full duplex : LTE can be either full duplex (meaning that transmitting and receiving can happen simulataneously), or half duplex (meaning that transmitting and receiving can happen, but not at the same time).