Antwort Is Internet a full-duplex? Weitere Antworten – Is internet full-duplex
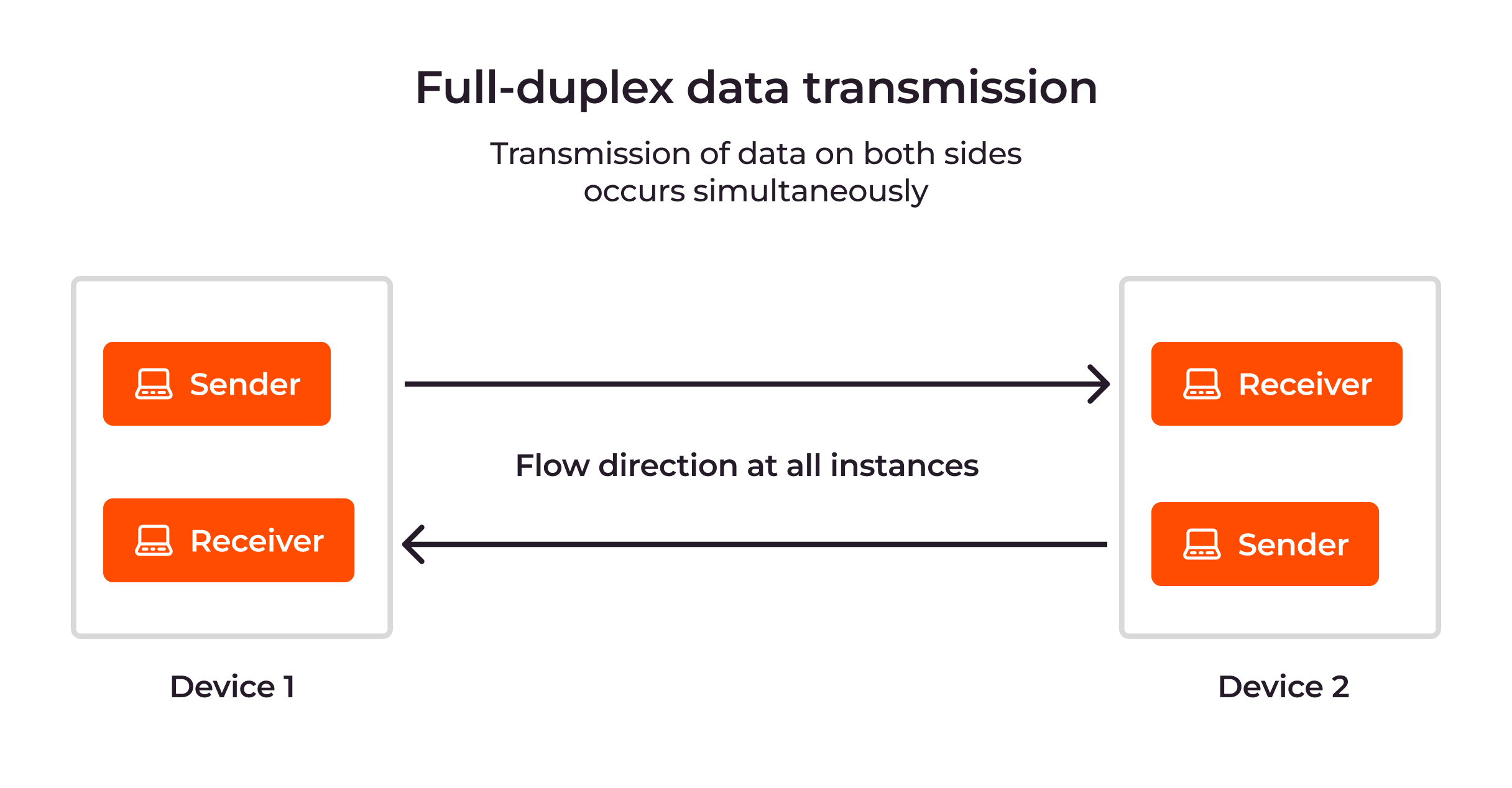
Full duplex means that data flowing up to the internet runs at the same time as data down from the internet (using your computer as point of view) Most of the transport within the internet is full duplex, but there are links that are half duplex – which means UL request occurs, then down link response occurs after.99.9% of the time Wireless is half duplex. There are experiments that can result in a "full duplex" wireless network but that's all lab-based and not real-world. With Wireless the devices cannot send and receive simultaneously and they cannot sense collisions.In data networking, Ethernet hubs are half-duplex devices by nature, as they create a single shared channel of communication. Ethernet switches, on the other hand, can use a connection in either half- or full-duplex mode.
What is 100 Mbps full-duplex : A switch that can deliver 100Mbps symmetrical, full duplex can transmit and receive at a rate of 100Mbps. Even if it is full duplex, a network switch with asymmetrical bandwidth cannot send AND receive at 100Mbps. Asymmetrical switches will use an uneven split to transmit at 70Mbps and receive at 30Mbps, for example.
Why is Wi-Fi not full-duplex
Wireless networks have commonly been built on half-duplex radios. A wireless node cannot transmit and receive simultane- ously, because the interference generated by outgoing signals can easily overwhelm the incoming signals that are much weaker, so called self-interference effect.
Is Wi-Fi a duplex : A wired Ethernet network is full duplex, meaning a device can send and receive, or upload and download, simultaneously. WiFi is half duplex, so if a client is sending data to the AP(Access Points), the AP can not also send data to the same or any other client at the same time.
Wireless networks have commonly been built on half-duplex radios. A wireless node cannot transmit and receive simultane- ously, because the interference generated by outgoing signals can easily overwhelm the incoming signals that are much weaker, so called self-interference effect.
An HTTP connection uses half-duplex communication; only one party can communicate at a time, and the server's message is always in response to a request from a client.
Is Gigabit Internet full-duplex
Designed for Efficiency: Gigabit Ethernet was designed for full-duplex, ensuring optimal speed and performance. Half-duplex would significantly limit its potential.Basically, yes full duplex 1Gbps means 2Gbps maximum ideal transmission. Depends, as always, on all the components in the action: NIC, cabling, and switches. Practically, won't see it often. Like the others said full duplex does mean you can download a gig and upload a gig at the same time.100BASE-TX is the predominant form of Fast Ethernet, and runs over two pairs of wire inside a Category 5 or above cable. Cable distance between nodes can be up to 100 metres (328 ft). One pair is used for each direction, providing full-duplex operation at 100 Mbit/s in each direction.
In-band full duplex communication has a rich set of potential applications – it is defined in the NGMN Whitepaper as a Technology Building Block for 5G. In the 5G network architecture, it can enable efficient implementation of new radio features to achieve greater spectral efficiency and boost network capacity.
Is 802.11ac full duplex : As with all 802.11 standards, 802.11ac is half-duplex, shared medium radio technology that works best when employed in wireless networking environments designed by qualified professionals.
Why can’t Wi-Fi be full-duplex : With internet access the great majority of data usually is sent from the internet to the user's machine, a variable amount, but relatively little goes the other way. If Wi-Fi ran as full duplex there would have to be allocated radio bands in each direction which would take up precious bandwidth.
How is Internet half-duplex
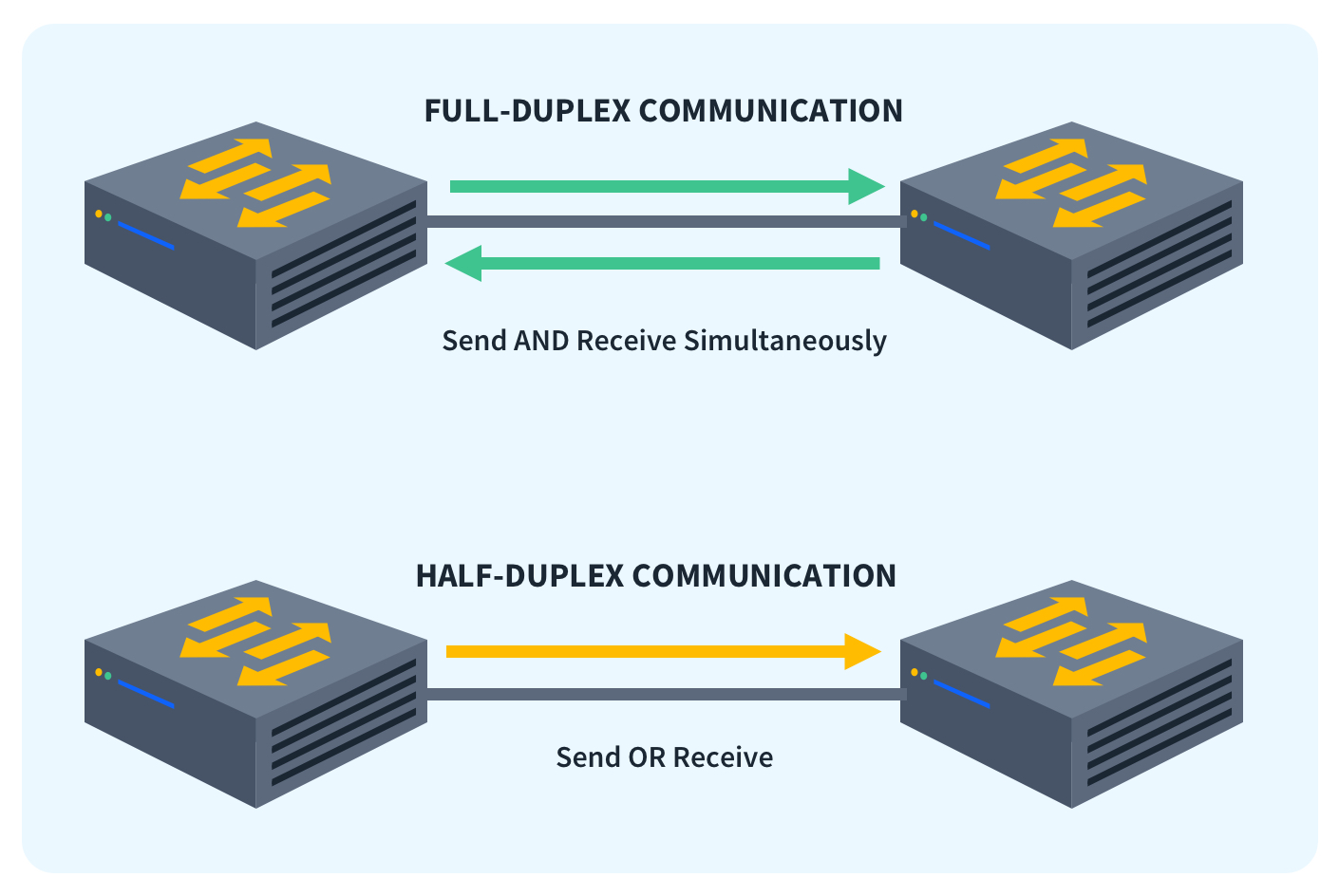
Half-duplex devices can only transmit in one direction at one time. So although data can move in two directions, it cannot be at the same time. Both devices are capable of transmitting and receiving so when one device is sending, the other is receiving.
Half-duplex and full-duplex are two common methods of transmitting data. Half-duplex is when data can only go in one direction at a time. Full-duplex is when data can flow in both directions at the same time.However, modern Ethernet switches predominantly operate in full-duplex mode, enabling simultaneous two-way communication between connected devices and significantly improving network performance.
Is 5G full-duplex : In-band full duplex communication has a rich set of potential applications – it is defined in the NGMN Whitepaper as a Technology Building Block for 5G. In the 5G network architecture, it can enable efficient implementation of new radio features to achieve greater spectral efficiency and boost network capacity.