Antwort Is 802.11 g old? Weitere Antworten – Is 802.11g still used
Many home networks today still operate using 802.11g routers. At 54 Mbps, these routers can keep up with most high-speed home internet connections, including basic video streaming and online gaming. G-compatible routers can be found inexpensively through both retail and secondhand sales outlets.In basic terms, 802.11n is faster than 802.11g, which itself is faster than the earlier 802.11b. On the company website, Apple explains that 802.11n offers "greater performance, more range, and improved reliability".802.11n is certainly "old" for a Wi-Fi standard in the 2020s, but there are still plenty of 802.11n radios out there. 802.11n devices were still some of the most common throughout the late 2010s so you can expect to continue to see them in the wild for a bit longer.
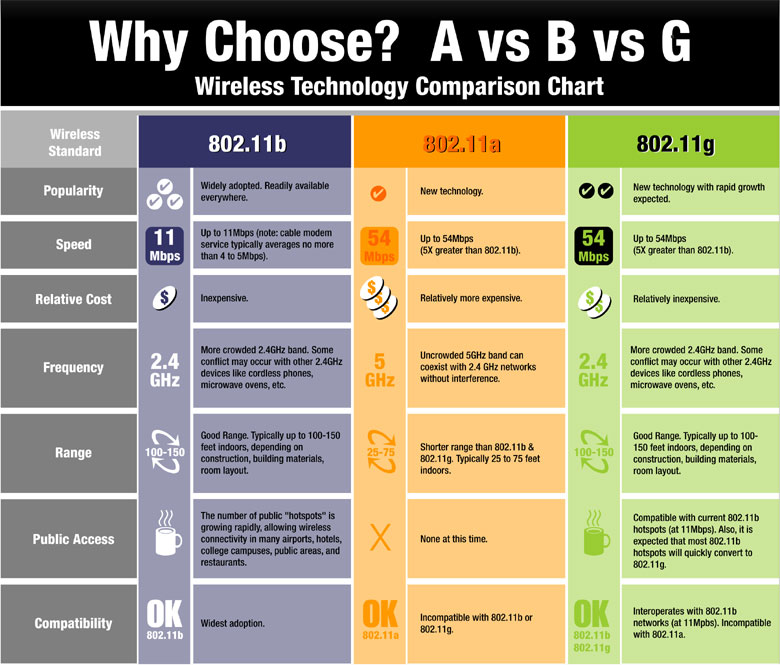
What version of Wi-Fi is 802.11 g : 802.11g is the third modulation standard for wireless LANs. It works in the 2.4 GHz band (like 802.11b) but operates at a maximum raw data rate of 54 Mbit/s.
Is 802.11 b better than G
802.11b and 802.11g both work under the 2.4GHz frequency range. This means that they are inter-operable with each other. All 802.11g devices can communicate with 802.11b devices. The advantage of 802.11g is that you will be able to transfer files between computers or networks at much faster speeds.
Where is 802.11 g used : 802.11g Devices for Wireless Networking
The standard supports communications between computers, broadband routers and other devices. 802.11g and 802.11b both operate in the widely used 2.4 GHz range, which may lead to interference issues. Bluetooth devices, microwaves and cordless telephones also operate in this range.
The major disadvantage of 802.11g Wireless LAN Technology is that it costs more than 802.11b technology. The Appliances present in the surroundings may interfere on the unregulated signal frequency since the operating frequency is 2.4GHz.
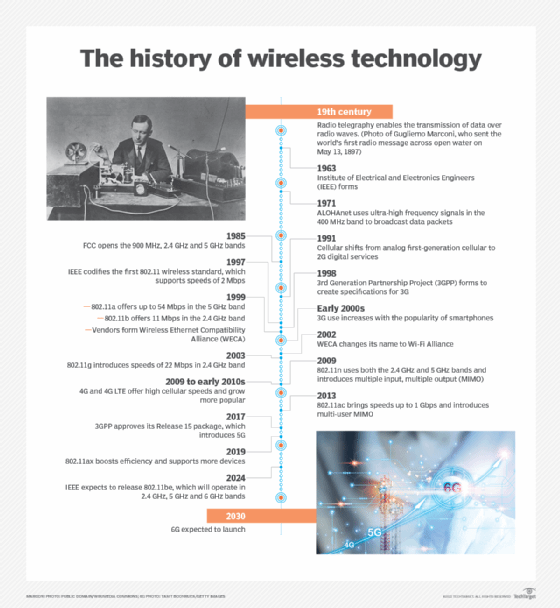
In memoriam of the first amendment to the IEEE 802.11 wireless networking standard hailing all the way since 1999, 802.11b was superseded by 802.11a and g in 2003 which are much more efficient. 802.11n was available in draft form in 2007 and was ratified in 2009 while 802.11ac was ratified last September.
Does 802.11g support 5GHz
Frequency Ranges of the 802.11 network-types:
802.11ac: 5GHz band. 802.11n: 2.4GHz & 5GHz bands: 802.11n equipment is made for either 2.4GHz or 5.8 frequency band: 5.8 is typically much less cluttered with signal-traffic. 802.11a: 5GHz band. 802.11b and 802.11g: 2.4GHz only: Operate only in the 2.4GHz frequency band.802.11b and g only support 2.4 GHz. 802.11n can use either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, but if the only other versions are b and g, n will also be using 2.4 GHz. If it also supports the earlier 802.11a or the newer 802.11ac 5 GHz would be available.IEEE 802.11g™, or Wi-Fi 3, was introduced in 2003. It allowed for faster data rates of up to 54 Mbit/s in the same 2.4 GHz frequency band as IEEE 802.11b, thanks to an OFDM multi-carrier modulation scheme and other enhancements.
The following are the main advantages of 802.11g over 802.11b:
- Higher bandwidth at 54 Mbps.
- Cheaper than 802.11a, and costs close to 802.11b. 802.11g uses 2.4GHz frequency band, just like 802.11b.
- Backward compatible with 802.11b standard.
What is 802.11g used for : 802.11g is a proposed standard that describes a wireless networking method for a WLAN that operates in the 2.4GHz radio band (ISM: Industrial Scientific Medical frequency band). It transfers data at up to 54Mbps.
How fast is 802.11 g : 54 MbpsDifferent Wi-Fi Protocols and Data Rates
| Protocol | Frequency | Maximum data rate (theoretical) |
|---|---|---|
| 802.11g | 2.4 GHz | 54 Mbps |
| 802.11a | 5 GHz | 54 Mbps |
| 802.11b | 2.4 GHz | 11 Mbps |
| Legacy 802.11 | 2.4 GHz | 2 Mbps |
When did 802.11 g come out
IEEE 802.11g™, or Wi-Fi 3, was introduced in 2003. It allowed for faster data rates of up to 54 Mbit/s in the same 2.4 GHz frequency band as IEEE 802.11b, thanks to an OFDM multi-carrier modulation scheme and other enhancements.
802.11g offers wireless transmission over distances of 150 feet and speeds up to 54Mbps compared with the 11Mbps of the 802.11b standard. Like 802.11b, 802.11g operates in the 2.4GHz range and therefore is compatible with it.Frequency Ranges of the 802.11 network-types:
802.11a: 5GHz band. 802.11b and 802.11g: 2.4GHz only: Operate only in the 2.4GHz frequency band.
Which is better 802.11 b or g : 802.11g offers wireless transmission over distances of 150 feet and speeds up to 54Mbps compared with the 11Mbps of the 802.11b standard. Like 802.11b, 802.11g operates in the 2.4GHz range and therefore is compatible with it.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/wireless-standards-802-11a-802-11b-g-n-and-802-11ac-816553-36294250342e404eabe7dc94bc7a40f9.png)