Antwort Is full-duplex better? Weitere Antworten – What are the disadvantages of full-duplex
Disadvantages of Full-Duplex
- Higher Power Consumption: Increased operational costs and potential overheating due to higher power needs.
- Increased Cost: More expensive to implement because of the need for advanced hardware and infrastructure.
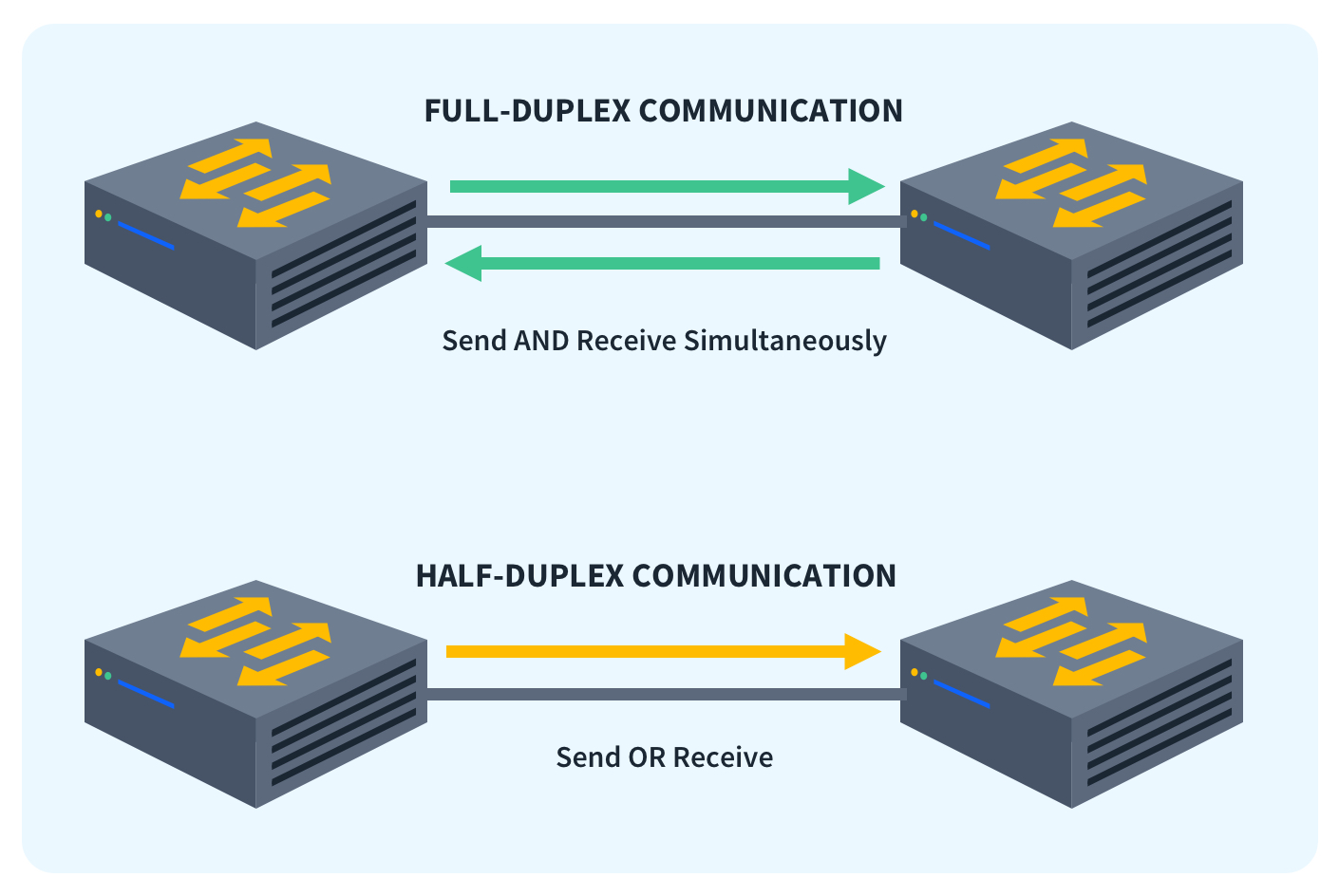
Full-duplex communication allows for faster data transfer as devices can both send and receive information simultaneously. This increases data transfer speeds compared to half-duplex or simplex communication.Full-duplex Ethernet does save time when compared to half-duplex because it alleviates collisions and frame retransmissions. Sending and receiving are separate functions, creating a system where there is full data capacity in each direction. In contrast, half-duplex can be used to conserve bandwidth.
How fast is 100Mbps full-duplex : Using the same example of moving two 150Mb files, a 100Mbps symmetrical, full duplex switch will deliver both files in 1.5 seconds. A 100Mbps asymmetrical half duplex switch with a 70/30 split will take 7.14 seconds to deliver both files.
Is half-duplex slower than full duplex
If we compare full duplex vs half duplex, full duplex point to point is much faster, and will provide faster throughput for voice, data and video transmission.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of full duplex mode : The advantage of Full-duplex mode is that both the stations can send and receive the data at the same time. The disadvantage of Full-duplex mode is that if no dedicated path exists between the devices, then the capacity of the communication channel is divided into two parts.
Effects of Full-Duplex Operation
While full-duplex operation has the potential to double the bandwidth of an Ethernet link segment, it usually won't result in a large increase in performance on a link that connects to a user's computer.
If we compare full duplex vs half duplex, full duplex point to point is much faster, and will provide faster throughput for voice, data and video transmission.
Does full-duplex increase bandwidth
Effects of Full-Duplex Operation
While full-duplex operation has the potential to double the bandwidth of an Ethernet link segment, it usually won't result in a large increase in performance on a link that connects to a user's computer.Basically, yes full duplex 1Gbps means 2Gbps maximum ideal transmission. Depends, as always, on all the components in the action: NIC, cabling, and switches. Practically, won't see it often. Like the others said full duplex does mean you can download a gig and upload a gig at the same time.If we compare full duplex vs half duplex, full duplex point to point is much faster, and will provide faster throughput for voice, data and video transmission.
Half-duplex systems are usually used to conserve bandwidth, at the cost of reducing the overall bidirectional throughput, since only a single communication channel is needed and is shared alternately between the two directions.
What are the advantages of full duplex over half-duplex : There is no need for collision detection as the network card can transmit and receive data independently of each other. Full duplex is more efficient than half duplex because there is no need for a delay before sending data to avoid collisions.
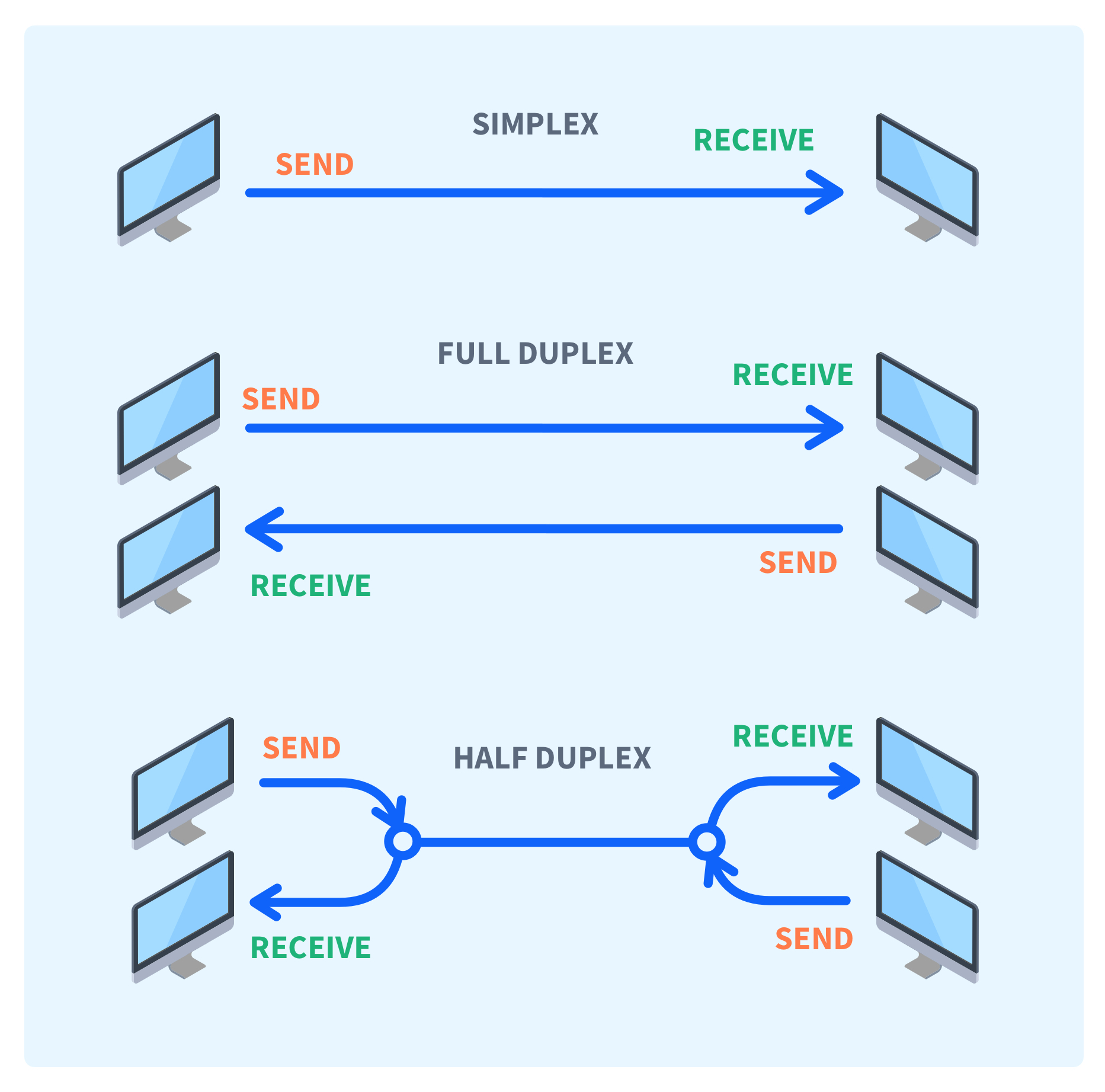
Is simplex faster than full duplex : The simplex mode provides less performance than half duplex and full duplex. The Half Duplex mode provides less performance than full duplex. Full Duplex provides better performance than simplex and half duplex mode. Simplex utilizes the maximum of a single bandwidth.
When to use full duplex
For all links between hosts and switches, or between switches, the full-duplex mode should be used. However, for all links connected to a LAN hub, the half-duplex mode should be used in order to prevent a duplex mismatch that could decrease network performance.
If you have a larger or multi-generational household
Considering how it handles larger WiFi loads more efficiently than a 1Gbps plan, picking up a 2Gbps Fibre Broadband will help to minimise any such conflicts over the Internet connection.In most circumstances, full-duplex is faster than half-duplex. A full-duplex medium can transfer information in both directions, simultaneously. A half-duplex medium can transfer information in either direction, but only one direction at a time.
Is half-duplex slower than full-duplex : If we compare full duplex vs half duplex, full duplex point to point is much faster, and will provide faster throughput for voice, data and video transmission.