Antwort Is full duplex better than half-duplex? Weitere Antworten – What are the advantages of full duplex over half-duplex
Differences Between Full and Half-Duplex Systems
Full-duplex Ethernet does save time when compared to half-duplex because it alleviates collisions and frame retransmissions. Sending and receiving are separate functions, creating a system where there is full data capacity in each direction.Full duplex has the potential to double the link throughput by allowing for continuous transmission in both directions on the same frequency.Disadvantages:
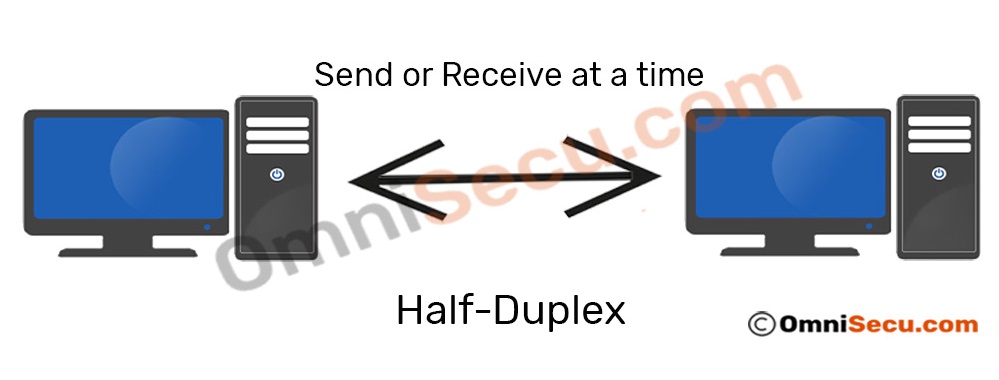
- Half-duplex mode is less reliable than Full-Duplex mode, as both devices cannot transmit at the same time.
- There is a delay between transmission and reception, which can cause problems in some applications.
How fast is full duplex vs half-duplex : Using the same example of moving two 150Mb files, a 100Mbps symmetrical, full duplex switch will deliver both files in 1.5 seconds. A 100Mbps asymmetrical half duplex switch with a 70/30 split will take 7.14 seconds to deliver both files.
Is full duplex better
Full-Duplex has Greater Throughput
The ability to send and receive data at the same time greatly increases the rate of transmission. This is especially beneficial when high data rates are required, such as video streaming and VoIP. So not only is data sent faster, but more can be sent at the same time.
Why choose half-duplex : Advantages. One of the notable advantages of half duplex mode is its simplicity. It allows communication in both directions using a single path for transmitting and receiving data.
Quick Definition: Full-duplex enables simultaneous two-way communication, which allows data to flow freely bidirectionally. Half-duplex enables two-way communication, but not simultaneously. Half-duplex requires switching between a sending and receiving mode.
Full-Duplex has Greater Throughput
The ability to send and receive data at the same time greatly increases the rate of transmission. This is especially beneficial when high data rates are required, such as video streaming and VoIP. So not only is data sent faster, but more can be sent at the same time.
What does 100 Mbps half-duplex mean
100BASE-T (fast ethernet over 2 wire pairs) is full duplex, meaning 100Mbit per direction, simultaneously. It is possible to configure a 100Mbit network interface in half duplex, meaning that the total bandwidth available for send+receive is 100Mbit (as opposed to 200Mbit for full duplex)Half-duplex has limited throughput since data can only be sent one way at a time. This dramatically impedes a network's speed and reliability.Half-duplex systems are usually used to conserve bandwidth, at the cost of reducing the overall bidirectional throughput, since only a single communication channel is needed and is shared alternately between the two directions.
Full-duplex breaks one of the fundamental assumption in wireless network design; current networks are either half-duplex in time (like WiFi) and frequency (like most cellular).
Why is full duplex faster : Full-duplex communication allows for faster data transfer as devices can both send and receive information simultaneously. This increases data transfer speeds compared to half-duplex or simplex communication. (Simplex communication is unidirectional data transmission, like a keyboard.)
Is Wi-Fi full or half-duplex : Also, some older Ethernet devices can only use half-duplex communications, even when connected to a full-duplex switch. Lastly, Wi-Fi networks are half-duplex on a per-channel basis. Each radio channel, as with walkie-talkies, can send or receive — but not both at the same time.
Is 5G full duplex
In-band full duplex communication has a rich set of potential applications – it is defined in the NGMN Whitepaper as a Technology Building Block for 5G. In the 5G network architecture, it can enable efficient implementation of new radio features to achieve greater spectral efficiency and boost network capacity.
Full-Duplex has Greater Throughput
The ability to send and receive data at the same time greatly increases the rate of transmission. This is especially beneficial when high data rates are required, such as video streaming and VoIP. So not only is data sent faster, but more can be sent at the same time.Full duplex could double the capacity of wireless networks, making it a key technology for 5G.
Why can’t Wi-Fi be full duplex : With internet access the great majority of data usually is sent from the internet to the user's machine, a variable amount, but relatively little goes the other way. If Wi-Fi ran as full duplex there would have to be allocated radio bands in each direction which would take up precious bandwidth.