Antwort How accurate is the antigen test for COVID? Weitere Antworten – Will an antigen test detect Covid
Rapid antigen tests detect COVID-19 when people have a higher amount of virus particles in their system and are more contagious. But a negative antigen test doesn't necessarily mean you don't have COVID-19. Trust a positive antigen test, but be more skeptical about a negative one.Q: My patient is asymptomatic and has no known exposures but returned a positive COVID-19 rapid antigen test. Could it be a false positive A: In general, a positive COVID-19 test means the patient has or recently had a COVID-19 infection (CDC, 2023). At-home false-positive tests for COVID-19 are uncommon.There are 3 types of results for a COVID-19 (coronavirus) PCR or antigen test: positive (COVID-19 found) negative (COVID-19 not detected) indeterminate, invalid or inhibitory.
Who approved COVID antigen test kit : The iHealth COVID-19 Antigen Rapid Test is an FDA-authorized, over-the-counter, self-administered test that delivers results in 15 minutes.
Do antigen tests still work
Another study, which tested the accuracy of rapid antigen tests from 2020 to 2022, found similar results. That said, researchers like us continue to “test the tests,” both in computer simulations and in the lab, to detect new SARS-CoV-2 variants.
How common is a false negative COVID test : While RT-PCR testing of key workers is of great importance (particularly those working with vulnerable groups), our results suggest that there may be little benefit to testing indiscriminately; in fact, conducting a single test on someone who had symptoms 10 days ago will have a nearly 25% chance of being a false- …
Evidence-Based Answer. SARS-CoV-2 antigen tests have an average sensitivity of 69.3% (95% CI, 66.2% to 72.3%) and specificity of 99.3% (95% CI, 99.2% to 99.3%).
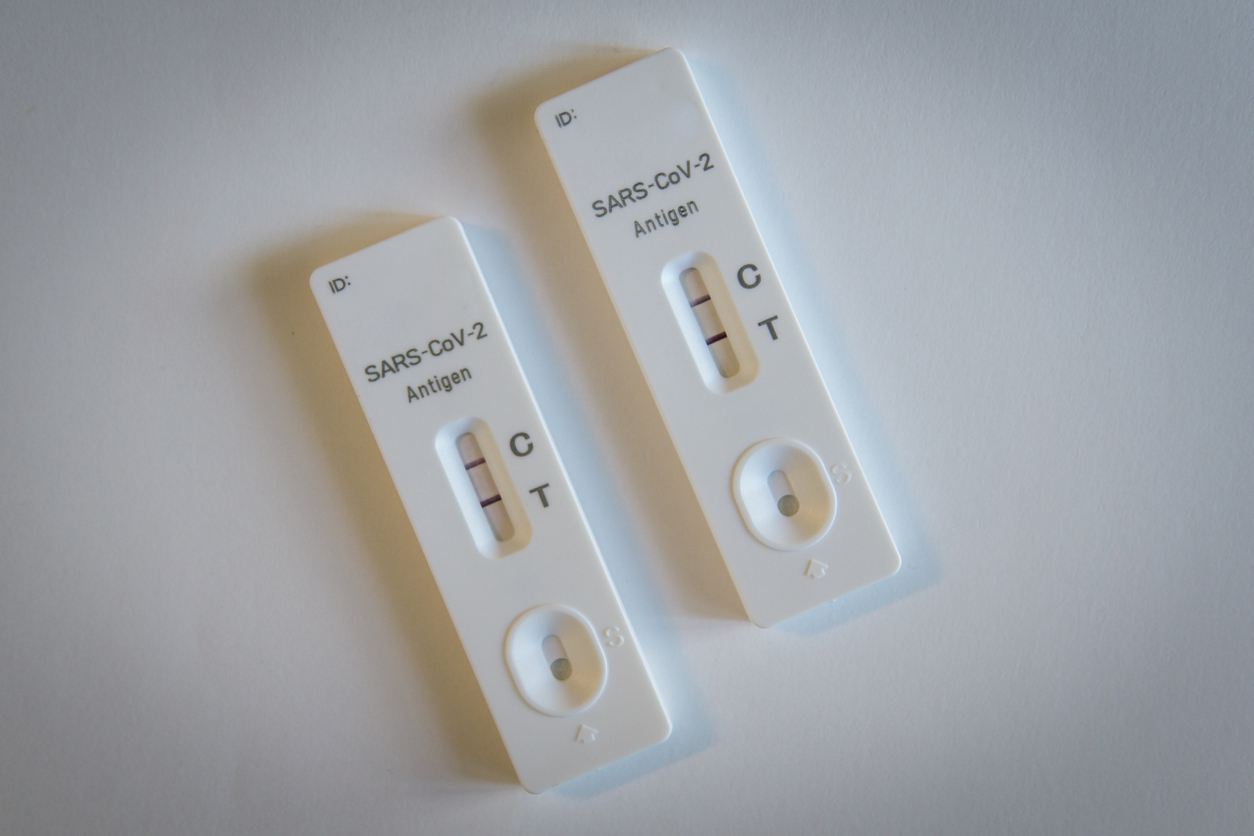
“A faint line means you're almost certainly positive,” he says.
Does a darker line mean more COVID
Kind of. If you test positive—faint or not—it means that you have infectious COVID-19 particles in your body, Dr. Russo says. But how dark the line is does give you a little insight into what's going on, Dr. Adalja says. “The less dark, the line is, the less viral material that is present,” he says.After clinician tests were collected, patients then performed and interpreted their own rapid test. The sensitivity of clinician and self-collected rapid testing was very good and relatively similar at 88.2% (clinician) vs. 83.9% (patient); notably, sensitivity was much lower in asymptomatic cases (63% [clinician] vs.“PCR tests are more reliable and accurate due to testing the specific genetic material of the virus, eliminating the interference from other viruses,” said Heather Seyko, a Laboratory Services manager for OSF HealthCare.
“The less dark, the line is, the less viral material that is present,” he says. “This could reflect diminishing contagiousness, or the start of it.”
Can I have COVID and test negative : A negative COVID-19 test means the test did not detect the virus, but this doesn't rule out that you could have an infection. If you used an antigen test, follow FDA recommendations for repeat testing. If you have symptoms: You may have COVID-19 but tested before the virus was detectable.
Can I test negative and still have COVID : A negative COVID-19 test means the test did not detect the virus, but this doesn't rule out that you could have an infection. If you used an antigen test, follow FDA recommendations for repeat testing. If you have symptoms: You may have COVID-19 but tested before the virus was detectable.
Can COVID tests be wrong
Overall, about one in five positive results would be wrong. They also found that trained laboratory staff noted the test result band was often weak and disagreed on whether the result was positive or negative for almost 4% of AbC-19 tests.
Antigen tests can give false positive results. If you do not have symptoms but you receive a positive antigen result, your health care provider may recommend a molecular test to confirm the result.However, individuals are typically contagious for about 10 days after the onset of symptoms. For those with mild to moderate symptoms, this period can be shorter, often around 5-7 days. For people with severe symptoms or those with a weakened immune system, contagiousness can last longer, potentially up to 20 days.
Am I still contagious after 5 days of COVID : However, individuals are typically contagious for about 10 days after the onset of symptoms. For those with mild to moderate symptoms, this period can be shorter, often around 5-7 days. For people with severe symptoms or those with a weakened immune system, contagiousness can last longer, potentially up to 20 days.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/are-at-home-covid-tests-accurate-enough-5210762_final-72d925b664ee4790a2821cc9e19f7a80.jpg)