Antwort How long is each PCR step? Weitere Antworten – How long does a PCR experiment take
The entire cycling process of PCR is automated and can be completed in just a few hours. It is directed by a machine called a thermocycler, which is programmed to alter the temperature of the reaction every few minutes to allow DNA denaturing and synthesis.RT-PCR Protocol
- Experiment process.
- (1) Primer design. Design and synthesize the primers of the target gene.
- (2) RNA extraction.
- (3) Reverse transcription(RNA→cDNA)
- (4) Real-time PCR.
- (5) Result analysis.
- The factors affecting Real-time PCR results.
PCR conditions
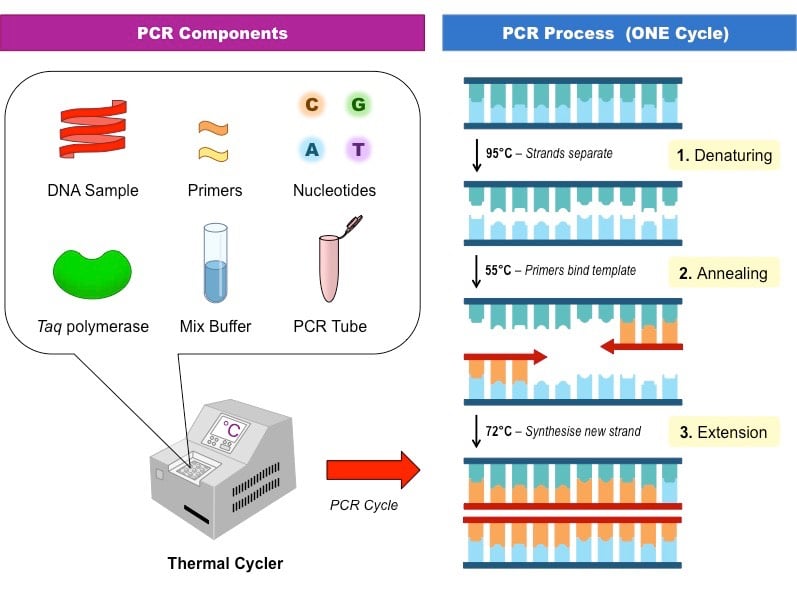
- Use higher denaturation temperatures (e.g., 98°C as opposed to 94°C or 95°C) to allow complete denaturation of the template.
- Keep annealing times for GC-rich templates as short as possible.
- Use primers with a higher Tm (>68°C), because annealing can occur at a higher temperature.
What does real-time PCR do : Real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR) is commonly used to measure gene expression. It is more sensitive than microarrays in detecting small changes in expression but requires more input RNA and is less adaptable to high-throughput studies (1). It is best suited for studies of small subsets of genes.
How fast is Taq polymerase
about 60 nucleotides per second
A single Taq synthesizes about 60 nucleotides per second at 70 °C, 24 nucleotides/sec at 55 °C, 1.5 nucleotides/sec at 37 °C, and 0.25 nucleotides/sec at 22 °C. At temperatures above 90 °C, Taq demonstrates very little or no activity at all, but the enzyme itself does not denature and remains intact.
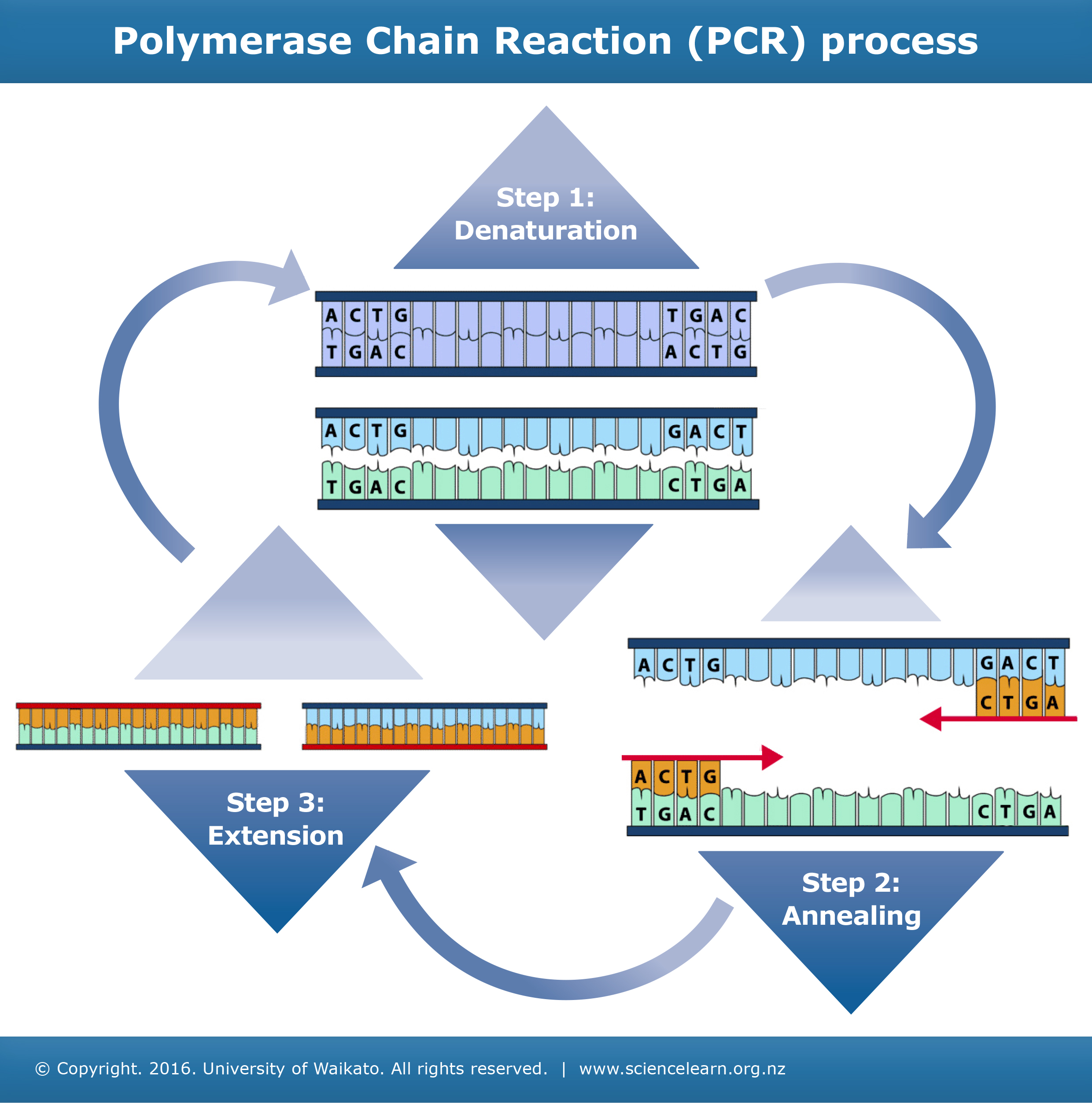
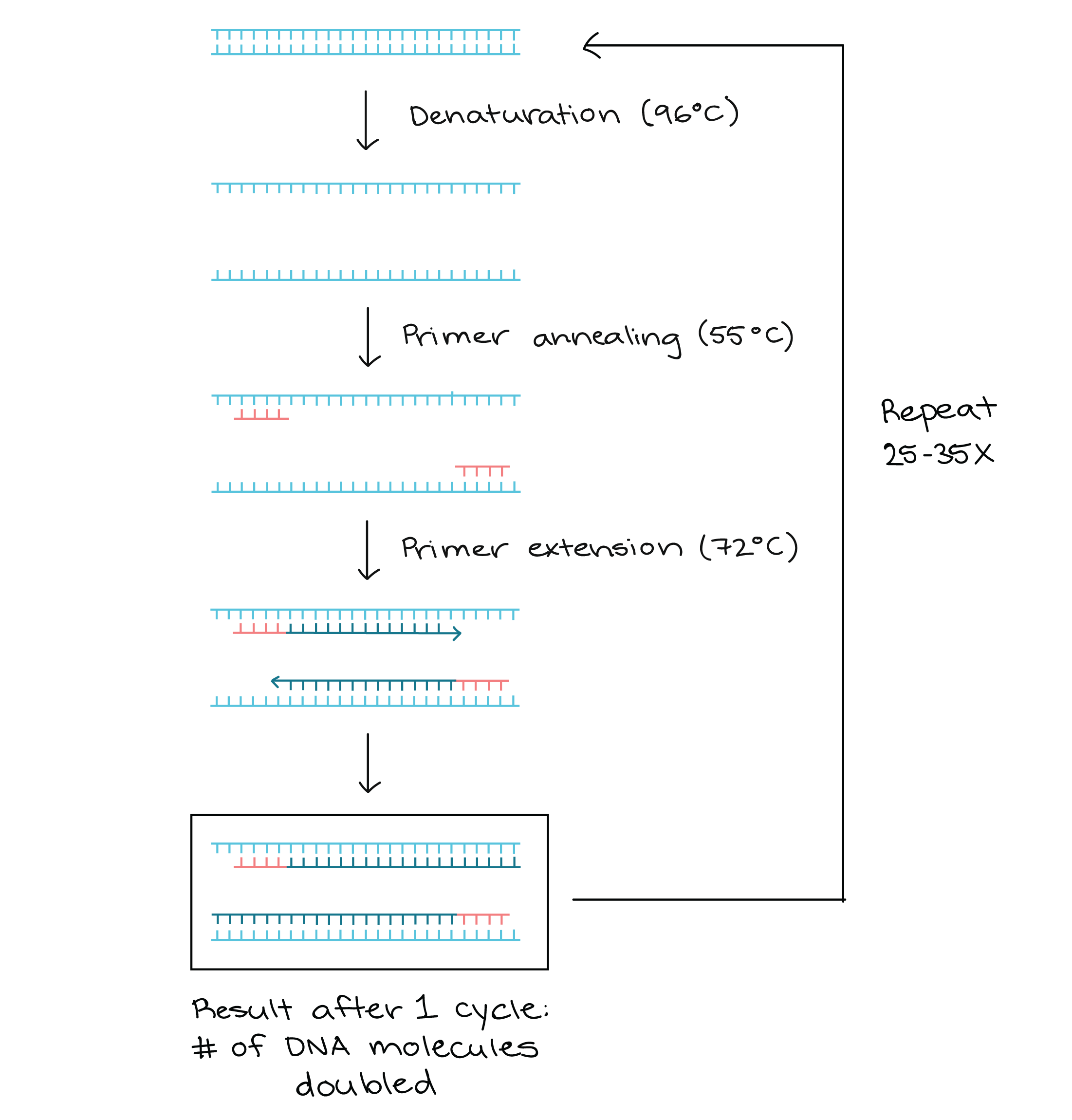
How long does annealing take in PCR : 30 sec to 1 min
The annealing step (30 sec to 1 min, at temperatures 45–60 °C), is required so that the primers bind to the complementary sequence on each of the DNA single strands. The primers are designed such that they bracket the target of interest and the region of sequence that lies between them is referred to as the amplicon.
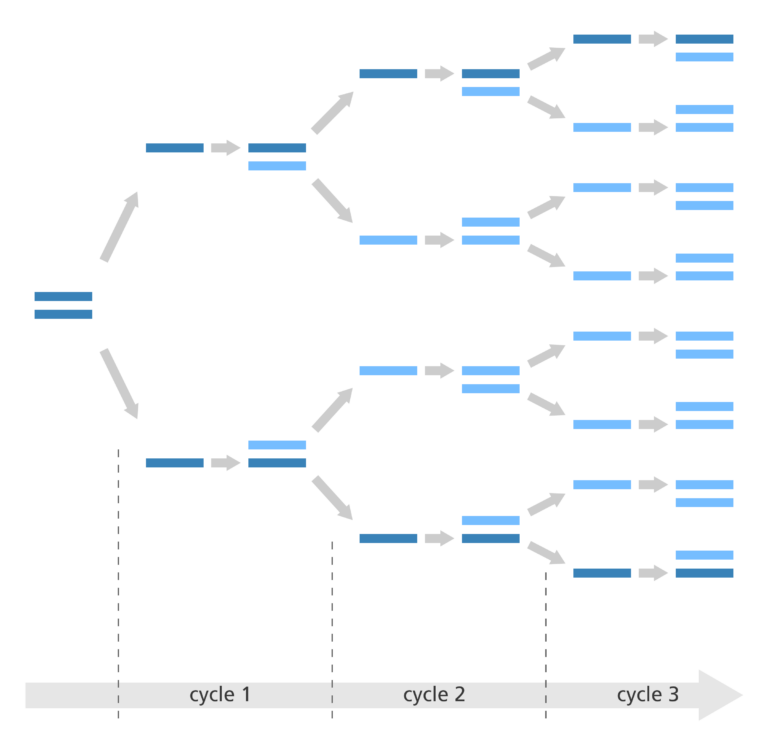
This process is repeated, usually around 40 times (40 cycles). A typical RT-qPCR run, as exemplified here, is completed in around 1 h 27 min. As this is a RT-qPCR run, quantification is achieved by measuring the intensity of fluorescence signals at the end of each cycle to deduce the amount of PCR product generated.
What is one-step RT-PCR As the name implies, one-step RT-PCR combines first-strand cDNA synthesis (RT) and subsequent PCR in a single reaction tube. This reaction setup can help simplify your workflow, reduces variation, and minimizes possible contamination.
How long should annealing time be
An annealing time of 30-45 seconds is commonly used in PCR reactions. Increase in annealing time up o 2-3 minutes did not appreciably influence the outcome of the PCR reactions.The number of cycles is usually carried out 25–35 times but may vary upon the amount of DNA input and the desired yield of PCR product. If the DNA input is fewer than 10 copies, up to 40 cycles may be required to produce a sufficient yield.Real-time PCR results can either be qualitative (the presence or absence of a sequence) or quantitative (copy number). Quantitative real-time PCR is thus also known as qPCR analysis. In contrast, PCR is at best semiquantitative.
15–60 seconds
The annealing step is typically 15–60 seconds. Annealing temperature is based on the Tm of the primer pair and is typically 45–68°C.
How fast is the DNA polymerase PCR : Compared to standard extension rates of Taq DNA Polymerase (~1kb/min), enzymes that are able to perform fast PCR have extension rates that are typically 2-4kb/min.
What is the duration of annealing time : An annealing time of 30-45 seconds is commonly used in PCR reactions. Increase in annealing time up o 2-3 minutes did not appreciably influence the outcome of the PCR reactions.
What is the best length for qPCR
150 to 200 bp
Nonviability qPCR guidelines generally recommend amplicon lengths below 150 to 200 bp for optimal qPCR efficiency.
The PCR purification protocol achieves rapid and efficient removal of short primers, dNTPs, enzymes, short-failed PCR products, and salts from PCR fragments >100 bp, typically in less than 10 minutes.Two-step RT-PCR entails two separate reactions, beginning with first-strand cDNA synthesis (RT), followed by amplification of a portion of the resulting cDNA by PCR in a separate tube. Therefore, two-step RT-PCR is useful for detecting multiple genes in a single RNA sample.
What is one-step vs two-step real-time PCR : The distinction between the two is fairly simple. In one-step RT-PCR, both major reactions (reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction) are carried out in a single tube. For a two-step process, the cDNA products of reverse transcription are transferred to a second tube for subsequent PCR.