Antwort Does Mexico still claim Texas? Weitere Antworten – How much did Mexico sell Texas for
$15 million
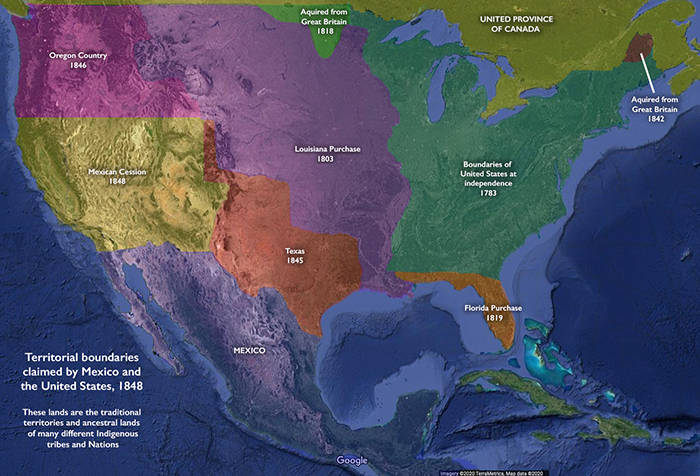
The U.S. government paid Mexico $15 million "in consideration of the extension acquired by the boundaries of the United States" and agreed to pay American citizens debts owed to them by the Mexican government.Mexico ceded nearly all the territory now included in the U.S. states of New Mexico, Utah, Nevada, Arizona, California, Texas, and western Colorado for $15 million and U.S. assumption of its citizens' claims against Mexico. Treaty of Guadalupe HidalgoRead more about the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo.The Mexican government saw Texas as an underutilized territory and decided to attract American settlers to improve its economic prospects. The Mexican government hoped that American settlers would cultivate the land and develop new industries, which would increase the value of Texas and stimulate the economy.
What part of the US used to be Mexico : Under the terms of the treaty negotiated by Trist, Mexico ceded to the United States Upper California and New Mexico. This was known as the Mexican Cession and included present-day Arizona and New Mexico and parts of Utah, Nevada, and Colorado (see Article V of the treaty).
Why did it take 9 years to annex Texas
Two controversial issues — the extension of slavery and a possible war with Mexico — proved to be major roadblocks to achieving statehood for nearly ten years. By 1844, U.S. supporters of annexation had made progress in their plan to unite Texas with the United States.
When did Mexico stop owning Texas : With the support of President-elect Polk, Tyler managed to get the joint resolution passed on March 1, 1845, and Texas was admitted into the United States on December 29.
Mexicans had overthrown the Spanish and wanted to prove they were capable of running all the territory they had won from Spain. Mexico also feared a domino effect—that giving up Texas would lead to the loss of their other northern territories.
It followed the 1845 American annexation of Texas, which Mexico still considered its territory because Mexico refused to recognize the Treaties of Velasco, signed by President Antonio López de Santa Anna after he was captured by the Texian Army during the 1836 Texas Revolution.
How long did Mexico own Texas
Mexican Texas is the historiographical name used to refer to the era of Texan history between 1821 and 1836, when it was part of Mexico. Mexico gained independence in 1821 after winning its war against Spain, which began in 1810. Initially, Mexican Texas operated similarly to Spanish Texas.Mexico had officially abolished slavery in Texas in 1829, and the desire of Anglo Texans to maintain the institution of chattel slavery in Texas was also a major cause of secession. Colonists and Tejanos disagreed on whether the ultimate goal was independence or a return to the Mexican Constitution of 1824.Summary. Colonized in the eighteenth century by the Spanish, the Republic of Texas declared its independence from Mexico on March 2, 1836. The Republic of Texas was not recognized by the United States until a year later in 1837.
Colonized in the eighteenth century by the Spanish, the Republic of Texas declared its independence from Mexico on March 2, 1836.
Why didn’t the US annex Texas : One reason that some people did not want to annex Texas as a state was the issue of slavery. Texas was a slave state and would have tipped the balance between the free states and slave states toward slavery. A second issue with making Texas a state was the worry that doing so would incite war with Mexico.
Why did Texas left Mexico : The most immediate cause of the Texas Revolution was the refusal of many Texas, both Anglo and Mexican, to accept the governmental changes mandated by "Siete Leyes" which placed almost total power in the hands of the Mexican national government and Santa Anna.
What did Mexico still consider Texas
A: Mexico did not recognize Texas independence after the Texas Revolution in 1836. Instead, Mexico continued to consider Texas as a province in rebellion against the mother country.
Certainly one of the most important reasons for Mexico's loss of Texas was the historic expansionism of the United States, which had been growing by leaps and bounds even prior to the American war of independence.Certainly one of the most important reasons for Mexico's loss of Texas was the historic expansionism of the United States, which had been growing by leaps and bounds even prior to the American war of independence.
When did Mexico lose Texas : He had done that in Coahuila (in 1824, Mexico had merged Texas and Coahuila into the enormous state of Coahuila y Tejas). Austin called Texians to arms and they declared independence from Mexico in 1836.