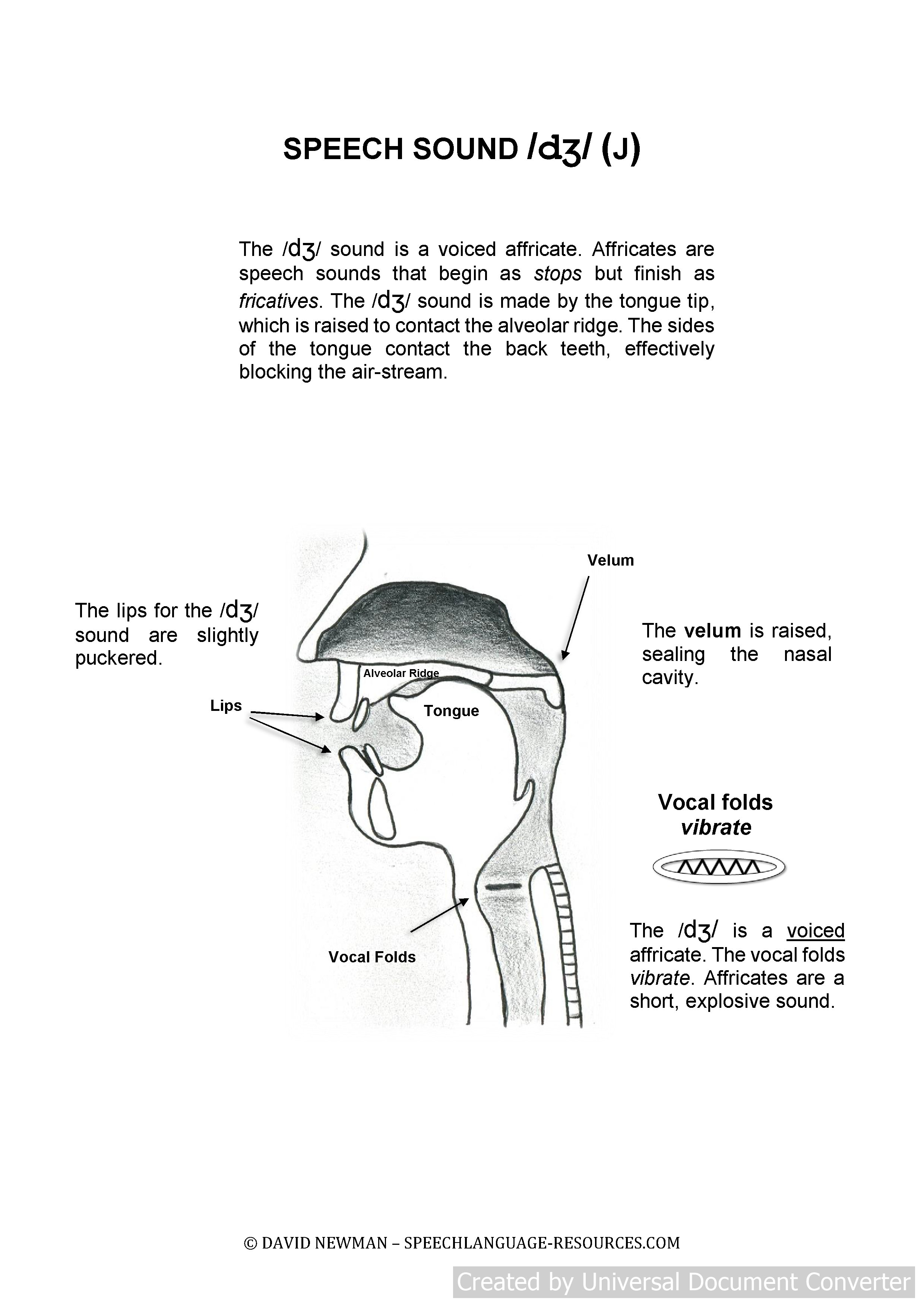
Antwort Is ʒ an affricate? Weitere Antworten – What is the phonetic symbol ʒ
Ezh (Ʒ ʒ) /ˈɛʒ/, also called the "tailed z", is a letter, notable for its use in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) to represent the voiced postalveolar fricative consonant.This is the sound as in the words. Think thing and walking it's a sound from the single consonant group The Sound is called the V nasal which means that you curl your tongue up against the back ofAnd my tongue is slightly rounded pushed back a little towards the soft palate.
Is the C sound fricative : The sound of a hard ⟨c⟩ often precedes the non-front vowels ⟨a⟩, ⟨o⟩ and ⟨u⟩, and is that of the voiceless velar stop, /k/ (as in car). The sound of a soft ⟨c⟩, typically before ⟨e⟩, ⟨i⟩ and ⟨y⟩, may be a fricative or affricate, depending on the language.
When to use ʒ
If a word begins or ends with /ʒ/ then it must be a loanword or a foreign word. Also, most words that have /ʒ/ are enclosed in vowels. Examples: equation – usually.
What sound is ʒ and dʒ : Both sounds are made by pushing air between the lower teeth and the roof of the mouth, but dʒ begins with a brief "d" sound, and ʒ does not.
The sound /ʒ/ is a voiced, alveo-palatal, fricative consonant.
Include asia asia or pleasure pleasure or television television ja the sound ja did you get this was this any helpful. Let me know in the comments and by using the like button thanks for your support.
Is ʊ unrounded
Handbook of the International Phonetic Association defines [ʊ] as a mid-centralized (lowered and centralized) close back rounded vowel (transcribed [u̽] or [ü̞]), and the current official IPA name of the vowel transcribed with the symbol ⟨ʊ⟩ is near-close near-back rounded vowel.To produce this sound, the tip of the tongue is placed against the roof of the mouth behind the upper front teeth; then, while exhaling, the space between the tongue and the palate is narrowed, creating a friction-like sound similar to the ⟨s⟩ sound (IPA: [ʒ]) in the English word leisure.To produce this sound, the tip of the tongue is placed against the roof of the mouth behind the upper front teeth; then, while exhaling, the space between the tongue and the palate is narrowed, creating a friction-like sound similar to the ⟨s⟩ sound (IPA: [ʒ]) in the English word leisure.
You use your vocal cords for /v/, /z/, and /ʒ/, but not for /f/, /s/, /ʃ/. Aside from that, they're identical. Just for completeness: /ʃ/ is called the voiceless palato-alveolar sibilant, and /ʒ/ the voiced palato-alveolar sibilant.
Are ʒ and Z post-alveolar fricatives : The voiced fricative alveolar /z/ becomes a voiced fricative post-alveolar /ʒ/ when followed by /j/. In theory, this should happen in the same way when the next sound is the voiceless post-alveolar /ʃ/, and this is what most books about English pronunciation say.
Which word has ʒ sound in it : Some common words which practice the pronunciation of /ʒ/ include the following: equation – usually. ending in "sion": conclusion – confusion – decision – division – occasion – provision – television – vision.
What is the difference between dʒ and ʒ
/dʒ/ is an affricate consonant; it can't last long. /ʒ/ is a fricative consonant; this means it is possible to make it sound for a long time: /ʒʒʒ/. However, in normal speech /ʒ/ has a length similar to other consonants.
Its symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet is ⟨ɤ⟩, called "ram's horn." This symbol is distinct from the symbol for the voiced velar fricative, ⟨ɣ⟩, which has a descender, but some texts use this symbol for the voiced velar fricative. Close-mid back unrounded vowel.The voiced fricative alveolar /z/ becomes a voiced fricative post-alveolar /ʒ/ when followed by /j/. In theory, this should happen in the same way when the next sound is the voiceless post-alveolar /ʃ/, and this is what most books about English pronunciation say.
When to use ʃ or ʒ : These sounds exist in many parts of Latin America). /ʃ/ is the sound we make when we want to ask for silence (Shhhh…!) and /ʒ/ is its voiced counterpart.